Kicking off with Reinforcement Learning, this fascinating field of artificial intelligence mimics how humans learn from their environment through trial and error. By interacting with various scenarios, agents make decisions to maximize rewards, learning to adapt and improve over time. The insights gained from reinforcement learning offer a powerful toolkit for solving complex problems across diverse industries.
This approach encompasses fundamental concepts such as agents, environments, states, actions, and rewards, creating a dynamic framework for the learning process. Whether it’s training a robot to navigate a maze or optimizing financial trading strategies, reinforcement learning’s unique ability to learn from consequences makes it an intriguing area of study with vast applications.
Reinforcement Learning Fundamentals
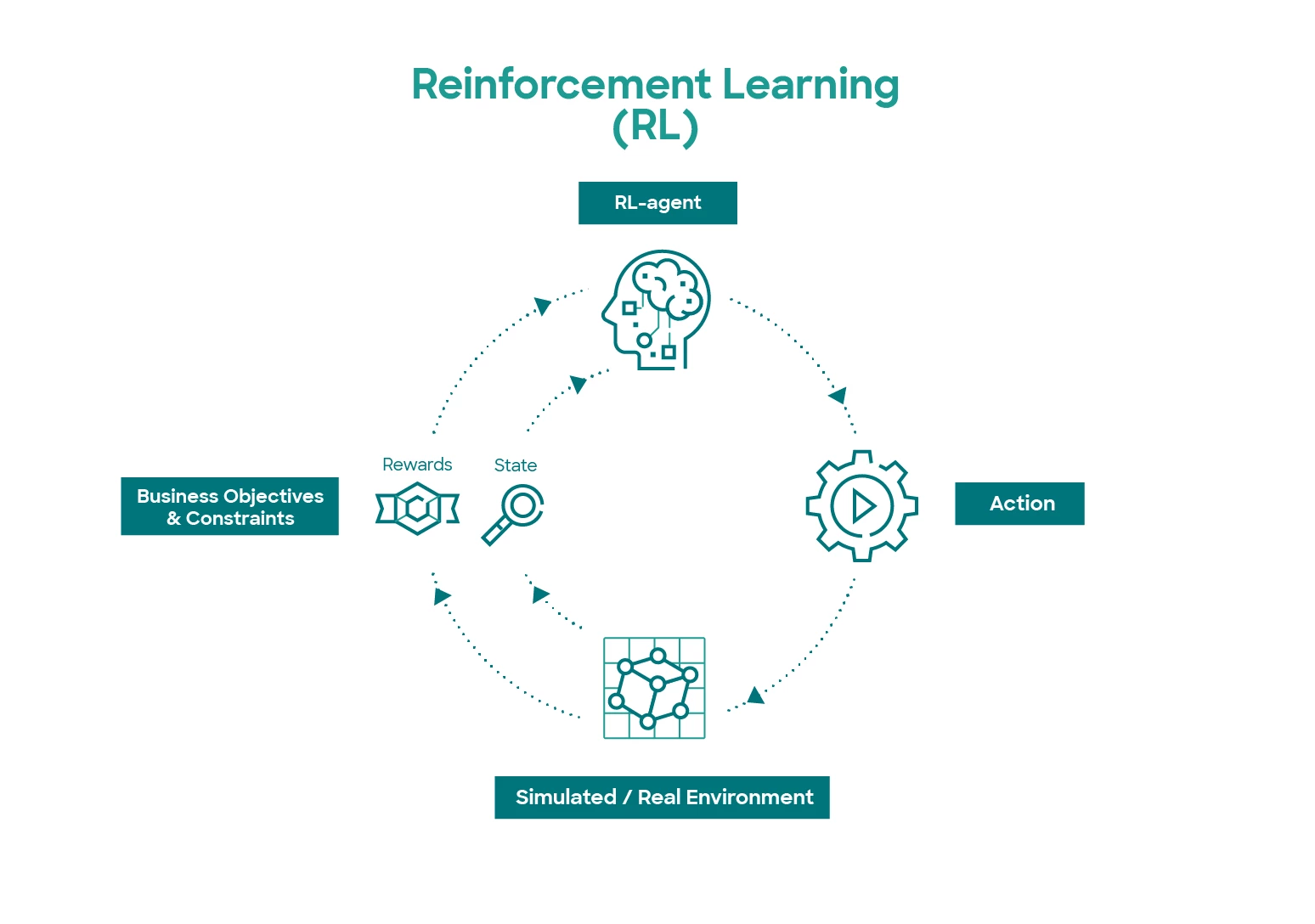
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a subset of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by interacting with an environment. The primary goal of the agent is to maximize cumulative rewards over time, which requires learning optimal strategies based on the consequences of its actions. This process mimics how humans and animals learn through experiences—trial and error.
