Metadata sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. In our data-driven world, understanding metadata is essential, as it serves as the backbone of digital information management. Metadata provides context, improves searchability, and enhances user experience across various platforms, making it a critical asset for everything from libraries to social media.
The term ‘metadata’ refers to data about data, encapsulating vital information that describes, organizes, and manages content. For instance, in a digital photograph, metadata might include the date it was taken, the camera settings used, and even the GPS coordinates of where it was shot. This information not only aids in identifying and retrieving content but also plays a significant role in enhancing search engine optimization (), ensuring that relevant content is easily discoverable.
Understanding the Definition and Importance of Metadata in Digital Contexts
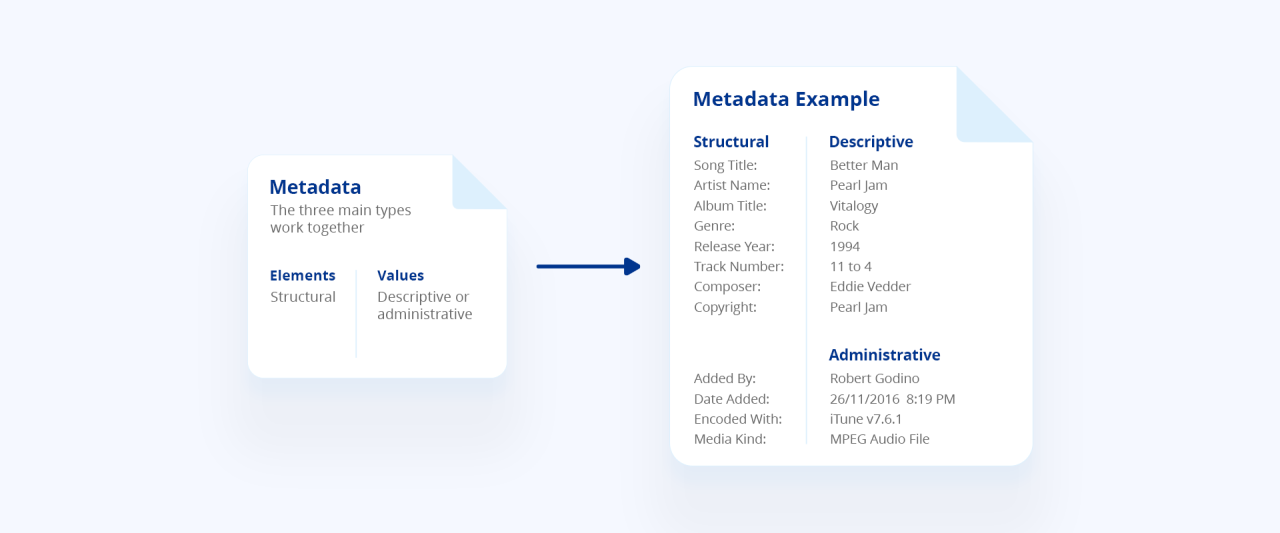
Metadata is essentially data about data. In digital contexts, it serves as an invaluable tool for organizing, identifying, and managing information across various platforms and systems. Metadata provides context that allows users to understand the content of data without needing to delve into the data itself. This context is crucial in an era where vast amounts of information are generated every second, and the ability to efficiently retrieve and utilize this information is paramount.
The significance of metadata can be observed across numerous digital environments, from websites to databases and digital libraries. For example, in the context of a digital photograph, metadata includes information such as the date and time the photo was taken, the camera settings, and even the geographical location. This metadata allows users to sort, filter, and search for images based on specific criteria rather than sifting through thousands of images manually. Similarly, in the world of academic research, metadata in the form of bibliographic details—such as author names, publication dates, and abstracts—enables researchers to find relevant literature efficiently.
Types of Metadata and Their Purposes
Different types of metadata serve distinct functions, enhancing the usability and accessibility of data. Here are some core types of metadata:
- Descriptive Metadata: This type provides information for discovery and identification of data. For instance, in a library catalog, the title, author, and s of a book are examples of descriptive metadata.
- Structural Metadata: It helps to organize and manage complex objects by outlining how different components are related, such as chapters of a book or sections of a webpage.
