Blockchain Security is revolutionizing the way we perceive and manage digital transactions. As the backbone of cryptocurrencies and various decentralized applications, understanding its principles is essential for anyone navigating this frontier. This technology not only promises enhanced security but also decentralization, making it more resilient against cyber threats.
By delving into the fundamentals of blockchain security, we can uncover the complex components that protect against vulnerabilities. From cryptographic techniques to regulatory influences, each aspect plays a vital role in maintaining the integrity of blockchain systems and preparing us for future challenges.
Understanding the fundamentals of Blockchain Security
Blockchain technology is revolutionizing the way we think about data integrity and security. At its core, blockchain security involves a combination of principles and technologies that create a robust framework capable of safeguarding transactions and preventing unauthorized access. Understanding these fundamentals is essential for anyone looking to navigate the evolving landscape of digital currencies and decentralized applications.
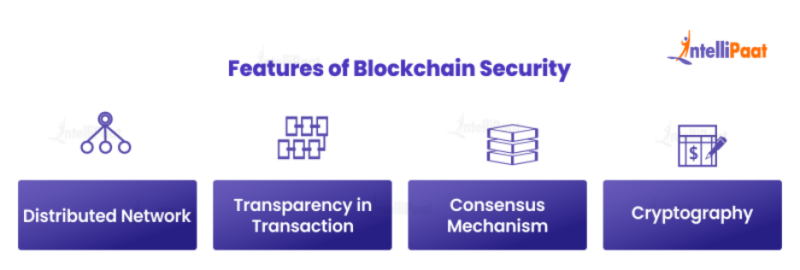
The primary components that contribute to the security and resilience of blockchain technology include cryptographic hashing, consensus mechanisms, and decentralized networks. Cryptographic hashing ensures that each block in the chain is linked to its predecessor in a way that any tampering would result in an altered hash, thus making fraud easily detectable. Consensus mechanisms, such as Proof of Work and Proof of Stake, play a crucial role in validating transactions across the network, ensuring that all participants agree on the state of the ledger, which mitigates the risk of double-spending. Additionally, decentralization is a defining characteristic of blockchain, distributing data across numerous nodes, thereby reducing the chances of a single point of failure or attack.
Decentralization and its Role in Enhancing Security Features
Decentralization is a cornerstone of blockchain security, as it fundamentally alters how data is handled and stored. By distributing information across a network of nodes rather than relying on a central authority, the integrity of the blockchain is significantly enhanced. This architectural choice minimizes risks associated with centralized points of weakness.
The following points illustrate the security benefits of decentralization:
- Redundancy: Multiple copies of the same data exist across various nodes, ensuring that even if one node fails or is compromised, the data remains intact and accessible from other nodes.
- Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it is virtually impossible to alter it without the consensus of the majority of the network, which deters malicious alterations.
- Increased Resistance to Attacks: Decentralized networks are less susceptible to attacks like Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS), as taking down a single node has minimal impact on the overall system.
- Trustless Transactions: Users do not need to rely on a central authority to validate transactions, as the blockchain itself provides a transparent and verifiable ledger accessible to all participants.
The significance of decentralization in blockchain security cannot be overstated. By empowering users with control over their own data and reducing reliance on intermediaries, decentralization fosters an environment where security is inherently woven into the fabric of the technology.
Common vulnerabilities in Blockchain systems
Blockchain technology is often lauded for its security and transparency; however, it is not immune to vulnerabilities. Various blockchain platforms have exhibited weaknesses due to design flaws, implementation errors, and the inherent complexities of cryptographic protocols. Understanding these vulnerabilities is crucial for developing more secure blockchain systems and mitigating risks associated with malicious attacks.
Different blockchain implementations may expose specific vulnerabilities, which can be exploited by malicious actors, leading to severe consequences such as financial loss, data breaches, and network disruptions. Some prevalent security weaknesses include coding errors, insufficient consensus mechanisms, and inadequate access controls.
