Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) sets the stage for a deeper understanding of cybersecurity, acting as a gatekeeper that elevates security beyond mere passwords. In an age where digital threats lurk around every corner, MFA introduces an additional layer of protection that ensures only authorized users gain access to sensitive information. By requiring multiple forms of verification, such as something you know, something you have, or something you are, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
As we delve into this topic, we’ll explore the various types of authentication factors employed in MFA, how these methods enhance security, and the implications for businesses in today’s digital landscape. With real-world examples and a discussion on best practices, this overview will equip you with a solid understanding of why MFA is crucial for safeguarding against cyber threats.
Multi-factor Authentication Overview
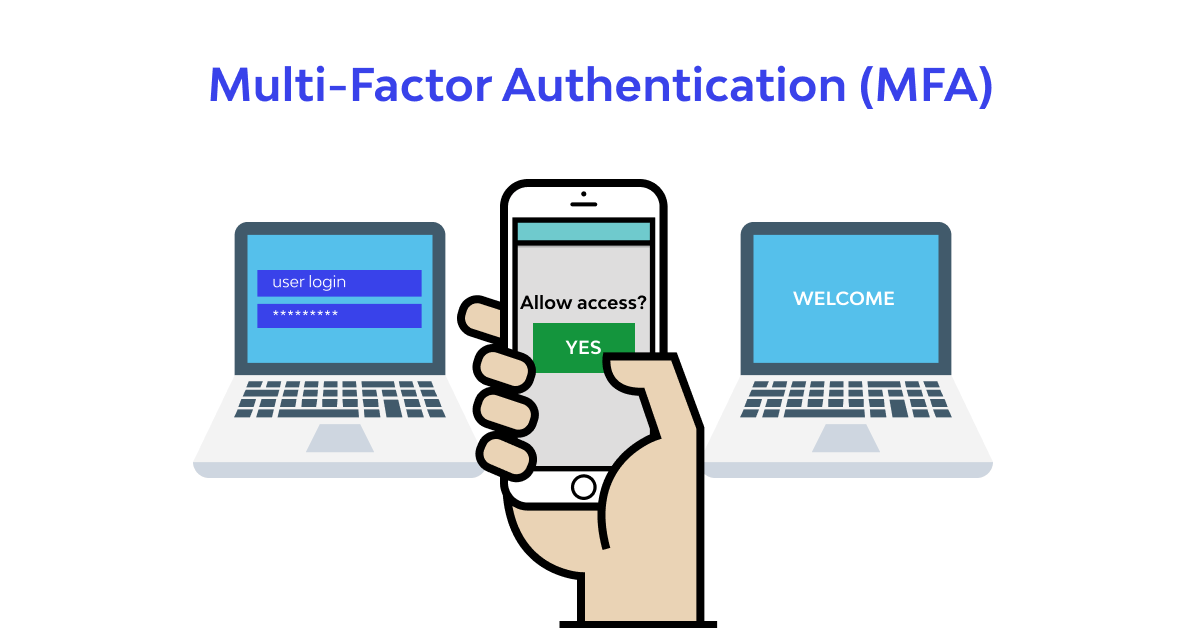
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is a security mechanism that enhances the protection of user accounts by requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access. In today’s digital landscape, where cyber threats are ever-evolving, relying solely on passwords is no longer sufficient. MFA adds layers to security, making it significantly tougher for unauthorized users to gain access to sensitive information, thus playing a pivotal role in cybersecurity.
MFA is fundamentally designed to ensure that even if one authentication factor is compromised, it doesn’t provide a complete foothold for an attacker. By leveraging various types of authentication factors, MFA significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access. The three primary types of authentication factors commonly utilized in MFA include:
Types of Authentication Factors
Understanding the different types of authentication factors is essential for grasping how MFA operates. Each factor serves as a barrier against unauthorized access and increases overall security. Here are the three main types:
- Something You Know: This factor typically involves knowledge-based credentials, such as passwords or PINs. Users must provide this information to gain access, making it the first line of defense.
- Something You Have: This includes physical devices or tokens, such as smartphones, smart cards, or hardware tokens, which generate time-sensitive codes. These devices are necessary to complete the authentication process.
