Virtualization stands as a groundbreaking technology that reshapes the way computing environments operate. By enabling multiple virtual instances to run on a single physical hardware setup, virtualization optimizes resource use, reduces costs, and enhances operational flexibility.
This innovative approach has evolved significantly over the years, impacting various sectors and prompting a shift in how organizations manage their IT infrastructures. Whether it’s through hardware, software, or network virtualization, the underlying principles remain consistent—creating a more efficient and adaptive computing environment.
Virtualization Technology Overview
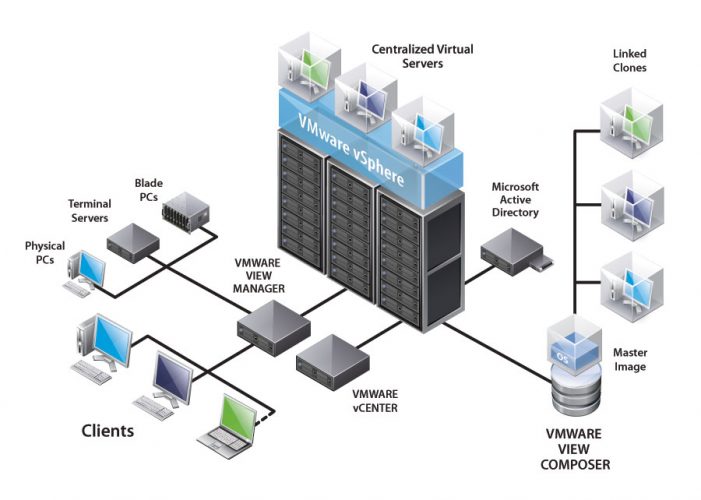
Virtualization technology has revolutionized the way computing resources are managed, enabling the abstraction of physical hardware to create multiple virtual environments. This allows businesses to optimize their IT infrastructure, reduce costs, and improve flexibility. By creating virtual representations of hardware, software, or network resources, virtualization enables more efficient use of physical resources, leading to better performance and scalability.
The core principle of virtualization lies in its ability to separate workloads from the underlying hardware. This is primarily achieved through a hypervisor, which sits between the hardware and the operating system, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine. This abstraction not only simplifies resource management but also enhances disaster recovery processes and supports better load balancing across servers. Virtualization fosters a move towards cloud computing and has become integral to modern data centers, where efficiency and scalability are paramount.
Types of Virtualization
Understanding the various types of virtualization is essential for leveraging their full potential in different computing environments. The key types include hardware virtualization, software virtualization, and network virtualization. Each has its unique characteristics and applications:
- Hardware Virtualization: This involves creating virtual machines (VMs) that emulate physical computers. Each VM runs its own operating system and applications independently, allowing different OS instances to coexist on a single hardware platform. Major players in this space include VMware, Microsoft Hyper-V, and KVM.
- Software Virtualization: This type abstracts software applications from hardware, allowing them to run in isolated environments. It is commonly used in development and testing scenarios, where different software stacks may be required. Tools like Docker implement this concept using container technology.
- Network Virtualization: This enables the creation of virtual networks that function independently of the physical networking hardware. It provides flexibility in managing, provisioning, and allocating network resources. Technologies such as Software-Defined Networking (SDN) exemplify this type of virtualization.
The evolution of virtualization technologies has been marked by significant advancements since its inception in the 1960s. Initially developed for mainframes, virtualization has transitioned into the x86 architecture, leading to widespread adoption in enterprise environments. The rise of cloud computing in the 2000s further accelerated virtualization’s impact, allowing organizations to scale resources dynamically and improve operational efficiency. Companies like Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Microsoft Azure have embraced virtualization to offer scalable cloud solutions, enabling businesses to innovate without the constraints of traditional hardware limitations.
Benefits of Virtualization in IT Infrastructure
Virtualization has emerged as a transformative technology within the realm of IT infrastructure, offering a multitude of benefits that significantly enhance operational efficiency. By abstracting physical resources and enabling multiple virtual environments to run on a single hardware platform, virtualization fosters a more adaptable, cost-effective, and resource-optimized IT landscape. Organizations that have embraced this technology have discovered not only increased agility but also substantial savings on operational costs.