Prevalent Security Weaknesses
It is essential to identify and understand the most common vulnerabilities present in blockchain systems. These weaknesses can allow attackers to compromise the integrity, availability, and confidentiality of the blockchain. Some notable vulnerabilities include:
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code, can have bugs or loopholes that attackers can exploit. For example, the DAO hack in 2016 resulted from a vulnerability in the smart contracts utilized by the Decentralized Autonomous Organization, leading to the theft of approximately $60 million worth of Ether.
- 51% Attack: In a 51% attack, a single entity or group gains control of more than half of the blockchain’s hashing power. This allows them to manipulate transaction history, double-spend coins, and disrupt the network. An infamous example is the attack on the Bitcoin Gold network in 2018, where attackers exploited the lack of proper decentralization.
- Sybil Attack: This attack involves creating multiple fake identities to gain influence over the network. Malicious actors can flood the network with these identities, allowing them to control the consensus process. This poses a significant threat to both public and private blockchains.
- Private Key Exposure: The security of blockchain networks relies heavily on the protection of private keys. If these keys are compromised, attackers can gain unauthorized access to wallets and execute transactions. A prominent incident occurred in 2019 when the exchange Cryptopia was hacked due to insufficient security practices, leading to the loss of millions in cryptocurrencies.
- Insufficient Testing and Audits: Many blockchain projects launch without thorough testing and auditing of their code, leading to vulnerabilities. For instance, the Parity wallet hack in 2017 was attributed to a simple code error, resulting in the locking of over $150 million worth of Ether.
“The security of blockchain systems is only as strong as the weakest link in their design and implementation.”
Understanding these vulnerabilities is the first step toward creating more resilient blockchain solutions. By identifying potential risks, developers and organizations can implement better safeguards and practices to protect their blockchain networks from malicious exploitation.
Cryptography’s role in Blockchain Security
Cryptography is the backbone of blockchain security, ensuring that transactions are secure, confidential, and tamper-proof. By employing various cryptographic techniques, blockchains maintain the integrity of data while facilitating trust among users. This essential aspect of technology not only protects sensitive information but also establishes a framework for decentralized communication and transaction validation.
Types of Cryptographic Techniques Used in Blockchain
A variety of cryptographic techniques are employed to secure blockchain transactions and protect the integrity of the network. These methods are fundamental to how blockchains operate and provide essential security features. The following techniques play a crucial role in this process:
- Symmetric Cryptography: Uses the same key for both encryption and decryption, ensuring fast processing and efficiency. Although not commonly utilized in public blockchains, it is useful in private networks for securing data.
- Asymmetric Cryptography: Involves a pair of keys: a public key, which is shared with everyone, and a private key, which is kept secret. This method is crucial for user authentication and securing transactions.
- Hash Functions: These functions convert input data of any size into a fixed-size output, known as a hash. Hash functions ensure data integrity and are essential in linking blocks in a blockchain.
- Digital Signatures: A combination of hash functions and asymmetric cryptography allows users to create a unique signature for their transactions. This ensures authenticity and non-repudiation.
Importance of Public and Private Keys
Public and private keys are fundamental components of blockchain security. They facilitate secure transactions and protect users’ identities and assets.
The public key serves as an address for receiving funds, while the private key is used to authorize transactions. This separation helps maintain security and privacy, as only the owner of the private key can access their assets. The significance of these keys is evident in the following points:
- Ownership: The private key grants ownership of the digital assets. Losing the private key means losing access to those assets permanently.
- Security: Public keys can be shared openly without compromising the security of funds, as only the private key can unlock the associated assets.
- Authentication: Transactions signed with a private key can be verified against the corresponding public key, ensuring the integrity and authenticity of each transaction.
How Hashing Functions Contribute to Blockchain Security
Hashing functions are vital to the security mechanisms within blockchain systems. They create a unique digital fingerprint for each block of data, enabling the validation and integrity of the entire chain.