- Something You Are: This biometric factor involves unique physical characteristics of the user, such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. It is a highly secure method, as it is intrinsically linked to the individual.
MFA dramatically enhances security compared to single-factor authentication, which relies solely on one method, typically a password. Single-factor systems are vulnerable to various attacks, such as phishing, keylogging, or brute force attempts. In contrast, MFA employs multiple layers of verification, creating a more robust security framework.
For instance, even if an attacker successfully obtains a user’s password through social engineering, they would still need access to the second factor, such as a smartphone app that generates a time-limited authentication code. This added complexity makes it exponentially more difficult for cybercriminals to compromise accounts, significantly reducing the likelihood of data breaches and unauthorized access.
In summary, MFA is an essential component of contemporary cybersecurity strategies. By employing diverse authentication factors, it mitigates risks and protects sensitive information from the ever-growing threats posed by cyberattacks.
Types of Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is a crucial security measure that enhances protection for users by requiring more than one method of verification. This approach significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access to accounts and sensitive information. Understanding the various types of MFA methods available is essential for both individuals and organizations looking to bolster their security posture.
MFA can generally be categorized into three primary types: something you know, something you have, and something you are. Each type offers distinct advantages and disadvantages, which are essential to understand for effective implementation.
Methods of Multi-factor Authentication
The three main types of MFA methods can be broken down as follows:
1. Something You Know
This category typically refers to knowledge-based factors such as passwords or PINs. Users must input this information to gain access.
“Passwords alone are not enough; they can be easily compromised.”
Advantages:
– Familiarity: Most users are accustomed to using passwords, making this method easy to implement.
– No additional equipment required: Users simply need to remember their password.
Disadvantages:
– Vulnerability to attacks: Passwords can be guessed, stolen, or phished.
– Weakness in user choice: Users often choose simple passwords which can be easily cracked.
Examples:
– Traditional accounts and services, including email providers and social media platforms, utilize passwords as a primary verification method.
2. Something You Have
This method involves physical items that users possess, such as smartphones, hardware tokens, or smart cards. These items generate a one-time code or provide a means for authentication.
“Tokens provide an additional layer by requiring possession of a physical device.”
Advantages:
– Stronger security: Even if a password is compromised, an attacker would still need the physical item to gain access.
– Variety of options: Users can select from various forms, from mobile apps to hardware tokens.
Disadvantages:
– Dependency on physical items: If a user loses their token or phone, accessing their account can become challenging.
– Cost: Physical tokens may incur additional costs for organizations.
Examples:
– Google Authenticator and Authy are popular apps that generate time-based one-time passwords (TOTP). Hardware tokens like YubiKey also fall under this category.
3. Something You Are
This type involves biometric factors, such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or voice recognition. It relies on unique physical characteristics to authenticate users.
“Biometric authentication leverages the uniqueness of human traits.”
Advantages:
– High security: Biometrics are difficult to replicate or steal.
– Seamless user experience: Users can authenticate quickly without needing to remember additional information.
Disadvantages:
– Privacy concerns: Users may feel uncomfortable sharing biometric data due to potential misuse.
– False rejections or acceptances: Biometric systems may not always recognize authorized users or can mistakenly grant access to unauthorized individuals.
Examples:
– Apple’s Face ID and Touch ID are widely recognized biometric authentication methods utilized in their devices. Similarly, fingerprint scanners on smartphones have become commonplace.
Understanding these various MFA methods aids users and organizations in choosing the right combination of factors to enhance security while considering usability and cost. The right balance can significantly mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access and data breaches.
The Importance of Multi-factor Authentication in Business
In an era where digital threats are escalating, businesses must prioritize the security of sensitive data. Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) serves as a robust defense mechanism that significantly enhances the protection of critical information. By requiring multiple forms of verification before granting access, MFA reduces the risk of unauthorized breaches and fosters a secure environment for both businesses and their customers.