One of the primary advantages of virtualization is the significant cost savings it can deliver. Traditional IT infrastructure often requires substantial investments in physical hardware, maintenance, and energy costs. Virtualization reduces these needs by allowing multiple virtual machines (VMs) to share the same physical server resources. This consolidation minimizes hardware expenses and lowers energy consumption, providing a greener, more sustainable operational model. For instance, a study by VMware found that companies can reduce their total cost of ownership (TCO) by up to 50% through server virtualization.
Resource optimization is another critical benefit associated with virtualization. By deploying virtual machines, organizations can efficiently allocate resources based on demand, ensuring that critical applications always have the necessary computing power. This dynamic allocation helps in balancing workloads and enhances overall performance. For example, a major retail chain implemented virtualization in its data centers, allowing it to scale resources up or down during peak shopping seasons. This flexibility helped them handle surges in online transactions without compromising performance.
Effective Utilization of Virtualization
Organizations across various industries have effectively leveraged virtualization to enhance their operations. Some notable examples include:
- Healthcare Sector: A prominent hospital network deployed virtualization to optimize its electronic health record (EHR) system. By virtualizing servers, they achieved faster access to patient records, improved data security, and reduced hardware costs, ultimately enhancing patient care.
- Financial Services: A large bank utilized virtualization to facilitate disaster recovery. By maintaining virtual replicas of critical systems in off-site locations, they ensured business continuity during outages, significantly reducing downtime and potential financial losses.
- Education Institutions: A university implemented virtualization to create a flexible learning environment. By providing virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) to students, they enabled access to software and resources from any device, promoting a more collaborative learning experience.
Despite its numerous advantages, virtualization also introduces certain challenges. These include complexities in management, potential performance bottlenecks, and security concerns. To mitigate these challenges, organizations can adopt best practices such as implementing robust management tools that provide visibility into virtual environments, utilizing performance monitoring software to identify and resolve bottlenecks, and establishing comprehensive security protocols tailored to virtual infrastructures. Regular training for IT staff on virtualization technologies can also enhance operational efficiency and security.
“Virtualization is not just a cost-saving mechanism but a strategic enabler for business agility and innovation.”
Understanding Hypervisors and Their Roles
Virtualization technology has transformed the way IT infrastructures are managed and utilized. At the heart of this technology are hypervisors, which serve as the critical software layer that enables virtualization by allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine. Understanding the various types of hypervisors and their respective roles is essential for anyone looking to leverage virtualization effectively.
Hypervisors can be categorized into two primary types: Type 1 (bare-metal) and Type 2 (hosted). Each type serves a unique purpose in virtualization environments, and their functions can significantly influence performance, scalability, and resource management.
Types of Hypervisors and Their Functions
Type 1 hypervisors run directly on the hardware of the host machine, allowing for better performance and resource allocation. They do not require a host operating system, which minimizes overhead and increases efficiency. Examples of Type 1 hypervisors include VMware ESXi, Microsoft Hyper-V, and Xen.
Type 2 hypervisors, on the other hand, operate on top of a conventional operating system. They rely on the host OS for resource management and hardware interaction, which can introduce some latency. Examples of Type 2 hypervisors include VMware Workstation, Oracle VirtualBox, and Parallels Desktop.
When considering which type of hypervisor to use, it’s important to evaluate their advantages and specific use cases. Below is a comparison highlighting the key differences:
| Feature | Type 1 Hypervisor | Type 2 Hypervisor | Common Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Performance | High performance due to direct access to hardware | Moderate performance, influenced by the host OS | Data centers, enterprise environments |
| Installation | Requires direct installation on hardware | Installed on a host operating system | Development, testing, personal use |
| Resource Management | Efficient utilization of resources | Dependent on host OS’s resource management | Small to medium-scale deployments |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large environments | Less scalable, suited for limited environments | Virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI), cloud computing |
In summary, selecting the appropriate hypervisor type is crucial for achieving optimal performance and meeting specific operational needs. Type 1 hypervisors are better suited for enterprise applications requiring high efficiency and scalability, while Type 2 hypervisors provide flexibility and ease of use for smaller setups or development environments.