The role of hashing functions encompasses several critical aspects:
- Data Integrity: Each block contains a hash of the previous block, creating a secure chain. If any data within a block changes, the hash will also change, indicating tampering.
- Efficient Verification: Hashing allows for quick verification of data integrity without needing to review the entire blockchain, enhancing system efficiency.
- Collision Resistance: A good hash function minimizes the chances of two different inputs producing the same hash, which is essential for maintaining trust in the blockchain’s data.
The strength of a blockchain’s security lies in its cryptographic foundation, ensuring that every transaction is both secure and verifiable.
Best practices for securing Blockchain applications
In the rapidly evolving world of blockchain technology, securing applications is crucial for developers to ensure the integrity and safety of transactions. With the increasing prevalence of cyber threats, implementing robust security measures has never been more essential. This section Artikels effective practices that every blockchain developer should adopt to safeguard their applications.
Effective security measures for blockchain developers
To build secure blockchain applications, developers must adopt various security measures. These measures help in mitigating risks associated with vulnerabilities in the code and the underlying infrastructure.
- Use formal verification: Implement formal methods to mathematically prove the correctness of smart contracts, ensuring that they behave as intended without any flaws.
- Implement strong cryptography: Use advanced cryptographic techniques such as SHA-256 for hashing and ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature Algorithm) for digital signatures to secure transactions and identities.
- Employ multi-signature wallets: Utilize wallets that require multiple signatures for transaction approval, which adds an extra layer of security against unauthorized access.
- Conduct thorough code reviews: Regularly review and audit the code for vulnerabilities and weaknesses, employing both automated tools and manual inspections.
- Limit access and permissions: Use the principle of least privilege when granting access to the blockchain network and its resources to reduce the attack surface.
Ensuring data integrity and authenticity in blockchain transactions
Data integrity and authenticity are paramount in blockchain applications, as they ensure that the information recorded is accurate and trustworthy. Implementing the following methods can help maintain these critical attributes.
- Utilize hashing algorithms: By hashing data before storing it on the blockchain, developers can create unique representations of that data, which helps detect any unauthorized modifications.
- Implement timestamping: Adding timestamps to transactions improves traceability and allows verification of the order and timing of events on the blockchain.
- Leverage public and private keys: Use asymmetric cryptography to create secure digital identities, ensuring that transactions can only be signed by authorized individuals.
- Incorporate consensus mechanisms: Utilize consensus protocols like Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS) to validate transactions, ensuring that only valid and agreed-upon transactions are added to the blockchain.
Importance of regular security audits and updates in maintaining security
Regular security audits and updates are essential for identifying vulnerabilities and enhancing the overall security posture of blockchain applications. Continuous monitoring and updating ensure that applications remain resilient against emerging threats.
- Conduct periodic security assessments: Schedule regular audits to evaluate the effectiveness of the current security measures and identify areas for improvement.
- Stay updated with security patches: Monitor and apply updates provided by blockchain platforms and libraries to mitigate known vulnerabilities.
- Engage third-party security firms: Consider hiring external experts to conduct independent security audits for an unbiased assessment of your application’s security.
- Educate and train development teams: Provide ongoing security training for developers to ensure they are aware of the latest security threats and best practices.
The impact of regulatory frameworks on Blockchain Security
The evolving landscape of blockchain technology has prompted regulators worldwide to establish frameworks aimed at ensuring security and trust. These regulatory measures play a significant role in shaping the security practices adopted by blockchain entities. Understanding the impact of such regulations is crucial for stakeholders in the blockchain ecosystem, as it directly influences the way security measures are implemented and maintained.
Regulations can significantly influence the security practices of blockchain entities by establishing a baseline for compliance. When regulatory frameworks are in place, organizations are often required to adopt specific security standards, which can lead to enhanced security measures. Compliance with these regulations not only helps mitigate risks but also fosters trust among users and stakeholders. For instance, financial institutions that utilize blockchain technology must comply with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) guidelines, which mandate rigorous security protocols.
