Hybrid Cloud combines the best of both worlds, merging public and private cloud resources to create a flexible and efficient computing environment. This versatile framework allows businesses to tailor their IT infrastructure according to their specific needs, offering a unique blend of scalability, cost savings, and enhanced security. As organizations face increasing demands for agility and innovation, understanding the dynamics of hybrid cloud becomes essential for staying competitive.
By leveraging hybrid cloud solutions, companies can effectively manage workloads across various environments, optimizing performance while maintaining control over sensitive data. This approach not only addresses business requirements but also adapts to changing market conditions, making it a formidable asset in any digital transformation strategy. The concept of hybrid cloud is not just about technology; it’s about transforming how organizations operate and deliver value.
Understanding the Concept of Hybrid Cloud
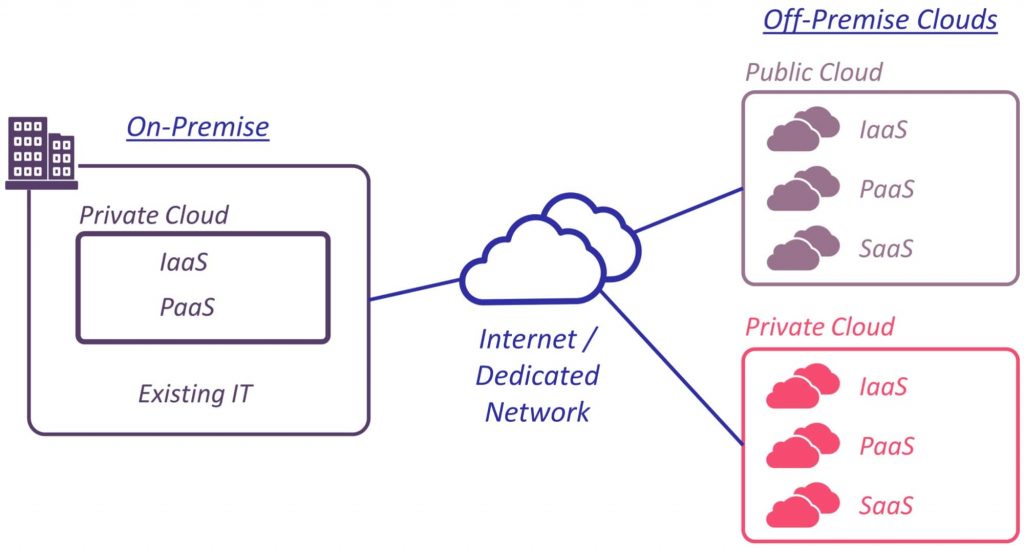
Hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines the use of both public and private cloud services. It allows businesses to utilize the scalable infrastructure of a public cloud while maintaining control over sensitive data within a private cloud. The hybrid model offers flexibility, enabling organizations to deploy various workloads according to their specific needs. This approach aligns with the growing demand for agile and cost-effective IT solutions, allowing enterprises to respond swiftly to dynamic market conditions.
The operation of a hybrid cloud relies on several fundamental principles. First, it integrates on-premises infrastructure with cloud resources, ensuring smooth data flow and application functionality. This integration is facilitated by standardized interfaces and protocols, which allow distinct cloud environments to communicate seamlessly. Moreover, hybrid cloud architectures emphasize security and compliance, as organizations can choose where to store their data based on regulatory requirements. The scalability of hybrid clouds means businesses can easily adjust resources as their demands fluctuate, optimizing operations and managing costs effectively.
Key Components of a Hybrid Cloud Environment
To grasp the full potential of a hybrid cloud, it’s essential to understand its core components. These elements work together to create a cohesive and efficient environment. The following are the key components that make up a hybrid cloud:
- Private Cloud: This is a dedicated cloud infrastructure operated solely for an organization, providing enhanced security and data privacy.
- Public Cloud: Public cloud services are offered by third-party providers and are accessible to multiple organizations, delivering cost-effective scalability.
- Networking: Connectivity between the private and public clouds is achieved through secure connections, such as VPNs or dedicated lines, ensuring data can flow freely.