- Administrative Metadata: This type is crucial for managing resources, including details on how and when data was created, ownership, and rights information.
- Statistical Metadata: Often used in research contexts, it provides information about the data collection process, such as methodologies and sample sizes, ensuring transparency in data analysis.
The relationship between metadata and information retrieval is fundamental to effective search optimization. Metadata facilitates improved search engine performance by providing relevant s and tags that search engines can index. When a user searches for specific terms, the presence of well-structured metadata ensures that the most relevant results are displayed. Thus, high-quality metadata directly contributes to the accuracy and efficiency of information retrieval processes, enabling users to find exactly what they need in a fraction of the time it would take without metadata.
Effective metadata is the backbone of data organization and retrieval in the digital age.
Exploring Different Types of Metadata Used in Various Industries
Metadata plays a crucial role across a multitude of industries, enhancing the way information is stored, retrieved, and utilized. Understanding the different types of metadata—descriptive, structural, and administrative—provides insight into its distinct functionalities and applications. Each type serves a unique purpose, contributing to the organization and accessibility of information in fields like libraries, archives, and digital media, thereby improving user experience and operational efficiency.
Classifications of Metadata
There are three primary classifications of metadata that cater to various needs across industries:
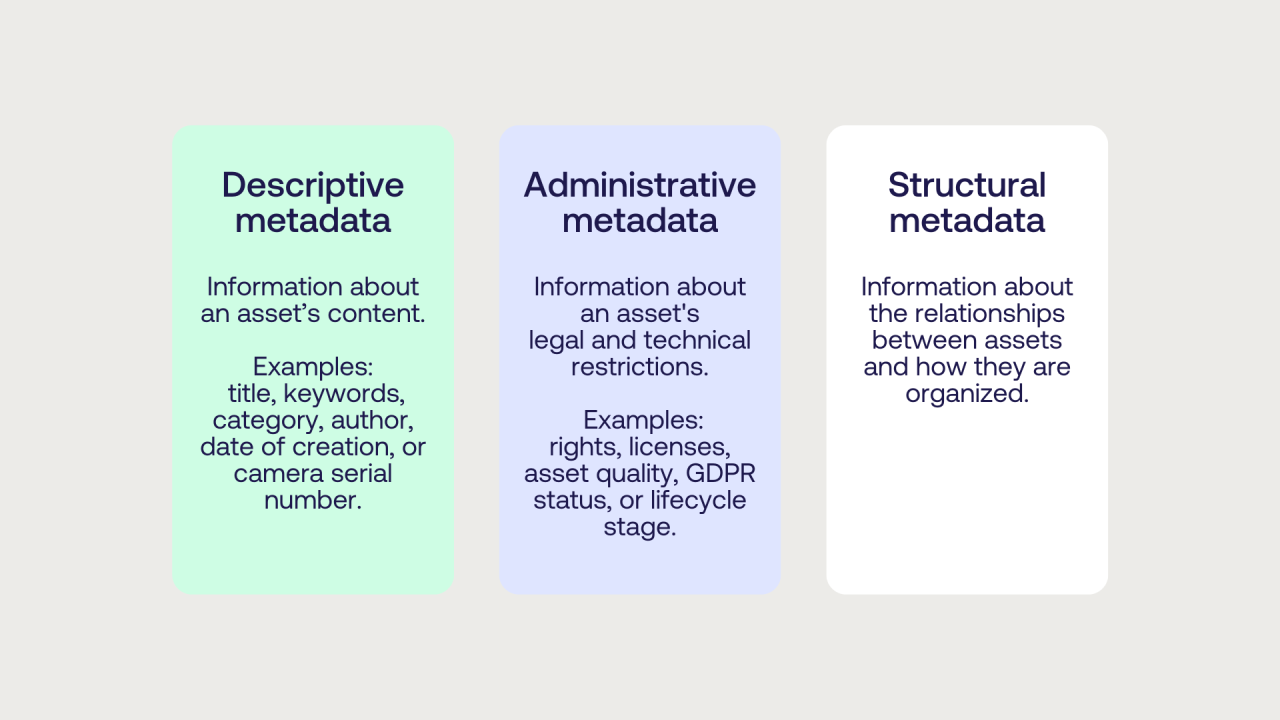
- Descriptive Metadata: This type of metadata provides information about the content, enabling users to discover and identify data easily. It includes details like titles, authors, subjects, and s. For example, in a library catalog, descriptive metadata helps patrons find books based on their interests.