Influence of Compliance on Security Measures
Compliance with regulatory frameworks enhances security measures within blockchain technologies by mandating adherence to best practices. Organizations that prioritize compliance are more likely to adopt robust security protocols and conduct regular audits and assessments. This proactive approach to security can prevent breaches and ensure the integrity of the blockchain. Here are some key aspects highlighting the role of compliance in security:
-
Establishment of Security Standards:
Regulatory frameworks often specify security standards that organizations must adhere to, thereby improving overall security practices.
-
Regular Audits and Assessments:
Compliance requirements typically involve periodic security assessments, which help identify vulnerabilities and enforce corrective measures.
-
Enhanced User Trust:
Compliance with regulations can enhance user confidence, as individuals and businesses are more likely to engage with organizations that demonstrate commitment to security.
Approaches to Blockchain Security Regulation Across Jurisdictions
Different jurisdictions approach blockchain security regulation in varied ways, reflecting their unique legal, economic, and cultural contexts. This diversity in regulatory frameworks can impact how blockchain entities operate and secure their systems. Understanding these approaches reveals the broader implications for blockchain security on a global scale. Some notable examples include:
-
United States:
The U.S. has adopted a fragmented approach, with federal and state regulations that vary significantly. Agencies like the SEC and CFTC oversee cryptocurrency and blockchain activities, often focusing on consumer protection and fraud prevention.
-
European Union:
The EU has initiated comprehensive legislation, such as the MiCA (Markets in Crypto-Assets) regulation, which aims to create a unified regulatory environment, emphasizing user protection and data security.
-
China:
China has taken a restrictive stance on cryptocurrencies but promotes blockchain technology for various applications. The focus is primarily on domestic security and technological advancement rather than open market participation.
Future trends in Blockchain Security
As blockchain technology continues to expand across various industries, the security landscape is evolving in tandem. Emerging technologies and innovative practices are paving the way for a more secure future in blockchain. This section delves into the trends that are shaping the future of blockchain security, offering insights into the forthcoming changes in threats and the measures needed to counter them.
Emerging Technologies in Blockchain Security
The advent of new technologies is crucial for enhancing blockchain security. Among these, several key innovations are noteworthy:
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: With the potential rise of quantum computing, traditional encryption methods are at risk. Post-quantum cryptographic algorithms are being developed to secure blockchain networks against future quantum attacks.
- Multi-Signature Wallets: These wallets require multiple private keys to authorize transactions, significantly increasing security and reducing the risk of single points of failure.
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs: This cryptographic method allows for transactions to be verified without revealing sensitive information, enhancing privacy and security on the blockchain.
- Decentralized Identity Solutions: These solutions empower users to control their digital identities, reducing the risks associated with centralized data breaches.
Evolving Threats and Security Measures
As blockchain technology matures, so do the strategies employed by malicious actors. Understanding these evolving threats is essential for developing effective countermeasures. Key trends include:
- Increased Phishing Attacks: With the rise of decentralized finance (DeFi), attackers are crafting more sophisticated phishing schemes to target users, necessitating advanced educational campaigns and robust security protocols.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: As smart contracts become more prevalent, the exploitation of their coding flaws is on the rise, leading to the necessity for rigorous auditing and testing of smart contracts before deployment.
- 51% Attacks: Although less common, the potential for 51% attacks remains a concern, particularly for smaller blockchains, highlighting the need for enhanced consensus mechanisms and community vigilance.
Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Blockchain Security
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to transform blockchain security strategies significantly. Its application can lead to more proactive security measures through:
- Threat Detection and Response: AI algorithms can analyze transaction patterns and detect anomalies in real-time, enabling quicker responses to potential security breaches.
- Automated Security Audits: AI can facilitate continuous monitoring and auditing of blockchain networks, identifying vulnerabilities before they can be exploited.
- Fraud Prevention: Machine learning models can learn from historical data to predict and prevent fraudulent activities on blockchain platforms.