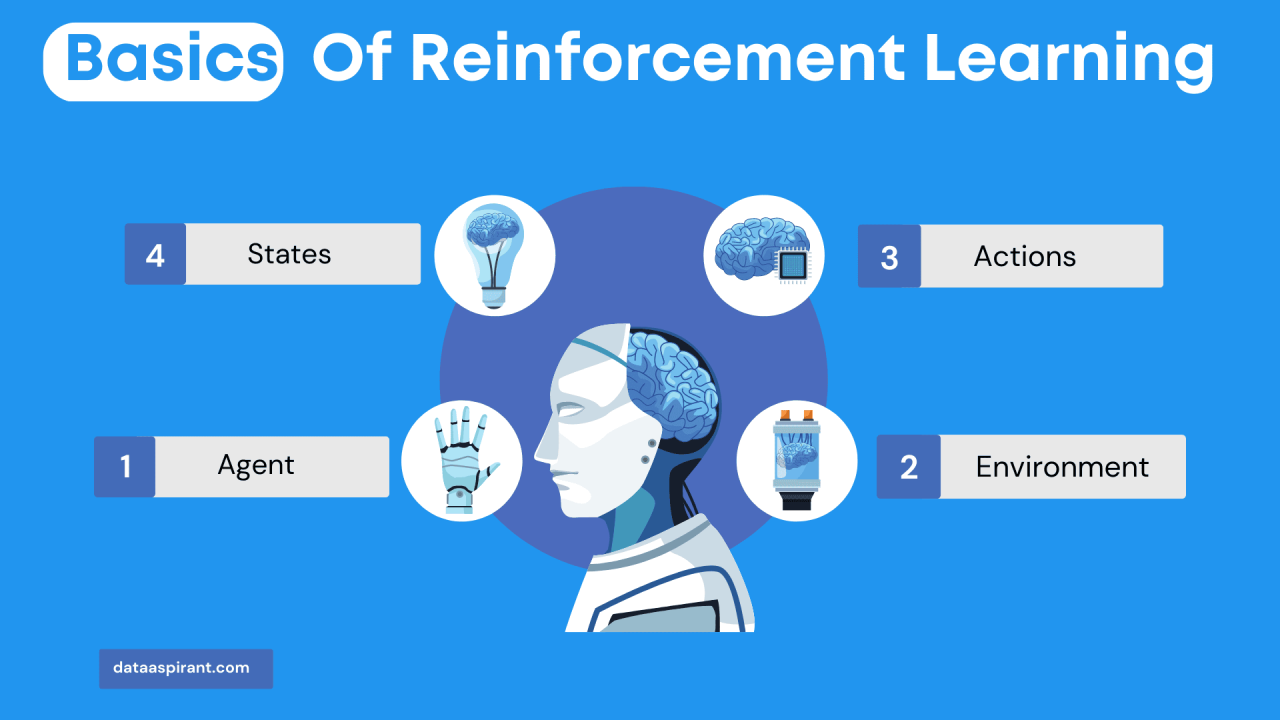
The fundamental components of reinforcement learning include agents, environments, states, actions, and rewards. The agent is the learner or decision-maker; the environment encompasses everything the agent interacts with. States represent the current situation of the agent within the environment, while actions are the choices available to the agent. Rewards provide feedback from the environment based on the actions taken, guiding the agent toward favorable outcomes.