- Structural Metadata: Structural metadata describes the organization and relationship between different components of a resource. It often Artikels how various parts of a document or dataset fit together. In digital media, structural metadata helps in navigating multimedia presentations, such as identifying chapters in an eBook or sequences in a video.
- Administrative Metadata: This type includes information necessary for managing resources over time, such as creation dates, file types, and rights management. In archives, administrative metadata is critical for preserving the integrity of collections, helping archivists maintain records of provenance and access permissions.
Utilization of Metadata in Libraries, Archives, and Digital Media
The application of metadata varies significantly between libraries, archives, and digital media, each tailoring its use to meet specific needs.
– In libraries, descriptive metadata is vital for cataloging books and resources, making it easy for users to search via online databases. For example, the Library of Congress uses MARC (Machine-Readable Cataloging) records to facilitate the organization of information across libraries, allowing for easy cross-referencing and searching.
– Archives often rely heavily on administrative metadata to maintain the authenticity and integrity of records. Archival institutions use tools like EAD (Encoded Archival Description) to provide detailed descriptions of collections, ensuring that users can access historical documents while adhering to copyright and usage rights.
– Digital media platforms leverage both descriptive and structural metadata for enhanced user experiences. For instance, streaming services like Netflix utilize metadata to categorize films and shows based on genre, actors, and viewing patterns, while structural metadata helps users navigate through series and related content effortlessly.
“Metadata not only enhances the discoverability of resources but also empowers users by improving navigation and personalization across various platforms.”
In summary, metadata serves as the backbone of information management across industries, playing a pivotal role in how data is structured, discovered, and utilized. By understanding the classifications and their applications, businesses and organizations can effectively leverage metadata to enhance user experience and operational efficiency.
The Role of Metadata in Enhancing Data Management and Organization
Metadata serves as a critical component in the realm of data management, acting as the backbone that supports the organization, accessibility, and usability of data. It refers to the descriptive information that provides context to the actual data, enabling users to understand its origin, purpose, and usage. By enhancing metadata practices, organizations can ensure that their data assets are well-managed, easily retrievable, and effectively utilized.
Metadata contributes to effective data management practices in various ways. Firstly, it facilitates better data discovery. Users can search and retrieve information quickly when metadata is structured consistently, allowing for efficient data retrieval. Secondly, metadata enhances data governance by providing clear information regarding data lineage, ownership, and compliance requirements. This is especially vital in organizations that handle sensitive data, as it helps ensure adherence to regulations and policies. Furthermore, metadata supports data integration by providing necessary context for different data sets, making it easier to combine and analyze diverse information sources.
Key Benefits of Effective Metadata in Data Organizations
Implementing robust metadata standards leads to numerous benefits for data organizations. The following points Artikel some key advantages:
- Improved Data Discovery: Metadata enables users to locate relevant datasets quickly, enhancing search capabilities.
- Increased Data Quality: Well-defined metadata reduces misunderstandings and errors, leading to higher quality data outputs.
- Enhanced Data Governance: Metadata provides necessary details regarding data compliance and ownership, supporting effective data management policies.
- Streamlined Data Integration: It offers context for merging datasets, simplifying the integration process and improving analytical capabilities.
- Better Data Lifecycle Management: Metadata helps organizations track data usage and lifecycle, optimizing storage and archival strategies.
- Facilitated Collaboration: Clear metadata fosters collaboration among teams by providing a shared understanding of data assets.
- Efficiency in Data Management: Automation of processes such as data classification and archiving is made easier through effective metadata.
When creating and maintaining useful metadata in data management systems, it is crucial to adhere to best practices that ensure its effectiveness. Organizations should consider the following insights:
1. Standardization: Establish a consistent metadata standard across the organization to ensure uniformity and interoperability of data assets.
2. Documentation: Maintain comprehensive documentation that describes the metadata structure, including definitions and usage guidelines to promote understanding.
3. Regular Updates: Ensure that metadata is regularly updated to reflect any changes in data sources or structures, maintaining its relevance over time.