MFA is crucial for businesses today as cyberattacks become increasingly sophisticated. A single stolen password can lead to devastating consequences. Implementing MFA acts as a vital safeguard against such threats, ensuring that even if one authentication factor is compromised, unauthorized access remains thwarted. The following incidents demonstrate the catastrophic impact of neglecting MFA in security protocols.
Real-World Incidents of Security Breaches
The absence of MFA has led to significant breaches across various industries, affecting countless organizations and individuals. The following examples underscore the vital need for implementing MFA:
- Twitter Breach (2020): In July 2020, a coordinated attack compromised numerous high-profile accounts, including those of public figures and celebrities. Attackers gained access to internal tools by exploiting a lack of MFA, resulting in high-profile scams and misinformation.
- Uber Data Breach (2016): Uber suffered a massive data breach when attackers accessed the personal information of 57 million users and drivers. The root cause was inadequate security measures, including the absence of MFA, which allowed hackers to exploit stolen credentials.
- Yahoo Breach (2013-2014): One of the largest data breaches in history involved the exposure of 3 billion accounts. A significant factor was the lack of MFA, which enabled attackers to gain unauthorized access to user accounts and sensitive data over an extended period.
The implementation of MFA not only strengthens security but also plays a pivotal role in enhancing customer trust and business reputation.
Impact of MFA on Customer Trust and Business Reputation
Businesses that adopt MFA demonstrate a commitment to protecting their customers’ data, which can significantly impact their reputation in the marketplace. Customers are more likely to engage with and remain loyal to companies that prioritize their security.
The following factors illustrate how MFA influences customer trust and business reputation:
- Increased Confidence: Customers feel safer knowing that their personal information is safeguarded by multiple layers of authentication, which may encourage them to engage more with the business.
- Brand Loyalty: Companies that proactively protect customer data can enhance their brand loyalty, as satisfied customers are more likely to recommend the business to others.
- Compliance and Risk Management: By implementing MFA, businesses not only reduce the risk of data breaches but also meet regulatory compliance standards, thereby enhancing their credibility in the eyes of customers and partners.
“The implementation of Multi-factor Authentication is not just an option; it’s a necessity in today’s digital landscape.”
Challenges and Limitations of Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is a critical security measure that enhances the protection of sensitive data by requiring multiple forms of verification. However, organizations face several challenges and limitations in its implementation. Understanding these challenges is essential for optimizing MFA while ensuring user satisfaction and compliance with security protocols.
MFA technologies, while effective, are not without their obstacles. Common challenges range from user resistance to implementation complexities. It’s important for organizations to navigate these issues effectively to maintain security without compromising user experience.
Common Challenges in Implementing MFA
Organizations often encounter a variety of challenges when introducing MFA systems. These challenges can impact both security efforts and user engagement. Key challenges include:
- User Resistance: Employees may resist the adoption of MFA due to the perceived inconvenience and extra steps required during login processes.
- Complexity of Implementation: Integrating MFA into existing systems can be complex and may require significant technical resources and training.
- Cost Considerations: The financial investment for MFA solutions, including software, hardware, and training, can be a deterrent for some organizations.
- Usability Issues: If MFA methods are too cumbersome or time-consuming, users may find ways to bypass them, leading to security vulnerabilities.
Limitations of MFA Technology
Despite its strengths, MFA technology also presents limitations that organizations must consider. These limitations can affect the overall effectiveness of the security posture.
There are several inherent limitations to MFA, including:
- User Experience Concerns: MFA can lead to friction in the user experience, particularly if the methods are seen as cumbersome or overly complicated.
- Bypass Methods: Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in MFA methods, such as SIM swapping or phishing tactics, to gain unauthorized access.
- Dependence on Technology: If the devices or services used for MFA fail or are unavailable, users may be locked out, leading to productivity loss and frustration.
Mitigation Strategies for Organizations
To address the challenges and limitations of MFA, organizations can adopt several proactive strategies that balance security and user experience. These strategies help ensure that MFA is both effective and user-friendly.
Implementing a user-focused approach can alleviate some of the common issues:
- Education and Training: Providing comprehensive training on the importance of MFA can help mitigate user resistance and improve compliance.