The learning process in reinforcement learning occurs through trial and error, which is central to developing effective strategies. At the outset, the agent may not have any knowledge of the environment or the rewards associated with its actions. Through exploration, the agent takes various actions and observes the resulting states and rewards. Initially, this exploration can seem random, and the agent may take actions that yield little to no rewards. However, as the agent accumulates experiences, it begins to recognize patterns and correlations between actions and outcomes.
Over time, the agent employs an exploration-exploitation strategy. Exploration involves trying out new actions to discover their potential rewards, while exploitation focuses on leveraging known actions that yield higher rewards. This balance is crucial because excessive exploration can lead to suboptimal performance, while too much exploitation may prevent the agent from discovering even better strategies.
As the agent iteratively interacts with the environment, it updates its understanding of the value of each state-action pair using algorithms like Q-learning or policy gradients. With each iteration, the agent refines its policy—a strategy that dictates the best action to take in a given state—ultimately leading to improved decision-making capabilities. This cycle of exploration, learning, and optimization is what enables reinforcement learning systems to adapt and thrive in dynamic environments.
Key Components of Reinforcement Learning
Understanding the key components of reinforcement learning provides insights into how these systems function effectively. Each element plays a critical role in the learning and decision-making process:
- Agents: The decision-making entity that learns through interaction.
- Environments: The external system that provides the context in which the agent operates.
- States: Specific situations or configurations of the environment that the agent observes.
- Actions: Choices made by the agent that can influence the environment.
- Rewards: Feedback received from the environment that indicates the success of an action.
The interplay of these components allows reinforcement learning systems to effectively learn from their surroundings, adapt to new situations, and refine their strategies to achieve desired outcomes. This dynamic process is what makes reinforcement learning both powerful and applicable in various real-world domains, such as robotics, gaming, and autonomous systems.
Different Types of Reinforcement Learning Approaches
Reinforcement learning (RL) is a versatile field within machine learning, characterized by its varied approaches to training agents. Understanding the different methodologies available can significantly enhance the effectiveness of an agent’s learning process. This section explores the primary types of reinforcement learning approaches, including model-free and model-based methods, as well as the distinctions between policy-based and value-based methods.
Model-Free and Model-Based Methods
Reinforcement learning methodologies can generally be categorized into two main types: model-free and model-based methods.
Model-free methods do not depend on a model of the environment; instead, they learn the value of actions directly from experiences. These methods often utilize trial and error, allowing the agent to refine its strategies over time without a predefined framework of the environment dynamics. One prominent example of model-free methods is Q-learning, a value-based approach where the agent learns the value of the action in each state to maximize total expected reward.
Conversely, model-based methods involve creating a model of the environment, which allows the agent to simulate different states and actions. By understanding how the environment operates, the agent can make predictions and plan its actions more effectively. An example of a model-based approach is the Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS), frequently used in complex games like Go. In MCTS, the agent builds a tree of possible future states, helping it to choose the most promising actions.
Policy-Based and Value-Based Methods
Within reinforcement learning, there are further distinctions to be made between policy-based and value-based methods.
Policy-based methods focus on learning a policy that maps states to actions directly, optimizing the expected return for each action taken in a given state. This approach is beneficial in high-dimensional action spaces or when the action space is continuous. Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) is a commonly used policy-based method, known for its robustness and efficiency in various applications, including robotics and game playing.
On the other hand, value-based methods aim to evaluate the value of being in a given state or the value of taking specific actions in those states. The learning process involves estimating the value function, which helps the agent determine the best action to take based on the expected future rewards. A well-known example is the Deep Q-Network (DQN), which combines deep learning with Q-learning. DQN has been successfully applied in video games, where the agent learns to play by receiving feedback from its environment.
Understanding these distinctions and the application of different methods in real-world scenarios can greatly enhance the design and effectiveness of reinforcement learning models, ultimately leading to more intelligent and adaptable agents.