- Management Tools: These tools facilitate the orchestration of workloads across different environments, enabling efficient resource management and monitoring.
- APIs and Integration Services: These allow applications running in different environments to communicate, ensuring data consistency and operational efficiency.
The differences between hybrid cloud, public cloud, and private cloud are significant. A hybrid cloud combines both public and private clouds, offering flexibility and enhanced security. In contrast, a public cloud provides shared infrastructure and services across multiple organizations, leading to lower costs but less control. Meanwhile, a private cloud grants exclusive access to dedicated resources, ensuring maximum security and customization for specific organizational needs.
“The hybrid cloud model empowers organizations to be agile, secure, and efficient in their IT operations.”
Analyzing the Benefits of Hybrid Cloud Solutions

Hybrid cloud solutions have emerged as a game-changer for businesses looking to optimize their IT infrastructure. By combining the best features of public and private clouds, organizations can enjoy a flexible, scalable, and secure environment tailored to their unique needs. This approach not only enhances operational efficiency but also drives innovation through improved resource management and data accessibility.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Traditional IT Infrastructures
One of the standout advantages of hybrid cloud solutions is their cost-effectiveness when compared to traditional IT infrastructures. Businesses can significantly reduce their capital expenditure (CapEx) by leveraging cloud resources instead of investing heavily in physical hardware and maintenance. The hybrid model allows organizations to utilize a pay-as-you-go approach for public cloud services, which can lead to substantial savings.
For instance, a small to medium-sized enterprise (SME) can maintain essential workloads on a private cloud while utilizing public cloud resources for peak loads. This flexibility minimizes the need for over-provisioning and reduces wasted resources.
“Hybrid cloud enables organizations to pay only for the resources they use, leading to optimized budget management.”
The operational expenditure (OpEx) can also be lowered as businesses avoid the ongoing costs associated with maintaining on-premises infrastructure. In addition, hybrid cloud solutions often come with built-in redundancy and disaster recovery options, which further protect against unforeseen costs from data loss or outages.
Enhancing Flexibility and Scalability for Organizations
Hybrid cloud solutions provide unparalleled flexibility and scalability, essential for modern enterprises facing dynamic market demands. The ability to scale resources up or down in real-time allows organizations to respond swiftly to changing workloads without incurring excessive costs.
This model supports a wide range of applications, from mission-critical operations to experimental projects. For example, a retail business can quickly scale its cloud resources during peak shopping seasons without the need for extensive upfront investments in physical servers.
Additionally, the hybrid cloud environment accommodates various deployment strategies, whether it involves running legacy applications in a private cloud or leveraging public cloud services for new applications. This versatility ensures that businesses can tailor their IT strategies according to their specific operational needs.
“Flexibility in the hybrid cloud enables businesses to adapt faster to changing market conditions, driving competitiveness.”
Moreover, hybrid solutions facilitate seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments. This integration allows businesses to maintain control over sensitive data while enjoying the benefits of cloud computing, such as enhanced collaboration and remote access to resources.
By utilizing hybrid cloud solutions, organizations not only position themselves to leverage technological advancements but also create a robust framework for future growth and innovation.
Exploring Common Use Cases for Hybrid Cloud Deployments
Hybrid cloud solutions are rapidly gaining traction among businesses looking for flexibility, scalability, and enhanced performance. By combining on-premises infrastructure with public cloud resources, organizations can optimize their IT operations while addressing various business challenges. This model allows for efficient resource utilization, cost management, and improved disaster recovery capabilities, making it a compelling choice across numerous industries.
One of the significant advantages of hybrid cloud is its versatility, which can be illustrated through various real-world examples and applications across different sectors. The following industries predominantly benefit from hybrid cloud solutions:
Industries Benefiting from Hybrid Cloud Solutions
Numerous industries have successfully adopted hybrid cloud strategies, leveraging its unique capabilities to address specific operational needs. Here are some notable examples:
- Healthcare: The healthcare industry utilizes hybrid cloud to securely store and analyze patient data while complying with regulations like HIPAA. For instance, a major hospital network may use on-premises servers for critical patient information and connect to a public cloud for additional analytics and storage needs during peak loads.