- Choosing User-Friendly Solutions: Organizations should select MFA solutions that offer a balance between security and ease of use, such as biometric options or mobile authentication apps.
- Backup Authentication Methods: Implementing backup methods for MFA can help prevent user lockouts due to technology failures.
- Regular Security Assessments: Conducting ongoing assessments can help organizations identify and address vulnerabilities in their MFA systems.
Incorporating user feedback and making iterative improvements to MFA processes can enhance security while maintaining a positive user experience.
Future Trends in Multi-factor Authentication

As multi-factor authentication (MFA) continues to evolve, it is essential to examine the future trends that will shape the landscape of digital security. With the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, organizations are integrating innovative technologies to enhance their authentication processes. The next few years will likely see significant advancements that not only improve security but also streamline user experiences.
Emerging MFA technologies are likely to redefine security practices across various sectors. The adoption of decentralized identity frameworks, for instance, holds the potential to empower users by giving them control over their personal data. This shift could lead to a more secure and user-friendly authentication process, reducing reliance on central authorities and minimizing data breaches. Additionally, the integration of blockchain technology with MFA systems can enhance transparency and accountability, making it easier to verify user identities without compromising sensitive information.
Role of Biometrics and AI in MFA Evolution
The incorporation of biometrics and artificial intelligence (AI) into multi-factor authentication is becoming increasingly important. Biometrics, which includes fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and voice identification, provides a unique and secure method of verifying identity. These technologies are not only convenient but also difficult to replicate, making them a robust addition to MFA.
AI plays a pivotal role in improving the efficiency and accuracy of biometric systems. For instance, AI algorithms can analyze biometric data in real time, adjusting to variations in user behavior and enhancing detection capabilities. This evolution, however, is not without risks. The reliance on biometric data raises concerns about privacy, data security, and the potential for misuse. Security breaches involving biometric databases can have severe consequences, as compromised biometric data cannot be changed like passwords.
To contextualize the impact of biometrics and AI on MFA, consider the rise of mobile payment systems. Companies like Apple and Google are implementing advanced biometric verification methods, such as Face ID and fingerprint sensors, which have transformed how users authenticate transactions. While these innovations enhance security, they also necessitate robust measures to safeguard biometric data against potential breaches.
Projection of MFA Changes in the Next Five Years
Looking ahead, the next five years are poised to bring significant innovations in multi-factor authentication. As organizations increasingly adopt a zero-trust security model, MFA will become more integral to the security framework. The following trends are expected to emerge:
- Contextual Authentication: Future MFA solutions will leverage contextual information, such as device location and user behavior patterns, to determine the legitimacy of access attempts. This adaptive approach enhances security by dynamically adjusting the level of authentication required based on risk assessment.
- Seamless User Experiences: The focus will shift toward creating frictionless authentication processes. Technologies such as passwordless authentication and single sign-on (SSO) systems will become commonplace, reducing user fatigue while enhancing security.
- Increased Adoption of FIDO Standards: The Fast Identity Online (FIDO) Alliance is driving the adoption of passwordless authentication methods. As organizations recognize the limitations of traditional password systems, FIDO-compliant solutions will become more prevalent, offering stronger security without the need for passwords.
- Integration of AI-Powered Risk Assessment: Organizations will increasingly use AI to analyze user behavior and detect anomalies. This integration will enable proactive threat detection, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to potential security breaches before they escalate.
The ongoing evolution of multi-factor authentication is set to significantly enhance security practices across industries. By combining emerging technologies like biometrics and AI with innovative approaches to user authentication, organizations can create a more secure and user-friendly digital environment.
Best Practices for Implementing Multi-factor Authentication
Implementing Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is vital for enhancing security in today’s digital landscape where breaches and cyber threats are prevalent. Organizations can significantly reduce their vulnerability by adopting MFA strategies to secure sensitive data and systems. This guide Artikels best practices for implementing MFA, ensuring a smooth deployment and effective use.
Key Steps for Successful MFA Deployment
An effective MFA deployment requires careful planning and execution. Here are the key steps organizations should follow:
- Assess Current Security Posture: Before implementing MFA, evaluate your existing security measures. Identify gaps and determine how MFA can address these vulnerabilities. For example, a financial institution may find that passwords alone are insufficient to secure customer accounts.