Real-World Applications of Virtualization
Virtualization has transformed the way businesses operate across various industries, enabling them to optimize resources, enhance flexibility, and improve disaster recovery. Its implementation not only streamlines operations but also fosters innovation by allowing companies to experiment with new technologies without significant upfront investments. This section explores notable applications of virtualization in healthcare, finance, and education, along with a deeper look at its role in disaster recovery and business continuity.
Applications of Virtualization in Various Industries
Virtualization serves as a backbone for numerous sectors by enhancing operational efficiency and reducing costs. Some notable applications include:
- Healthcare: Virtualization is widely used in healthcare for managing electronic health records (EHRs). Organizations can create virtual data centers that securely store patient data, allowing healthcare professionals to access critical information anytime, anywhere, while ensuring compliance with regulations such as HIPAA.
- Finance: Financial institutions utilize virtualization to enhance data security and increase operational efficiency. For example, banks can deploy virtual servers to run multiple applications on a single physical server, reducing hardware costs and enabling rapid deployment of services to meet customer demands.
- Education: Educational institutions leverage virtualization to provide students with access to software applications and learning environments without needing physical installations on their personal devices. Virtual labs allow students to engage in hands-on experimentation while minimizing hardware requirements.
Virtualization for Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity Planning
Virtualization plays a critical role in disaster recovery (DR) and business continuity planning (BCP) by allowing organizations to prepare for unforeseen disruptions. It enables the rapid recovery of IT services, ensuring minimal downtime and protecting valuable data.
Organizations implement virtualization strategies that include creating snapshots of virtual machines (VMs) to maintain up-to-date copies of their systems. In the event of a disaster, these snapshots can be quickly restored, minimizing data loss and operational disruptions. The benefits of virtualization in this context include:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Traditional disaster recovery solutions often require duplicate hardware, which can be expensive. Virtualization allows companies to use existing infrastructure to create DR solutions, significantly reducing costs.
- Speed of Recovery: With virtualization, businesses can recover systems and applications in a fraction of the time compared to traditional methods. This rapid recovery is crucial for maintaining customer trust and ensuring operational continuity.
- Scalability: Virtualized environments are inherently scalable. Organizations can easily adjust resources based on their evolving needs, making it easier to expand disaster recovery solutions as the company grows.
A comprehensive disaster recovery plan utilizing virtualization involves regularly updating backups, conducting tests to ensure recovery procedures function as intended, and maintaining clear documentation. This proactive approach not only safeguards against data loss but also enhances overall business resilience.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of Virtualization
A notable example of successful virtualization implementation is XYZ Corporation, a mid-sized retail company aiming to improve its IT efficiency and disaster recovery capabilities. Before virtualization, the company relied on physical servers, leading to high maintenance costs and slow recovery times.
XYZ Corporation transitioned to a virtual environment using VMware technology, creating multiple virtual servers on fewer physical machines. This shift resulted in a 50% reduction in hardware costs and a significant decrease in energy consumption. Moreover, the company implemented a robust disaster recovery strategy, enabling them to restore services within minutes instead of hours.
The outcomes were profound. Not only did operational efficiency improve, but employee productivity also increased due to the reduced downtime and streamlined processes. Furthermore, customer satisfaction soared as the company could quickly adapt to market demands without major disruptions. XYZ Corporation’s successful virtualization strategy illustrates the transformative power of this technology, allowing businesses to thrive in an increasingly competitive landscape.