- Financial Services: Financial institutions are often required to maintain strict compliance and security standards. Many banks implement hybrid solutions to manage sensitive data internally while taking advantage of the cloud for customer-facing applications and services. A prominent bank might utilize a hybrid model to run its trading platforms on-premises while leveraging the public cloud for customer relationship management (CRM) systems.
- Retail: Retailers frequently experience fluctuating demands. By using hybrid cloud, they can scale their online operations during peak shopping seasons while maintaining their core inventory and transaction systems on-premises. An example would be a large retail chain that migrates its customer data analysis to the cloud but retains its point-of-sale systems locally.
- Manufacturing: The manufacturing sector employs hybrid cloud for IoT applications, enabling real-time data collection and analysis from equipment. A manufacturing company might run its production management system on-premises while using a public cloud for advanced analytics and machine learning to optimize processes.
Specific Scenarios Illustrating Hybrid Cloud Versatility
Hybrid cloud deployments offer unique solutions for various business scenarios, demonstrating their adaptability. Here are a few illustrative cases:
- A tech startup utilizes a hybrid cloud to develop new applications, keeping sensitive customer data on private servers while using public cloud resources for development and testing environments. This setup allows for rapid innovation without compromising data security.
- An educational institution uses hybrid cloud to host its learning management system (LMS) on-premises, ensuring compliance with data protection laws while leveraging cloud resources for additional storage and computational needs during online course assessments.
- A media company employs hybrid cloud for content production, utilizing on-premises servers for video editing and production while extending storage and distribution to the cloud to handle large files and deliver content worldwide.
- An e-commerce platform implements hybrid cloud to manage promotional campaigns. During high-traffic events, it can rapidly scale resources in the cloud while maintaining its core operations on local servers, ensuring a seamless customer experience.
“Hybrid cloud enables businesses to strike the right balance between control and flexibility, paving the way for innovative solutions and efficient operations.”
Addressing Security Challenges in Hybrid Cloud Environments
The hybrid cloud model, which combines on-premises infrastructure with public and private cloud services, offers organizations flexibility and scalability. However, this architecture introduces unique security challenges that need to be managed effectively. Understanding these risks and implementing best practices is crucial in safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining compliance with regulations.
Security Risks Associated with Hybrid Cloud Infrastructures
Organizations leveraging hybrid cloud environments face various security risks that can potentially compromise their data integrity and privacy. Key risks include:
- Data Breaches: Sensitive information stored in the cloud can be vulnerable to unauthorized access if proper security measures are not implemented.
- Inconsistent Security Policies: The disparity in security measures between on-premises and cloud environments can lead to vulnerabilities, making data easier to breach.
- Misconfigured Cloud Services: Incorrect configurations can expose cloud resources, leading to data leaks and unauthorized access.
- Compliance Violations: Organizations must navigate different regulatory landscapes, and failure to comply can result in significant penalties.
- Insider Threats: Employees with access to both environments can intentionally or unintentionally compromise data security.
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Protection in Hybrid Cloud Setups
Implementing robust data protection strategies is essential in mitigating security risks in hybrid cloud environments. Organizations should consider the following best practices:
- Data Encryption: Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit to ensure that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable.
- Access Controls: Utilize role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance with internal and external policies.
- Unified Security Management: Employ comprehensive security management tools that provide visibility and control across both on-premises and cloud environments.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and test an incident response plan to address potential security breaches swiftly and effectively.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations for Organizations Using Hybrid Cloud
Organizations utilizing hybrid cloud infrastructures must navigate complex compliance and regulatory requirements. Key considerations include:
- Data Residency Regulations: Ensure that data storage complies with local laws regarding data residency, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe.
- Industry-Specific Regulations: Adhere to specific regulations relevant to the industry, such as HIPAA for healthcare or PCI-DSS for payment data.
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed logs and audit trails of data access and modifications to demonstrate compliance during audits.
- Third-Party Risk Management: Evaluate the security practices of cloud service providers to ensure they meet compliance standards and do not introduce additional risks.