“As we move forward, the integration of AI with blockchain technology will redefine how we approach security.”
Case studies of successful Blockchain Security implementations

The implementation of blockchain security has proven to be a game-changer for various organizations, enhancing their data integrity, transparency, and overall security. These case studies highlight how different sectors have leveraged blockchain technology to fortify their security protocols while providing valuable lessons for others considering similar paths.
One notable case is that of IBM, which has integrated blockchain into its supply chain solutions. By employing a permissioned blockchain platform, IBM has improved the traceability of products while ensuring that data remains secure and tamper-proof. This implementation has not only reduced fraud but also provided end-to-end visibility into the supply chain, enabling stakeholders to track products from their origin to their final destination.
IBM Supply Chain Solutions
IBM’s use of blockchain for supply chain management demonstrates the effectiveness of a secure framework in mitigating risks associated with product provenance. Key components of their implementation include:
- Permissioned Blockchain: Only authorized participants access the network, ensuring data confidentiality and integrity.
- Smart Contracts: Automated agreements that execute when predefined conditions are met, streamlining operations.
- Real-time Tracking: Continuous monitoring of goods throughout the supply chain enhances transparency and trust among stakeholders.
The lessons learned from IBM’s approach emphasize the importance of selecting the right type of blockchain, engaging stakeholders early, and investing in training to ensure that users understand the technology. These strategies ensure that organizations can minimize vulnerabilities and enhance security.
Another impactful case study involves the healthcare sector, specifically the implementation by Guardtime in Estonia. Guardtime has utilized blockchain technology to secure health records across the country, ensuring that patient data is immutable and accessible only to authorized individuals.
Guardtime Healthcare Initiative
The security framework adopted by Guardtime integrates several key elements that contribute to its effectiveness:
- Data Integrity: The use of cryptographic hashes ensures that health records cannot be altered without detection.
- Decentralization: By distributing data across multiple nodes, the system reduces the risk of a single point of failure.
- Regulatory Compliance: The framework adheres to strict data protection regulations, ensuring legal compliance while safeguarding patient privacy.
From Guardtime’s experience, organizations can learn that regulatory compliance is crucial in implementing blockchain solutions, particularly in sensitive sectors like healthcare. Furthermore, engaging with regulatory bodies during the development process can facilitate smoother adoption and enhance public trust.
Another significant example is the implementation by Walmart in its food supply chain. Walmart has harnessed blockchain technology to trace the origin of food products quickly, significantly reducing the time required to track produce from farm to store.
Walmart Food Safety Blockchain
Walmart’s blockchain implementation for food safety highlights the integration of security measures that bolster consumer trust. Some components of this implementation include:
- Traceability: The ability to trace the origin and journey of food products enhances accountability in the supply chain.
- Quick Response to Contamination: In the event of a food safety issue, Walmart can identify and remove contaminated products from shelves rapidly, protecting consumers.
- Collaborative Network: Walmart collaborates with suppliers to maintain data integrity and shared responsibility across the supply chain.
The takeaway from Walmart’s case is the importance of collaboration between suppliers and retailers to establish a trustworthy and secure supply chain. This collaborative approach ensures that all stakeholders are invested in maintaining data integrity and security.
Overall, these case studies illustrate how organizations across various sectors can successfully implement blockchain security. By adopting tailored security frameworks, emphasizing collaboration, and investing in the right technology, businesses can enhance their security posture and build trust with their stakeholders.
Comparing Blockchain Security with Traditional Security Models
Blockchain technology has emerged as a revolutionary approach to security, offering unique features compared to traditional security models. While conventional database systems have served us well for decades, the advent of blockchain introduces a new paradigm in how we understand data integrity, access control, and trust. This comparison highlights the fundamental differences in security mechanisms, their advantages and disadvantages, as well as scenarios where blockchain excels over traditional methods.