Applications of Reinforcement Learning in Various Industries
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a transformative technology, pushing the boundaries of how machines learn and make decisions. With its ability to optimize complex decision-making processes by learning from interactions with the environment, RL finds applications across various industries. From finance to healthcare and robotics, the impact of RL is profound, providing innovative solutions to traditional challenges.
Finance Industry Applications
In the finance sector, reinforcement learning is being utilized to enhance trading strategies and risk management. Algorithms trained with RL can analyze vast amounts of market data, learning to predict price movements and optimize investment portfolios.
- Algorithmic Trading: Firms like Jane Street have implemented RL to develop adaptive trading algorithms that respond to market conditions in real-time, significantly improving their trading efficiency and profitability.
- Risk Assessment: Companies are using RL to assess credit risk by simulating various financial scenarios and their potential impacts, enabling better lending decisions and risk management practices.
- Portfolio Management: The use of RL in portfolio management allows for dynamic asset allocation, adjusting investments based on performance and market fluctuations, thereby maximizing returns.
Healthcare Industry Applications
In healthcare, reinforcement learning is revolutionizing personalized medicine and treatment optimization. By learning from patient responses to various treatments, RL can aid in developing more effective healthcare solutions.
- Personalized Treatment Plans: Researchers at Stanford University have utilized RL to create personalized treatment plans for patients with chronic diseases, dynamically adjusting treatments based on real-time feedback and patient data.
- Drug Discovery: Companies like Atomwise are using RL to optimize the drug discovery process, enabling faster identification of viable drug candidates and reducing the time needed for bringing new drugs to market.
- Operational Efficiency: Hospitals are employing RL algorithms to manage operational logistics, such as optimizing staff schedules and resource allocation, resulting in improved patient care and operational efficiency.
Robotics Industry Applications
Reinforcement learning has made significant strides in robotics, allowing machines to learn complex tasks through trial and error. This adaptive learning process enhances the capabilities of robotic systems across various applications.
- Autonomous Navigation: Companies like Waymo are leveraging RL for self-driving technology, where vehicles learn to navigate complex road environments by continuously learning from their interactions with the surroundings.
- Industrial Automation: Robotics firms are employing RL to optimize manufacturing processes. For example, robots are trained to perform intricate assembly tasks, improving precision and efficiency in production lines.
- Human-Robot Interaction: Reinforcement learning is being used to enable robots to understand and predict human behaviors, allowing for more intuitive and effective collaboration between humans and machines in environments like warehouses and homes.
Challenges and Limitations of Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement Learning (RL) has emerged as a powerful framework for training intelligent agents to make decisions within complex environments. However, as practitioners delve deeper into RL, they encounter several significant challenges that hinder its practical applications. Understanding these challenges is crucial for leveraging RL effectively in real-world scenarios.
One of the primary challenges in reinforcement learning is the inherent difficulty in balancing the exploration-exploitation trade-off. Agents must explore new strategies to improve their performance, but they must also exploit known strategies that yield higher rewards. This balance is critical as improper handling can lead to suboptimal performance or even failure to learn effectively. The following points elaborates on the exploration-exploitation dilemma:
Exploration-Exploitation Trade-off
Balancing exploration and exploitation is vital for an agent’s success in RL. The strategy chosen can significantly impact the learning process. Here are some key aspects of this challenge:
- Exploration Inefficiency: Many algorithms struggle to efficiently explore vast state-action spaces, leading to slow learning and increased computational costs.
- Exploitation Risks: Overemphasizing exploitation can cause agents to converge prematurely on suboptimal strategies, missing out on potentially better options.
- Adaptive Exploration: Finding algorithms that can adaptively adjust their exploration strategies based on past performance remains a challenge.
Sample efficiency is another critical limitation faced by reinforcement learning algorithms. They often require a substantial amount of interactions with the environment to learn effectively. This excessive need for data can be costly and time-consuming, especially in environments where data acquisition is expensive or impractical. The following points highlight the concerns regarding sample efficiency:
Sample Efficiency Limitations
The need for high sample efficiency is crucial for the practical deployment of RL solutions. Several challenges arise here:
- Data Requirements: Traditional RL methods can require millions of interactions to converge, making them unfeasible for many applications.