The Future of Virtualization Technology
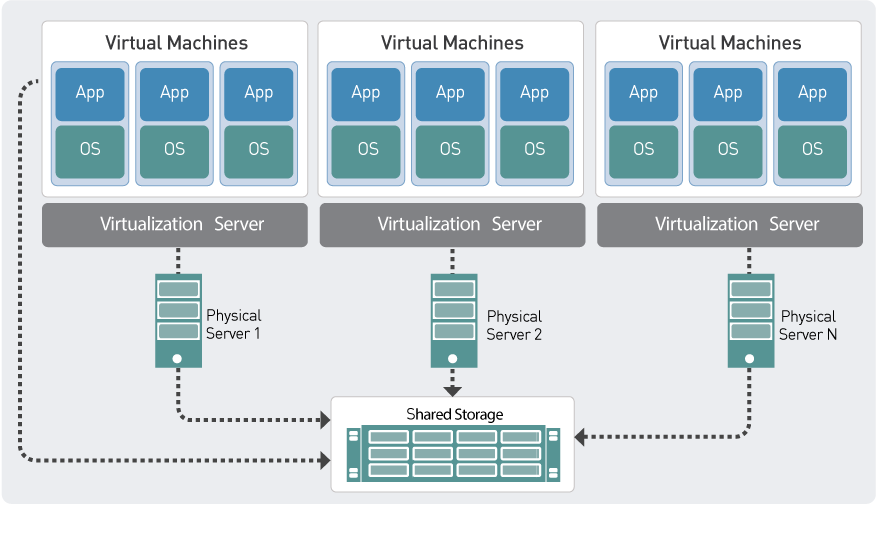
As the landscape of technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, virtualization stands out as a key player in the quest for efficiency and scalability. The future of virtualization technology is marked by emerging trends that not only enhance operational capabilities but also pose new challenges and ethical considerations for businesses navigating this complex terrain. It’s essential for organizations to understand these trends and their implications to remain competitive in a digitally transformed world.
Emerging Trends in Virtualization Technology
Several trends are shaping the future of virtualization technology, impacting how businesses operate and innovate. These trends include the increased adoption of microservices architecture, greater integration of artificial intelligence, and the rise of containerization. Each of these trends provides unique advantages and can fundamentally alter the operational framework of organizations.
- Microservices Architecture: This approach enables applications to be built as a suite of loosely coupled services, allowing for greater flexibility and faster deployment. Companies like Netflix have successfully leveraged this architecture to enhance their delivery and scalability.
- AI Integration: The incorporation of AI into virtualization can optimize resource allocation and improve predictive maintenance. For instance, VMware’s AI-driven analytics tools help businesses foresee hardware failures, reducing downtime.
- Containerization: Technologies like Docker and Kubernetes facilitate the development and deployment of applications in isolated environments, enhancing scalability and consistency across different platforms. The adoption of Kubernetes has surged, with major corporations, including Google and Microsoft, using it to manage containerized applications.
Cloud Computing’s Role in Virtualization
Cloud computing plays a pivotal role in the evolution of virtualization, providing the infrastructure necessary for virtualization technologies to thrive. The synergy between cloud computing and virtualization enhances resource utilization and operational efficiency, driving innovation across various sectors.
- On-demand Resources: Cloud platforms offer scalable resources that can be provisioned instantly through virtualization, allowing businesses to adapt quickly to changing demands.
- Cost Efficiency: By utilizing cloud-based virtualization, organizations can reduce capital expenditures on hardware and optimize operational costs through pay-as-you-go models.
- Enhanced Collaboration: Virtualization in the cloud fosters collaboration among distributed teams, enabling access to applications and data from any location, thus facilitating remote work environments.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite the advantages offered by virtualization technology, the future holds several challenges and ethical considerations that businesses must address. As the reliance on virtualization increases, so do concerns surrounding security, data privacy, and regulatory compliance.
- Security Risks: Virtual environments can be susceptible to cyber threats, including data breaches and unauthorized access. Organizations must invest in robust security measures to safeguard sensitive information.
- Data Privacy: With increased data virtualization, maintaining compliance with regulations such as GDPR becomes more complex. Businesses must implement stringent data management policies to protect customer information.
- Resource Allocation Ethics: The efficiency of virtualization may lead to ethical dilemmas regarding resource allocation. Companies must consider the implications of automation on employment and workforce dynamics.
“The future of virtualization technology not only promises transformation but also requires a commitment to ethical practices and responsible management.”