Security Features Comparison
In assessing the security features of blockchain versus traditional database systems, several key aspects come into play, such as decentralization, data integrity, and access control mechanisms.
1. Decentralization:
– Unlike traditional databases, which typically operate on centralized servers, blockchain relies on a distributed network of nodes. Each node maintains a copy of the entire blockchain, making it nearly impossible for a single point of failure or attack to compromise the system.
– This decentralized structure enhances security because there is no central authority that can be easily targeted.
2. Data Integrity:
– Blockchain utilizes cryptographic hashes to secure data. Each block contains a unique hash of the previous block, creating a chain that is tamper-evident. Any alteration in one block would invalidate all subsequent blocks, which discourages malicious attempts to alter data.
– Traditional databases often rely on user permissions and centralized authentication, which can be vulnerable to insider threats and unauthorized access.
3. Access Control:
– In blockchain, access control can be designed using smart contracts, which automatically execute actions based on predefined conditions. This automated process reduces the risk of human error and enhances security.
– Conversely, traditional models require manual intervention for access control, potentially leading to misconfigurations and security gaps.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Blockchain for Security
Blockchain security presents both significant benefits and notable drawbacks, shaping its implementation in various sectors.
Advantages:
– Enhanced Transparency: Transactions on a blockchain are recorded in a public ledger, allowing for verification and traceability, which increases trust among users.
– Immutability: Once data is recorded on a blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus from the network, making it highly resistant to fraud.
– Reduced Intermediaries: The peer-to-peer nature of blockchain reduces the need for third-party intermediaries, which can lower costs and expedite processes.
Disadvantages:
– Scalability Issues: As the size of the blockchain grows, processing times can slow, especially for public blockchains with high transaction volumes.
– Energy Consumption: Many blockchain networks, particularly those using Proof of Work, require significant energy and computational power, raising concerns about their environmental impact.
– Regulatory Uncertainty: The decentralized nature of blockchain can complicate compliance with existing laws and regulations, creating potential legal challenges for organizations.
Scenarios Where Blockchain Security Outperforms Conventional Approaches
Blockchain security has proven advantageous in various real-world scenarios, showcasing its capabilities beyond traditional methods.
– Financial Transactions: In the banking sector, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have illustrated how blockchain can facilitate secure, instantaneous cross-border transactions without the need for intermediaries. This not only reduces costs but also minimizes fraud risk.
– Supply Chain Management: Companies such as IBM and Walmart have implemented blockchain solutions to track products throughout the supply chain, ensuring transparency and authenticity. This approach helps combat counterfeiting and enhances trust among stakeholders.
– Healthcare Records Management: Blockchain can secure patient data, allowing for safe sharing between healthcare providers while maintaining patient privacy. This ensures that health records remain untampered and accessible only to authorized personnel.
In summary, while traditional security models have their strengths, blockchain technology presents innovative solutions that address many of their limitations. Its unique security features and capabilities continue to reshape how information is protected across various industries.
Wrap-Up
In summary, Blockchain Security is a multi-faceted domain that combines advanced technology with best practices to safeguard digital assets. As we move forward, keeping abreast of emerging threats and innovations will be crucial in ensuring robust security measures. The lessons learned from successful implementations and ongoing regulatory developments will pave the way for a more secure and resilient blockchain ecosystem.
General Inquiries
What are the main benefits of Blockchain Security?
Blockchain Security enhances data integrity, promotes transparency, and reduces the risk of fraud through decentralization.
How does decentralization improve security?
Decentralization distributes data across multiple nodes, making it difficult for malicious actors to target a single point of failure.
What is the role of public and private keys in Blockchain Security?
Public keys encrypt data for secure transactions, while private keys authenticate users and maintain data integrity.
Why are regular security audits important?
Regular security audits help identify vulnerabilities and ensure that blockchain systems remain up-to-date with the latest security measures.
How can organizations effectively implement Blockchain Security?
Organizations can implement Blockchain Security by following best practices, conducting audits, and staying informed about regulatory changes.