- Choose the Right MFA Solution: Select an MFA solution that aligns with your organization’s needs. Popular options include SMS-based verification, mobile authentication apps, and biometric methods. A tech company may opt for an app-based solution for its employees that integrates easily with existing systems.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Ensure that the chosen MFA solution can be seamlessly integrated with your current applications and services. This helps maintain user experience and reduces friction. For example, integrating MFA with an employee login portal can streamline access while enhancing security.
- Conduct a Pilot Program: Run a pilot program to test the MFA solution in a controlled environment. Involve a small group of users to gather feedback and identify potential issues. A healthcare provider could pilot MFA with a specific department before a full rollout.
- Roll Out Organization-wide: Once the pilot is successful, implement MFA across the organization. Communicate clearly about the changes and provide support during the transition.
- Monitor and Adapt: After deployment, continuously monitor the performance of your MFA solution. Make adjustments as necessary based on user feedback and threat landscape changes. For instance, if SMS codes are frequently intercepted, consider transitioning to app-based or biometric authentication.
User Education and Training Importance
User education and training are critical components in the implementation of MFA. Ensuring that users understand how to use MFA effectively can significantly enhance the overall security posture.
- Educate Users on MFA Benefits: Inform users about the advantages of MFA, such as increased security and protection against unauthorized access. Highlight real-world examples of data breaches where MFA could have prevented the incident.
- Provide Training Sessions: Conduct training sessions that demonstrate how to set up and use MFA. Consider interactive workshops that allow users to practice the process in a safe environment.
- Create Comprehensive Resources: Develop user-friendly resources, including guidebooks and video tutorials, to help users navigate the MFA process. These materials can serve as quick references to address common issues and queries.
- Encourage Feedback: Foster an environment where users can easily provide feedback on their experiences with MFA. This feedback can help identify areas for improvement and enhance user engagement.
“An informed user is an empowered user; educating staff on MFA ensures its success and effectiveness.”
By implementing these best practices, organizations can ensure a successful Multi-factor Authentication deployment that not only enhances security but also fosters a culture of cybersecurity awareness among users.
Regulatory Compliance and Multi-factor Authentication
Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) has become a vital component in the security frameworks of many organizations, directly influencing regulatory compliance across various industries. As cyber threats evolve, regulations have adapted to mandate stronger security measures, making MFA not just a best practice, but a requirement for compliance with certain laws and frameworks. Organizations that implement MFA not only enhance their security posture but also align themselves with legal obligations that help protect sensitive information.
The relationship between MFA and regulatory compliance can be seen in how certain regulations establish specific requirements for authentication mechanisms. Compliance with these regulations not only safeguards organizations against data breaches but also mitigates the potential for hefty fines and reputational damage. Some of the key regulations that mandate MFA usage include:
Key Regulations Mandating MFA
Compliance requirements vary by industry, but several regulations universally recognize the importance of MFA in securing sensitive data. The following are notable regulations that explicitly require MFA:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act): This U.S. regulation mandates MFA for healthcare providers and their business associates to ensure the confidentiality and security of patient information. Non-compliance can lead to significant penalties, making MFA an essential component of health data protection.
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation): The European Union’s GDPR requires organizations handling personal data to implement measures that protect this information. While not explicitly stating MFA, it emphasizes the need for appropriate security measures, of which MFA is increasingly recognized as a best practice to comply with data protection requirements.
- PCI DSS (Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard): For businesses that handle credit card transactions, PCI DSS requires the use of MFA as part of its security measures. This regulation is crucial for protecting cardholder data and involves strict compliance obligations that, if violated, can result in fines and loss of payment processing capabilities.
Organizations must adopt strategies to ensure their MFA implementations meet these regulatory compliance requirements. Key considerations include:
Ensuring Compliance with MFA Implementations
To effectively align MFA practices with regulatory requirements, organizations should consider the following strategies:
- Conducting a thorough risk assessment to identify vulnerabilities and determine the appropriate MFA solutions that fit regulatory standards.