- Ongoing Training: Provide ongoing compliance training for employees to ensure everyone understands regulations and best practices.
Evaluating Hybrid Cloud Management Tools and Platforms
In the increasingly complex landscape of hybrid cloud environments, selecting the right management tools and platforms is essential for optimizing performance, enhancing security, and ensuring seamless integration across different environments. Organizations need to evaluate various management solutions to find the right fit that meets their operational needs, enhances productivity, and supports scalability.
When evaluating hybrid cloud management tools, it’s important to consider several popular solutions that are specifically designed to cater to the unique requirements of hybrid infrastructures. Each tool comes with its distinct features and functionalities, which can greatly impact the management experience.
Popular Hybrid Cloud Management Tools
Several management tools have made their mark in the hybrid cloud space, providing organizations with the necessary capabilities to manage resources across public and private clouds. Here are some notable options:
- VMware vRealize Suite: This comprehensive management platform offers a range of tools for automation, reporting, and performance monitoring in hybrid environments.
- Microsoft Azure Arc: Azure Arc allows users to manage their on-premises and multi-cloud resources from a single control plane, enhancing visibility and governance.
- IBM Cloud Pak for Multicloud Management: This platform provides a unified view of applications and resources across different environments, focusing on automation and integration.
- Red Hat OpenShift: Primarily a container management tool but also supports hybrid cloud deployments, enabling efficient application delivery across cloud environments.
- CloudHealth by VMware: A robust solution for cloud cost management and optimization, helping organizations track and manage their cloud expenditures effectively.
The above management tools are equipped with functionalities that streamline operations, bolster security, and enhance visibility into hybrid cloud environments.
Comparison of Features and Functionalities
Evaluating the features and functionalities of different hybrid cloud management solutions can help organizations make informed decisions. Some critical parameters to consider include:
- Cost Management: Tools like CloudHealth offer detailed insights into cloud spending, enabling better budget management.
- Resource Optimization: VMware vRealize Suite provides advanced analytics for workload performance, allowing for optimized resource allocation.
- Integration Capabilities: Azure Arc excels in integrating with existing Microsoft services, simplifying the management of diverse resources.
- Automation Features: IBM Cloud Pak emphasizes automation, reducing manual intervention and accelerating deployment processes.
- Support for Containerization: OpenShift caters to organizations leveraging containers, offering advanced orchestration features.
By comparing these features, businesses can select a tool that aligns best with their operational requirements and strategic goals.
Ease of Use and Integration with Existing Systems
When selecting a hybrid cloud management platform, the importance of ease of use and integration cannot be overstated. A user-friendly interface and clear navigation help teams adopt tools quickly and reduce training time. Moreover, the ability to integrate seamlessly with existing systems ensures a smoother transition and minimizes disruptions during deployment.
Organizations should prioritize solutions that offer strong API support, enabling them to connect with their already established infrastructure easily. Such integration can facilitate better data flow and collaboration across different teams and services.
“Ease of use and integration are crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of hybrid cloud management tools.”
In conclusion, when evaluating hybrid cloud management tools, organizations must consider popular solutions, compare their features, and prioritize ease of use and integration capabilities to ensure successful management of their hybrid environments.
Understanding the Role of Edge Computing in Hybrid Cloud Strategies
Edge computing is emerging as a pivotal component in hybrid cloud strategies, bridging the gap between centralized cloud resources and the vast network of devices generating data. By processing data closer to its source, edge computing enhances response times, reduces latency, and optimizes bandwidth usage, enabling organizations to harness the full potential of their hybrid cloud setups.
In a hybrid cloud architecture, edge computing works synergistically with cloud services by distributing workloads and enabling more efficient data management. This integration allows businesses to leverage the strengths of both on-premises and cloud solutions, fostering a more agile and responsive IT environment. As organizations increasingly rely on real-time data processing, the role of edge devices becomes crucial for ensuring that data is not only collected but also analyzed and acted upon immediately, thereby driving operational efficiency and enhancing user experiences.