Security Implications in Virtualized Environments
The rise of virtualization technology has transformed IT infrastructure, leading to enhanced efficiency and resource optimization. However, this shift also introduces unique security challenges that differ significantly from traditional computing environments. Understanding these implications is essential for organizations seeking to protect their virtual assets and maintain data integrity.
Virtualization creates a new layer in the architecture of IT systems, where multiple virtual machines (VMs) operate on a single physical host. This can lead to differing security risks, such as hypervisor attacks, VM escape vulnerabilities, and inter-VM threats. Unlike traditional environments, where isolation is more straightforward, virtualized settings can inadvertently allow malicious actors to exploit shared resources, increasing the attack surface. The complexity of managing virtual environments also complicates security measures, making it crucial for organizations to adopt a proactive approach to safeguard their virtual assets.
Security Risks in Virtualized Environments
Virtual environments face distinct security challenges that require tailored strategies to mitigate risks. Below are key security risks associated with virtualization:
- Hypervisor Vulnerabilities: The hypervisor, which manages the VMs, can be a target for attackers. Compromising the hypervisor can lead to the hijacking of all VMs running on it.
- VM Escape: This occurs when an attacker exploits vulnerabilities to escape a VM and gain access to the host system or other VMs, potentially leading to data breaches.
- Resource Contention: When multiple VMs share physical resources, one compromised VM can affect the performance and security of others, making it challenging to contain attacks.
- Inadequate Isolation: VMs are often isolated from each other, but flaws in implementation can result in unintentional data leakage or unauthorized access between VMs.
- Configuration Errors: Misconfigurations in virtual environments are common and can create vulnerabilities, opening doors to unauthorized access or attacks.
Best Practices for Securing Virtual Machines and Hypervisors
To effectively secure virtual environments, organizations should implement specific best practices aimed at mitigating the unique risks posed by virtualization. These practices include:
- Regular Updates and Patching: Keeping hypervisors and VM software updated reduces the risk of exploitation from known vulnerabilities.
- Access Control: Employ strict access controls to limit who can interact with the hypervisor and manage VMs. Use role-based access to enforce minimum privilege principles.
- Network Segmentation: Isolate VMs on different network segments to limit the impact of a potential breach. Use firewalls and VLANs to enhance security boundaries.
- Monitoring and Logging: Implement continuous monitoring solutions to detect suspicious activities. Logging provides an audit trail that can be crucial during incident response.
- Backup and Recovery Strategies: Regularly back up VMs and ensure recovery processes are in place to protect against data loss due to attacks or failures.
Tools and Strategies for Enhanced Security
Several tools and strategies can bolster security in virtualized environments, helping organizations mitigate risks effectively. Here are some notable options:
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Use IDS specifically designed for virtual environments to monitor traffic and detect anomalies.
- Virtual Firewall Solutions: Deploy virtual firewalls to protect VMs from unauthorized access while monitoring and controlling traffic between them.
- Endpoint Protection: Implement endpoint security solutions that cater to virtual machines, ensuring protection from malware and other threats.
- Vulnerability Scanners: Utilize vulnerability scanning tools that can assess the security posture of VMs and hypervisors to identify potential weaknesses.
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): Deploy SIEM solutions to aggregate and analyze logs from virtual environments, providing insights into potential security incidents.
“The complexity of virtualization requires a multi-layered security approach to maintain a robust security posture.”
Performance Monitoring in Virtualized Systems
Performance monitoring in virtualized systems is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of IT environments. As organizations adopt virtualization to optimize resources and improve efficiency, monitoring performance has become an essential practice. This process involves tracking various metrics that provide insights into the health and efficiency of virtual machines (VMs) and the underlying physical hardware. Effective performance monitoring not only helps in identifying potential issues before they escalate but also assists in making informed decisions regarding resource allocation and system tuning.
Monitoring performance in virtualized environments relies on specific key performance indicators (KPIs) that reflect system health and efficacy. These KPIs typically include CPU usage, memory utilization, disk I/O rates, network throughput, and latency metrics. Various tools and methods can be employed to monitor these indicators effectively, including built-in hypervisor tools, third-party applications, and custom scripts. Hypervisors like VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V come equipped with performance monitoring capabilities that enable administrators to gather detailed analytics about VM performance and resource consumption.
