Beginning with Blockchain, the narrative unfolds in a compelling and distinctive manner, drawing readers into a story that promises to be both engaging and uniquely memorable.
This groundbreaking technology, which acts as a decentralized database, has the potential to transform various sectors by providing enhanced security, transparency, and efficiency. With its foundation built on cryptography and various consensus mechanisms, Blockchain has already begun to reshape financial services and much more, making it a critical subject for understanding the future of technology and business.
Discuss the foundational principles of blockchain technology
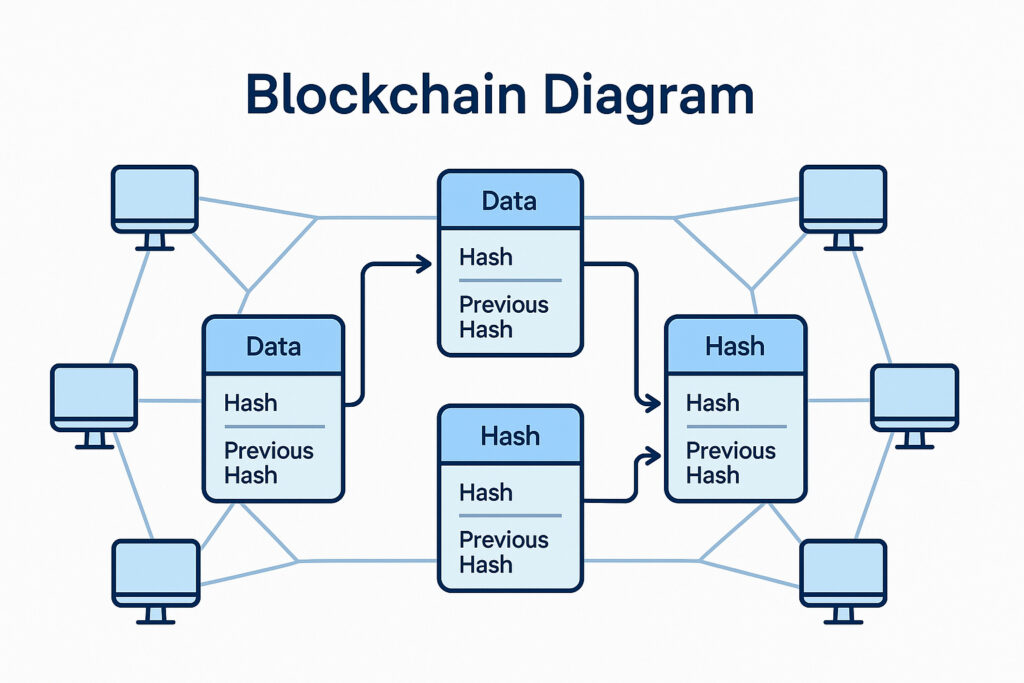
Blockchain technology operates on a set of foundational principles that ensure its efficacy and reliability as a decentralized database. At its core, blockchain is a distributed ledger that allows multiple participants to maintain and access a shared database without the need for a central authority. This decentralized nature eliminates single points of failure and enhances the integrity of the data. Every transaction that occurs on the blockchain is recorded in a block, which is then linked to previous blocks, forming a chain. Each block contains a unique cryptographic hash of the previous block, creating an immutable record that is resistant to tampering.
Decentralized Database Functionality
The decentralized structure of blockchain ensures that no single entity controls the entire network, thereby increasing transparency and trust among participants. Each participant, or node, in the network holds a copy of the entire blockchain, allowing for real-time updates and verification of transactions. When a new transaction is initiated, it is broadcast to the network, where it is verified by the consensus mechanism employed by the blockchain.
This mechanism can vary, but it typically involves complex algorithms that require nodes to reach an agreement on the validity of transactions before they are added to the blockchain. This ensures that once a transaction is confirmed, it cannot be altered without the consensus of the majority of the network participants.
Role of Cryptography in Security
Cryptography plays a crucial role in securing blockchain systems. Each transaction is encrypted using cryptographic techniques, ensuring that only authorized parties can access the information. The use of public and private keys is foundational; users possess a private key that allows them to sign transactions, while the public key enables others to verify the transaction’s authenticity.
Additionally, blockchain employs hashing algorithms to create a unique identifier for each block. This ensures that even the slightest modification in the data would result in a completely different hash, alerting the network to potential tampering. The use of cryptographic signatures and hashing thus guarantees the integrity and confidentiality of the data stored within the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms are essential for validating transactions on the blockchain, ensuring that all participants agree on the state of the network. Different blockchains utilize various consensus methods, each with its own advantages and trade-offs.
Some prevalent consensus mechanisms include:
- Proof of Work (PoW): This method requires participants to solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and create new blocks, as seen in Bitcoin.
- Proof of Stake (PoS): In this approach, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral, reducing energy consumption compared to PoW.
- Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS): This variant allows stakeholders to elect delegates who validate transactions on their behalf, increasing transaction speed.
- Practical Byzantine Fault Tolerance (PBFT): This consensus algorithm allows for a high degree of fault tolerance and can reach consensus quickly among a known set of participants.
The choice of consensus mechanism significantly affects the scalability, security, and decentralization of the blockchain network, impacting its overall performance and reliability.
Explore the various types of blockchain networks available today
Blockchain technology has rapidly evolved since its inception, giving rise to various types of blockchain networks tailored to meet diverse needs. Understanding these networks is essential for organizations and individuals looking to leverage the potential of blockchain. The three primary types of blockchain networks are public, private, and consortium blockchains, each with unique characteristics, uses, and implications for industries.