Impact of Edge Devices on Data Processing and Storage
Edge devices significantly influence data processing and storage in hybrid systems. By executing computations and data analyses at the edge, these devices minimize the volume of data that needs to be transmitted to the cloud, thereby conserving bandwidth and reducing costs. This decentralization of processing tasks leads to several advantages:
- Reduced Latency: Processing data at the edge allows for immediate insights and actions, which is essential for time-sensitive applications such as autonomous vehicles and industrial automation.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: By filtering and processing data locally, edge devices lower the amount of data sent to the cloud, which helps in managing bandwidth costs and improves overall system performance.
- Enhanced Reliability: In scenarios where internet connectivity is intermittent or slow, edge computing ensures that critical operations can continue without disruption, storing data locally until it can be synchronized with the cloud.
- Data Privacy and Security: Local data processing can mitigate risks associated with data transmission over networks, enabling organizations to maintain tighter control over sensitive information.
The integration of edge computing with hybrid cloud systems is particularly beneficial in various applications. For instance, in smart cities, data from sensors and IoT devices can be processed locally to manage traffic flows in real-time, significantly enhancing urban mobility. In healthcare, wearable devices can analyze patient data on-site, allowing for timely interventions even before the data is sent to cloud systems for deeper analysis.
By combining edge computing with hybrid cloud strategies, organizations can create a more responsive and efficient infrastructure that meets the demands of today’s data-driven landscape.
Future Trends in Hybrid Cloud Technologies
As organizations continue to adopt hybrid cloud models, several emerging technologies are set to redefine how businesses leverage their IT infrastructure. The future of hybrid cloud is not just about storage capacity or computing power; it’s about creating dynamic ecosystems that enhance flexibility, scalability, and efficiency. Companies are looking for solutions that provide seamless integration between on-premises and cloud environments, and several trends are shaping this evolution.
One of the most significant trends in hybrid cloud technology is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are rapidly advancing, enabling organizations to automate processes, improve decision-making, and enhance overall operational efficiency. By harnessing AI and ML, businesses can analyze vast amounts of data generated from hybrid cloud environments, allowing for real-time insights and predictive analytics that drive innovation.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning on Hybrid Cloud Solutions
The influence of AI and ML on hybrid cloud solutions is profound, affecting various aspects of cloud management and operations. These technologies are being utilized to enhance security, optimize resource allocation, and streamline workflows. The following are key areas where AI and ML are making significant inroads in hybrid cloud implementations:
- Automated Security Monitoring: AI-driven algorithms can detect anomalies in network traffic and user behavior, providing enhanced security measures that adapt to new threats dynamically.
- Resource Optimization: Machine learning models can analyze usage patterns and suggest optimal resource allocation, ensuring that businesses only pay for what they use while maximizing performance.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing historical data, machine learning can predict potential system failures or downtimes, allowing companies to take proactive measures and reduce operational disruptions.
- Improved Analytics: AI enhances data analytics capabilities within hybrid clouds, turning raw data into actionable insights that inform business strategies and operational improvements.
The implications of these advancements for businesses adopting hybrid cloud strategies are substantial. Organizations can expect increased agility, as AI and ML facilitate faster deployment of applications and services across hybrid environments. This is particularly relevant as companies face the ongoing challenge of rapidly changing market demands and the need for scalable solutions.
The potential for AI and ML in hybrid cloud environments points to a future where businesses can not only keep pace with technological advancements but also leverage these innovations to drive competitive advantage. Companies like Google and Amazon are already beginning to integrate AI into their cloud offerings, exemplifying how these technologies are set to evolve hybrid cloud solutions. As the industry progresses, we can anticipate an even greater emphasis on intelligent cloud management tools that automate routine tasks and enhance the overall user experience.
Designing an Effective Hybrid Cloud Strategy for Your Organization
An effective hybrid cloud strategy is essential for organizations looking to leverage the benefits of both public and private cloud environments. By integrating these two platforms, businesses can achieve greater flexibility, scalability, and cost efficiency. This strategy not only supports evolving technology demands but also aligns IT capabilities with organizational goals, enhancing overall performance.