Methods and Tools for Performance Monitoring
To implement effective performance monitoring in virtualized systems, organizations can benefit from using a range of methods and tools. Below are some of the most effective strategies:
- Hypervisor Monitoring Tools: Tools such as VMware vRealize Operations and Microsoft System Center provide comprehensive monitoring solutions that can track the performance of both VMs and the host infrastructure.
- Network Monitoring Tools: Solutions like SolarWinds or Nagios help monitor network performance, ensuring that virtualized network resources do not become bottlenecks.
- Custom Scripting: Administrators can create custom scripts using PowerShell or shell scripting to collect performance data tailored to their specific environment.
- Logging and Alerting Systems: Implementing logging frameworks enables the capture of detailed performance metrics over time, while alerting systems can notify administrators of significant deviations from the norm.
Performance monitoring is vital for maintaining optimal operations in virtualized systems. It allows administrators to proactively address performance bottlenecks, optimize resource allocation, and plan for future growth. Key reasons for the importance of performance monitoring include:
- Prevention of Downtime: By continually monitoring performance metrics, organizations can detect issues before they lead to system outages.
- Resource Optimization: Regular performance assessments help in identifying underutilized resources, allowing organizations to reallocate them effectively.
- Informed Decision-Making: Reliable performance data aids in strategic planning for capacity upgrades and resource investments.
- Cost Efficiency: By maximizing resource utilization, organizations can reduce operational costs associated with underused hardware.
To implement effective monitoring practices, follow these steps:
1. Identify Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Determine which metrics are critical for your virtual environment based on your organization’s needs.
2. Select Appropriate Tools: Choose monitoring tools that align with your infrastructure and can effectively capture the identified KPIs.
3. Establish Baselines: Record baseline performance metrics to understand normal operations and facilitate the detection of anomalies.
4. Set Up Alerts: Configure alerts to notify administrators of any performance issues that may arise, ensuring quick response times.
5. Regular Review and Analysis: Conduct regular performance reviews to analyze trends over time, allowing for informed adjustments to resource allocation and management strategies.
6. Document and Optimize: Keep detailed records of performance data and adjustments made. Continuously optimize based on findings to enhance overall system performance.
Consistent performance monitoring is integral to ensuring that virtualized systems operate efficiently, ultimately leading to improved productivity and reduced operational risks.
Virtualization and Resource Management
Virtualization plays a pivotal role in modern IT infrastructure by enabling the efficient management of resources. Through virtualization, multiple operating systems and applications can run on a single physical machine, which leads to improved resource utilization, cost savings, and simplified management. As organizations increasingly adopt virtualized environments, the importance of effective resource management becomes paramount to ensure optimal performance and service delivery.
The relationship between virtualization and resource management is integral, particularly in concepts like load balancing and resource allocation. Load balancing ensures that workloads are distributed evenly across available resources, preventing any single resource from becoming a bottleneck. Effective resource allocation involves dynamically assigning virtual resources to virtual machines based on demand, which can significantly enhance performance and responsiveness in a virtualized environment.
Load Balancing and Resource Allocation
Effective load balancing and resource allocation are essential for maintaining system performance and reliability. Below are key points highlighting the significance of these concepts in virtualization:
- Dynamic Resource Allocation: Virtualization technologies allow for the automatic adjustment of resources like CPU and memory based on real-time usage patterns. This flexibility helps in optimizing resource utilization without manual intervention.
- Load Balancing Algorithms: Various algorithms, such as Round Robin or Least Connections, can be integrated to distribute workloads evenly across servers. This maximizes throughput and minimizes response time.
- Virtual Machine Migration: Techniques like live migration enable moving virtual machines between physical hosts without downtime, allowing for better load distribution and maintenance without service interruption.
Tools for Resource Management
Several tools and software solutions have emerged to aid in the management of resources within virtualized environments, ensuring efficient operations and maximum performance. Examples include:
- VMware vSphere: A comprehensive suite for managing virtualized environments, offering features like automated load balancing and resource allocation.