- Regularly reviewing and updating MFA systems to ensure they comply with the latest regulatory changes and technological advancements.
- Providing comprehensive training to employees on the importance of MFA and how to use it effectively, helping to foster a security-conscious organizational culture.
- Implementing robust monitoring and auditing practices to track MFA usage and ensure compliance with the established regulatory frameworks.
“Implementing Multi-factor Authentication not only fortifies security but also ensures compliance with crucial regulations, thus safeguarding organizations from potential penalties.”
By understanding the intersection of regulatory compliance and MFA, organizations can better navigate the complexities of data protection while enhancing their overall security measures. The commitment to compliance not only protects sensitive information but also builds trust with customers and stakeholders in an increasingly digital landscape.
Comparing Multi-factor Authentication Tools
As businesses and individuals increasingly seek to bolster their security measures, Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) has emerged as a critical safeguard against unauthorized access. With a multitude of MFA tools available, selecting the right one can feel overwhelming. This overview will compare several popular MFA solutions, highlighting their distinct features, pricing, and user satisfaction levels to aid in making an informed decision.
Various MFA tools cater to different needs, whether for large enterprises or small businesses. Factors such as ease of integration, user experience, and customer support can significantly influence the effectiveness of an MFA tool. Below, we will explore key features, pricing structures, and user feedback for leading MFA solutions.
Comparison of Popular MFA Tools
In this section, we delve into a comparison of notable MFA tools available today, evaluating their essential features along with their pricing and user ratings. This information is crucial for organizations considering an MFA solution that aligns with their security requirements and budget.
| Tool Name | Key Features | Pricing | User Rating |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authy | Mobile app, SMS, and voice call authentication | Free for basic use; business plans from $9/month | 4.5/5 |
| Duo Security | Adaptive authentication, integrations with various apps | Free for up to 10 users; paid plans starting at $3/user/month | 4.7/5 |
| Google Authenticator | Time-based one-time passwords, simple setup | Free | 4.1/5 |
| Microsoft Authenticator | Passwordless sign-in, backup and restore features | Free | 4.6/5 |
| LastPass MFA | Biometric authentication, integration with LastPass password manager | $3/user/month | 4.3/5 |
The above table provides a structured understanding of the MFA tools in the market. Notably, Duo Security receives high user satisfaction ratings and offers adaptive authentication, making it a favorite among enterprises. Authy is recognized for its flexibility with mobile and voice call options, providing a user-friendly experience. In contrast, Google Authenticator, while free, has a simpler feature set, which may appeal to individual users and smaller teams.
User feedback indicates that Microsoft Authenticator is praised for its seamless integration with Microsoft services, making it an excellent choice for organizations already using Microsoft products. Meanwhile, LastPass MFA offers robust features for those who rely on its password management services, although its pricing may be a consideration for small businesses.
Overall, while each tool has its strengths, user feedback highlights the importance of considering specific organizational needs and existing infrastructure when selecting an MFA solution.
Closure
In conclusion, Multi-factor Authentication (MFA) is not just a trendy buzzword; it is an essential component of modern cybersecurity strategies. By implementing MFA, organizations not only protect their sensitive data but also foster trust with customers by demonstrating a commitment to security. As technology continues to evolve, the adoption of MFA will likely become even more critical, paving the way for a safer digital future.
FAQ Insights
What is Multi-factor Authentication (MFA)?
MFA is a security measure that requires two or more verification methods to gain access to a system, increasing protection compared to single-factor authentication.
How does MFA enhance security?
By requiring multiple forms of identification, MFA makes it significantly harder for unauthorized users to gain access, even if they have one credential, such as a password.
Are there any downsides to using MFA?
While MFA greatly enhances security, it can introduce usability challenges, such as longer login times and potential frustration for users who are not tech-savvy.
Can MFA be bypassed?
Yes, while MFA greatly reduces the risk, it is not foolproof, as sophisticated attackers may find ways to exploit vulnerabilities in the verification processes.
Is MFA necessary for all businesses?
While not every business may feel the immediate need for MFA, it is strongly recommended for any organization handling sensitive data or customer information.