Developing a hybrid cloud strategy involves several key steps that are crucial for ensuring success. These steps will guide organizations in creating a tailored approach that addresses their specific needs while fostering innovation and growth.
Key Steps in Developing a Hybrid Cloud Strategy
A systematic approach to developing a hybrid cloud strategy is vital. The following steps Artikel the essential actions organizations should take:
- Assessment of Current Infrastructure: Begin with a comprehensive evaluation of your existing IT infrastructure. Understand what applications and data can be migrated to the cloud, and which should remain on-premises. This assessment lays the foundation for effective deployment and management.
- Define Business Objectives: Align your hybrid cloud strategy with overall business goals. This means identifying how cloud solutions can support your organization’s mission, whether it be improving customer experience, enhancing operational efficiency, or driving innovation.
- Select Appropriate Cloud Providers: Choose cloud service providers that best fit your needs. Consider factors such as reliability, scalability, security, and compliance. Evaluate multiple providers to ensure that you select the right mix for both public and private cloud environments.
- Design Integration Plans: Develop a seamless integration strategy that connects on-premises infrastructure with cloud solutions. This includes defining how data will flow between environments and ensuring compatibility across systems.
- Implement Security Measures: Establish security protocols that safeguard data across both cloud environments. This includes identity management, encryption, and compliance with regulations, ensuring that sensitive information remains protected.
- Monitor and Optimize Performance: Regularly monitor the performance of your hybrid cloud environment. Use analytics to assess resource utilization and optimize costs, making adjustments as needed to enhance efficiency and performance.
Importance of Aligning Hybrid Cloud Strategies with Business Goals
Aligning your hybrid cloud strategy with your organization’s overarching goals is critical for maximizing value and achieving desired outcomes. When cloud initiatives are directly tied to business objectives, organizations are better positioned to respond to market changes, enhance customer satisfaction, and drive innovation.
The success of a hybrid cloud strategy is not merely about technology; it’s about enabling business transformation and agility.
By ensuring that your IT investments directly support business priorities, you can foster a culture of collaboration between IT and business units. This alignment not only helps in justifying cloud expenditures but also drives a shared understanding of how technology can facilitate growth.
Identifying Critical Stakeholders and Their Roles
Successful implementation of a hybrid cloud solution requires the involvement of various stakeholders across the organization.
Engaging the right stakeholders ensures that all perspectives are considered, leading to a more robust hybrid cloud strategy.
Key stakeholders typically include:
- IT Leadership: Responsible for setting the strategic direction and ensuring that the technology infrastructure aligns with the business needs.
- Security Teams: Tasked with safeguarding data and ensuring compliance with regulations in both cloud environments.
- Operations Teams: Focus on maintaining the continuity of services and optimizing performance and efficiency across systems.
- Business Unit Leaders: Provide insights on specific requirements and how cloud solutions can enhance their operational processes.
- Finance Teams: Evaluate the cost implications of hybrid cloud investments and ensure budget alignment with business objectives.
Summary
In conclusion, Hybrid Cloud stands as a transformative force in today’s technological landscape, offering businesses the flexibility to innovate while ensuring security and compliance. As organizations navigate the complexities of IT infrastructure, the hybrid model emerges as a strategic solution that aligns with evolving business goals. Embracing hybrid cloud technologies is not merely a trend; it signifies a commitment to future-proofing operations and enhancing competitiveness in an ever-changing world.
User Queries
What is a hybrid cloud?
A hybrid cloud is a computing environment that combines on-premises, private cloud, and public cloud services, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
How does hybrid cloud improve cost-efficiency?
It enables businesses to optimize their IT spending by utilizing scalable public resources for less sensitive workloads while keeping critical operations secured in private clouds.
Can hybrid cloud support all types of applications?
Yes, hybrid cloud can support a wide range of applications, particularly those requiring varying degrees of security and scalability.
What industries benefit the most from hybrid cloud?
Industries like healthcare, finance, and retail benefit significantly due to their need for data security, compliance, and the ability to scale quickly.
What are the key security concerns with hybrid cloud?
Key concerns include data breaches, compliance challenges, and the complexity of managing security across multiple environments.