- Microsoft System Center Virtual Machine Manager: Facilitates centralized management of virtualized resources, enabling administrators to allocate and monitor resources effectively.
- Red Hat Virtualization: An open-source solution that provides advanced features for resource allocation and load balancing, allowing for efficient management of virtual machines.
Manual Versus Automated Resource Management
Resource management in virtualization can be approached either manually or automatically, each with its advantages and disadvantages.
- Manual Resource Management: This approach typically involves human intervention for allocating and balancing resources, which can lead to inconsistencies, delays, and potential misallocations. While it allows for tailored decision-making, it is often time-consuming and prone to errors.
- Automated Resource Management: Automated tools utilize algorithms and policies to allocate resources dynamically, enabling real-time adjustments based on workload. This approach enhances efficiency, reduces human error, and allows IT staff to focus on strategic initiatives rather than routine tasks.
Integration of Virtualization with Containerization
The integration of virtualization and containerization plays a pivotal role in modern application deployment, enabling organizations to harness the strengths of both technologies. As businesses strive for efficiency, scalability, and faster delivery of applications, understanding how these two paradigms work together becomes essential for optimizing workflows and resources.
Virtualization abstracts the hardware layer, allowing multiple operating systems to run on a single physical server, while containerization encapsulates applications and their dependencies in lightweight, portable containers. Both approaches enhance resource utilization and facilitate a more agile development environment, but they do so in distinct ways. Virtualization typically involves running a hypervisor to manage virtual machines that operate in isolation, whereas containerization uses a shared kernel with minimal overhead, which allows for faster startup and lower resource consumption. Despite their differences, both technologies can be integrated to leverage their respective advantages.
Advantages and Challenges of Using Virtualization with Containerization
The combination of virtualization and containerization creates a powerful framework for application development and deployment. However, it is crucial to consider both the benefits and challenges that arise from this integration.
The following points highlight the advantages of using both technologies together:
- Improved Resource Efficiency: Virtualization allows for a higher density of applications on a single server, while containerization optimizes resource usage by sharing the host OS kernel.
- Isolation and Security: Virtual machines provide strong isolation between applications, enhancing security, while containers offer a lightweight alternative that still maintains a degree of separation.
- Faster Deployment: Containers can be deployed almost instantly, which, when combined with virtualized environments, speeds up the overall application lifecycle.
- Flexibility in Workloads: Using virtualization with containers allows for running diverse workloads, accommodating legacy applications alongside modern microservices.
On the other hand, the integration also presents several challenges:
- Complex Management: Managing both virtual machines and containers can lead to increased complexity in orchestration and monitoring.
- Resource Contention: If not properly configured, containers running on virtual machines might contend for resources, leading to performance issues.
- Networking Complexity: Networking can become more complicated, requiring robust configurations to ensure seamless communication between containers and virtual machines.
- Learning Curve: Teams may face a steep learning curve as they adapt to managing both technologies, requiring further training and expertise.
Ending Remarks
In conclusion, virtualization is not just a trend but a necessary evolution in the IT landscape that promises greater efficiency, cost savings, and flexibility. As businesses continue to integrate virtualization into their operations, they position themselves to adapt to future technological advancements while addressing the challenges that come with it.
Essential FAQs
What is virtualization?
Virtualization is the creation of a virtual version of physical hardware, allowing multiple virtual systems to operate on a single physical system.
How does virtualization improve resource management?
It enhances resource management by allowing for better allocation, load balancing, and optimized utilization of hardware resources.
What is a hypervisor?
A hypervisor is software that creates and manages virtual machines, enabling multiple operating systems to run on a single physical machine.
Is virtualization secure?
While virtualization introduces specific security challenges, proper practices and tools can significantly mitigate these risks.
How does virtualization benefit disaster recovery?
It simplifies disaster recovery by allowing quick backups and the ability to quickly restore systems in case of a failure.
Can virtualization be used in small businesses?
Yes, virtualization is scalable and can benefit small businesses by reducing hardware costs and simplifying IT management.