4. User Involvement: Engage end-users in the metadata creation process to capture relevant information that meets their needs, improving overall usability.
5. Automation Tools: Utilize metadata management tools that automate processes such as data cataloging and lineage tracking, enhancing efficiency and accuracy.
6. Training and Awareness: Conduct training sessions for employees to raise awareness about the importance of metadata and how to use it effectively.
By following these best practices, organizations can cultivate a robust metadata framework that underpins effective data management and enhances overall organizational performance.
Analyzing the Impact of Metadata on Digital Content Accessibility
Metadata plays a crucial role in enhancing the accessibility of digital content for various user groups. By providing contextual information about the content, metadata ensures that users, regardless of their abilities or technological proficiency, can navigate and utilize digital resources effectively. This structured information includes descriptions, s, and categorization that facilitate better searchability and usability, ultimately bridging the gap between content creators and end-users.
Proper metadata implementation significantly influences how users interact with digital content. For individuals with disabilities, such as visual impairments, specific metadata can describe images and provide alternative text that screen readers utilize. For those using different languages or cultural references, metadata can offer translations or context that increases comprehension. Furthermore, metadata helps search engines index content accurately, allowing users to find resources that meet their specific needs quickly.
Accessibility Outcomes with and without Proper Metadata
The accessibility of digital content can vary greatly based on whether or not metadata is implemented effectively. To illustrate this impact, the following table showcases differences in accessibility outcomes:
| Aspect | Without Proper Metadata | With Proper Metadata |
|---|---|---|
| Search Visibility | Content is often buried and difficult to find. | Content is easily searchable and discoverable. |
| User Navigation | Users struggle to understand and navigate content. | Clear categorization enhances user experience. |
| Support for Assistive Technologies | Limited or no compatibility with screen readers. | Full compatibility with assistive devices, improving access. |
| Language Accessibility | Content may not be available in user’s preferred language. | Metadata includes translations and contextual information. |
Case studies highlight the significant advantages of metadata in improving content accessibility. For instance, the National Library of Medicine leverages metadata to ensure that its extensive collection is accessible to researchers and the general public. By tagging resources with metadata that describes subject matter and relevance, they allow users to filter searches effectively, resulting in improved access for users with varying levels of expertise.
Another example is the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), which emphasizes the importance of structured data in web accessibility guidelines. Their implementation of metadata standards allows web developers to create content that is inherently more accessible to users with disabilities, showcasing how adherence to metadata protocols directly influences access to information.
By understanding and applying the principles of effective metadata, organizations can create more inclusive digital environments, ensuring that all users can benefit from the wealth of information available online.
Investigating the Relationship Between Metadata and Data Privacy
Metadata, often described as “data about data,” plays a crucial role in the management and utilization of information across various platforms. While it can enhance user experience by providing context and facilitating searchability, it simultaneously poses significant risks to data privacy and security. Understanding the implications of metadata is essential in a world increasingly reliant on data-driven decisions. The relationship between metadata and data privacy is complex, as metadata can inadvertently expose sensitive information about individuals and their behaviors.
The implications of metadata on data privacy and security are multifaceted. Metadata can include information such as timestamps, geolocation data, and user interaction patterns. This information can be valuable for improving services and tailoring experiences, but it also raises concerns regarding surveillance and unauthorized access to personal information. For instance, a seemingly innocuous photograph may have embedded metadata that reveals the exact location where it was taken, potentially compromising the privacy of the individual in the image.
Risks Associated with Improper Metadata Management
Improper management of metadata can lead to several risks that directly impact user privacy. The following points Artikel key concerns regarding inadequate metadata practices:
- Unintentional Data Leakage: Metadata can inadvertently reveal sensitive information if not adequately managed. For instance, sharing documents with embedded metadata may disclose authorship details or editing history, leading to unwanted exposure.
- Increased Vulnerability to Cyberattacks: Hackers can exploit improperly secured metadata to gain insights into user habits and vulnerabilities, increasing the risk of identity theft or fraud. Sensitive metadata, if accessed, can provide a roadmap for cybercriminals.
- Regulatory Non-Compliance: Organizations that fail to adhere to best practices in metadata management may find themselves violating data protection regulations, resulting in hefty fines and reputational damage.