- Sparse Rewards: Environments with sparse or delayed rewards can exacerbate the sample inefficiency problem, as agents struggle to learn from limited feedback.
- Generalization: Many RL algorithms fail to generalize well across different tasks or environments, often requiring retraining from scratch.
Addressing these challenges necessitates innovative strategies. Researchers and practitioners are exploring various approaches to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of reinforcement learning algorithms. Here are some potential solutions:
Strategies to Overcome Challenges
Implementing effective strategies can help mitigate the challenges associated with reinforcement learning. The following solutions are gaining traction:
- Transfer Learning: Utilizing knowledge gained from one task to improve learning efficiency in another can significantly reduce the required data.
- Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning: Breaking down complex tasks into simpler subtasks allows agents to learn more effectively and improve overall performance.
- Model-Based Approaches: Incorporating models of the environment can facilitate better planning and reduce the number of interactions needed for effective learning.
In summary, while reinforcement learning presents remarkable opportunities, its challenges, such as balancing exploration and exploitation, sample efficiency, and the need for effective learning strategies, must be addressed for practical application. Through innovative solutions and ongoing research, the landscape of reinforcement learning continues to evolve, promising greater applicability in real-world scenarios.
Future Trends in Reinforcement Learning Research
The landscape of reinforcement learning (RL) is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements in computational power, data availability, and algorithmic innovations. As researchers continue to delve deeper into this field, several emerging trends are shaping the future of RL. These developments not only promise to enhance the capabilities of RL systems but also have the potential to redefine the broader domain of artificial intelligence.
One of the most significant trends is the integration of RL with other machine learning paradigms, such as supervised and unsupervised learning. This hybrid approach aims to leverage the strengths of different methodologies, creating more robust and versatile models. Additionally, RL is increasingly being applied in complex, real-world environments, which require models to learn from sparse feedback and adapt to dynamic changes.
Interdisciplinary Approaches in Reinforcement Learning
The future of reinforcement learning is likely to be influenced heavily by interdisciplinary collaborations, drawing insights from various fields such as neuroscience, psychology, and economics. These collaborations can lead to innovative algorithms that mimic human learning processes and decision-making strategies.
For instance, researchers are exploring Neuro-inspired RL, which seeks to replicate neural mechanisms observed in the human brain. This approach aims to create more efficient learning algorithms by understanding how biological systems process information and adapt to their environments.
Additionally, the incorporation of Game Theory principles into RL can enhance the development of multi-agent systems. By modeling interactions among agents within competitive and cooperative frameworks, researchers can create more sophisticated AI systems capable of strategic reasoning.
Another exciting area is the application of RL in healthcare, where it can optimize treatment plans through personalized medicine. By analyzing patient data and learning through trial and error, RL models can help identify the most effective interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
As RL continues to mature, its potential applications are vast:
- Autonomous systems, such as self-driving cars, where RL can optimize navigation and decision-making in real-time.
- Robotics, enabling machines to learn complex tasks through interaction with their environment, enhancing precision and efficiency.
- Finance, where RL can assist in developing trading strategies that adapt to market conditions dynamically.
- Smart cities, using RL to optimize traffic flow and energy consumption, contributing to sustainability efforts.
The future of reinforcement learning is not just confined to technical advancements but also involves ethical considerations. As AI technologies become more integrated into society, understanding the societal impacts of RL systems, including fairness, accountability, and transparency, will be crucial for responsible development and deployment.
In summary, as reinforcement learning continues to evolve, its interdisciplinary nature will play a pivotal role in shaping the technology’s capabilities and its impact on the broader field of artificial intelligence. The fusion of diverse insights is expected to catalyze breakthroughs that will enhance both the efficiency and applicability of RL across various domains.
Comparison of Reinforcement Learning with Other Machine Learning Techniques
Reinforcement Learning (RL) is a unique branch of machine learning that emphasizes learning through interactions with an environment. Unlike other techniques such as supervised or unsupervised learning, RL focuses on discovering optimal actions to maximize cumulative rewards over time. This distinction leads to various applications and advantages that set RL apart from traditional methods.
Comparison with Supervised and Unsupervised Learning
In supervised learning, models are trained using labeled datasets, where the algorithm learns to predict outcomes based on input-output pairs. In contrast, unsupervised learning deals with unlabeled data, focusing on finding patterns or groupings within the dataset. RL, however, operates differently, relying on a system of rewards and penalties to learn optimal behaviors without explicit labels or outcomes.
The following points highlight the differences between these learning methods:
- Data Requirement: Supervised learning requires a large amount of labeled data, which can be time-consuming and costly to obtain. Unsupervised learning needs no labels, but it can sometimes yield less interpretable results. RL relies on feedback signals rather than labeled data, allowing exploration of actions in a dynamic environment.
- Learning Paradigm: Supervised learning is known for its predictability and interpretability, where the model’s performance can be directly evaluated against a known outcome. Unsupervised learning helps discover hidden structures in data. Conversely, RL is a trial-and-error-based method where the agent learns from the consequences of its actions, making it adaptable but less predictable.
- Problem-Solving Approach: Supervised learning excels in classification and regression tasks, while unsupervised learning is beneficial for clustering and association tasks. RL is particularly effective in scenarios involving sequential decision-making processes, such as robotics and game playing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Reinforcement Learning
Understanding the pros and cons of reinforcement learning provides insight into its suitability for specific tasks compared to traditional methods.
The unique advantages of RL include:
- Adaptability: RL agents can adapt to changing environments in real-time, learning appropriate strategies based on new experiences.
- Exploration of Complex Problems: RL is capable of handling complex decision-making tasks that require long-term planning and delayed rewards, which are challenging for supervised and unsupervised methods.
- Optimal Policy Development: RL focuses on finding optimal policies for decision-making, which can lead to better performance in dynamic environments.
However, there are notable disadvantages:
- Sample Efficiency: RL often requires a large number of interactions with the environment to learn effectively, which may not be feasible in all applications.
- Stability and Convergence Issues: The learning process can be unstable, and convergence to an optimal policy is not always guaranteed.
- Complexity of Implementation: Developing RL algorithms can be more complex than traditional methods, requiring a deep understanding of the environment’s dynamics and reward structure.
Examples of Reinforcement Learning Applications
Reinforcement learning has demonstrated its strengths in various real-world scenarios, often outperforming traditional machine learning techniques. Some notable examples include:
- Game Playing: RL has achieved remarkable success in games like Go and DOTA 2, where agents trained using RL techniques have defeated world champions by learning complex strategies through self-play.
- Robotics: In robotics, RL is used for teaching robots to perform tasks like walking or grasping objects, allowing them to learn from trial and error in real-time environments, which is difficult for supervised learning methods.
- Autonomous Driving: RL is employed in the development of self-driving cars, where agents learn to navigate through traffic by interacting with their surroundings and optimizing their driving strategy based on feedback.
Summary
In summary, reinforcement learning stands at the forefront of AI innovation, paving the way for numerous advancements that can reshape industries and improve efficiency. As challenges are addressed and new research trends emerge, the future looks promising for this technology. With its ability to learn and adapt, reinforcement learning holds the potential to revolutionize how machines interact with complex environments, bridging the gap between artificial intelligence and practical real-world applications.
FAQ Compilation
What is reinforcement learning?
Reinforcement learning is a type of machine learning where an agent learns to make decisions by taking actions in an environment to maximize cumulative rewards.
How does reinforcement learning differ from supervised learning?
Unlike supervised learning, which relies on labeled data, reinforcement learning learns from the consequences of actions taken in an environment without explicit guidance.
What are the main components of reinforcement learning?
The key components include the agent, environment, states, actions, and rewards, each playing a vital role in the learning process.
What industries benefit from reinforcement learning?
Industries such as finance, healthcare, and robotics are leveraging reinforcement learning to solve complex problems and improve operational efficiency.
What are some common challenges in reinforcement learning?
Practitioners often face challenges such as sample efficiency, balancing exploration and exploitation, and the complexity of real-world environments.