- Loss of User Trust: Users expect their data to be protected. If metadata management practices are poor, organizations risk losing customer trust, which can impact customer retention and overall brand loyalty.
Regulatory frameworks governing metadata usage are vital in safeguarding user privacy. Various laws, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States, establish guidelines for how organizations should handle personal data, including associated metadata. Compliance with these regulations is crucial, as it not only protects user privacy but also mitigates legal risks.
Ensuring compliance involves implementing robust data governance strategies that focus on the proper collection, storage, and sharing of metadata. Organizations must be transparent about their metadata practices and provide users with the ability to manage their privacy settings effectively. Establishing clear policies regarding data retention and deletion of metadata can further enhance user privacy and security.
“Proper metadata management is essential not only for regulatory compliance but also for building and maintaining user trust.”
Future Trends in Metadata and Their Potential Effects on Technology
As technology continues to evolve, so too does the role of metadata in shaping various sectors. The future of metadata technologies holds significant promise, as organizations increasingly recognize its value in enhancing data management, driving insights, and improving operational efficiency. The integration of advanced technologies, including artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), is poised to transform how metadata is utilized, managed, and optimized across industries.
The coming years will likely witness a surge in the sophistication of metadata applications. Organizations will rely on metadata not just for basic data organization but also for enhancing data quality, facilitating compliance, and supporting analytics. The increasing complexity of data landscapes requires nuanced metadata strategies that can address challenges such as data silos, interoperability issues, and real-time accessibility. As such, metadata will evolve from static descriptors to dynamic, context-rich entities that can adapt to changing data environments.
Emerging Trends in Metadata Practices
In light of these developments, it is essential for organizations to stay informed about emerging trends in metadata practices. Here are key trends worth monitoring:
- Automated Metadata Generation: Organizations are adopting tools that utilize AI to auto-generate metadata, saving time and improving accuracy.
- Semantic Metadata: The shift towards semantic web technologies facilitates richer data connections and enhances data discoverability through context-aware metadata.
- Metadata for Data Governance: Comprehensive metadata strategies will become indispensable for ensuring compliance and data governance, particularly in regulated industries.
- Interoperable Metadata Standards: The push for interoperable standards will enable seamless data sharing across platforms, enhancing collaboration and reducing friction in data exchanges.
- Integration with Big Data and IoT: As the Internet of Things (IoT) proliferates, metadata will play a crucial role in managing the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices.
The integration of AI and ML technologies into metadata management is transforming how organizations handle their data assets. These technologies can analyze large datasets, identifying patterns and trends that would be time-consuming or impossible for humans to discern. The capabilities of machine learning algorithms enable predictive analytics, which can assist organizations in making data-driven decisions more efficiently.
The adoption of AI in metadata allows for improved accuracy in data classification, enhanced search capabilities, and personalized data experiences.
As organizations embrace these transformative technologies, they will be better equipped to harness the full potential of their data, leading to more informed decision-making and innovative practices across sectors.
Final Summary
In summary, metadata is more than just a technical concept; it’s a pivotal element that shapes our interaction with digital content. By understanding its various types, the role it plays in data management, and its implications for accessibility and privacy, we can appreciate how metadata influences our digital landscape. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about the trends in metadata will be crucial for leveraging its full potential in enhancing user experience and safeguarding data privacy.
Query Resolution
What is the primary purpose of metadata?
The primary purpose of metadata is to provide context and meaning to data, making it easier to find, manage, and utilize.
How does metadata impact search engine optimization?
Metadata improves search engine optimization by providing essential information that search engines use to rank and retrieve content efficiently.
What are some common types of metadata?
Common types of metadata include descriptive metadata (describing the content), structural metadata (showing how data is organized), and administrative metadata (providing information on how to manage resources).
Can metadata pose privacy risks?
Yes, improper management of metadata can lead to privacy risks, such as exposing sensitive information that could be exploited by unauthorized parties.
How is metadata used in libraries?
In libraries, metadata is used to catalog resources, enabling efficient retrieval and organization of books, articles, and other materials.
What are the future trends in metadata technology?
Future trends include the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for enhanced metadata management, automation, and improved data accessibility.