Public, Private, and Consortium Blockchains
Public blockchains are open to anyone who wishes to participate. They allow users to read, write, and validate transactions without requiring permission. This type of blockchain is decentralized, offering transparency and security, but it can be prone to scalability issues. Notable examples of industries utilizing public blockchains include finance, with Bitcoin and Ethereum as leading platforms, enabling peer-to-peer transactions and smart contracts.
Private blockchains, on the other hand, are restricted to a specific group of users. Access is controlled by an organization or consortium, making these networks more efficient and faster than public blockchains. They are often used in industries that require confidentiality and regulatory compliance, such as healthcare and supply chain management. For instance, companies like Hyperledger Fabric are used by organizations like IBM to create private blockchains tailored to their internal processes.
Consortium blockchains share characteristics of both public and private blockchains. They are governed by a group of organizations rather than a single entity, allowing multiple stakeholders to participate while maintaining control over who can access the network. This type is prevalent in industries like banking and finance, where institutions collaborate on shared infrastructure while ensuring data privacy and security. R3 Corda, for example, is designed specifically for financial services, providing a platform for consortium blockchains among banks.
Exploring the advantages and disadvantages of each blockchain type highlights their practical applications.
- Public Blockchains:
- Advantages:
– High transparency and security through decentralization.
– Strong network effects due to a large number of participants. - Disadvantages:
– Slower transaction speeds and scalability issues.
– Potential for high energy consumption, as seen with Bitcoin mining.
- Advantages:
- Private Blockchains:
- Advantages:
– Faster transaction speeds and greater efficiency due to fewer nodes.
– Enhanced privacy and control over data access. - Disadvantages:
– Less transparency, which may lead to trust issues among stakeholders.
– Higher centralization may increase the risk of data manipulation.
- Advantages:
- Consortium Blockchains:
- Advantages:
– Balance of transparency and privacy, fostering collaboration among organizations.
– Scalability improvements due to a limited number of nodes. - Disadvantages:
– Governance challenges can arise, leading to conflicts among participants.
– Dependence on a few entities can create trust issues for external stakeholders.
- Advantages:
Analyze the impact of blockchain technology on financial services
Blockchain technology is fundamentally altering the landscape of financial services, providing innovative solutions that challenge traditional banking and payment systems. Its decentralized nature allows for greater efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced security. By facilitating direct transactions between parties without the need for intermediaries, blockchain is reshaping how value is exchanged and stored. This transformation is particularly evident in various applications ranging from cross-border payments to asset management, as more financial institutions recognize the potential benefits of this technology.
Reshaping traditional banking and payment systems
The integration of blockchain technology into financial services has led to substantial changes in how transactions are processed. Traditional banking systems often involve multiple intermediaries, which can slow down transactions and increase costs. In contrast, blockchain allows for peer-to-peer transactions, which can occur in real-time. This shift not only expedites processes but also minimizes the fees usually associated with international transfers.
Several notable case studies illustrate the practical implementation of blockchain in financial institutions:
1. Ripple: RippleNet utilizes blockchain to facilitate fast and low-cost international payments. Financial institutions using Ripple have reported transaction speeds of just seconds, a stark contrast to the days it can take traditional banks to process cross-border payments.
2. JP Morgan’s JPM Coin: JP Morgan Chase launched its own digital currency, JPM Coin, to enable instant payments between institutional clients. This private blockchain solution allows for secure transactions that settle in real-time, significantly improving operational efficiency for their clients.
3. Ant Financial: The Chinese fintech giant has implemented blockchain technology to streamline its remittance services. Ant Financial’s blockchain platform has successfully reduced processing times for international money transfers, enhancing customer experience while cutting costs.
The enhanced transparency and security provided by blockchain technology are game-changing for financial transactions. The inherent characteristics of blockchain, such as immutability and cryptographic security, ensure that every transaction is recorded in a trustless environment. This means that once a transaction is entered into the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, significantly reducing the risk of fraud.
Moreover, the transparency of blockchain allows all parties involved in a transaction to access the same information, fostering trust and accountability. In contrast to traditional systems where data is often siloed and controlled by a single entity, blockchain democratizes access to transaction records.
In sum, blockchain’s impact on financial services is profound, enabling faster transactions, reducing costs, and enhancing security and transparency. As more institutions adopt this technology, it is likely to not only reshape the financial ecosystem but also empower consumers with greater control over their financial assets.
Assess the challenges and limitations faced by blockchain technology
Blockchain technology has garnered significant attention for its potential to revolutionize various sectors by providing transparency, security, and efficiency. However, several challenges hinder its widespread adoption, which must be addressed for blockchain to reach its full potential. Understanding these challenges is crucial for developers, businesses, and policymakers as they navigate the complex landscape of blockchain solutions.
Major challenges hindering widespread adoption
The journey towards the mainstream adoption of blockchain technology is not without its obstacles. Key challenges include the lack of standardization, energy consumption concerns, and public perception issues.
- Lack of standardization: The absence of universally accepted protocols and standards can lead to fragmentation within the blockchain ecosystem. This inconsistency complicates interoperability among various blockchain platforms and may deter potential users.
- High energy consumption: Many blockchain networks, particularly those utilizing proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, require substantial computational power, leading to significant energy consumption. This raises concerns about sustainability and environmental impact, which can hinder adoption by eco-conscious entities.
- Public perception and trust: Blockchain is often associated with negative connotations, such as fraud and illicit activities due to its use in cryptocurrencies. This perception can lead to mistrust among potential users and stakeholders, hindering acceptance in legitimate sectors.
Scalability issues and potential solutions
Scalability remains one of the most pressing issues faced by blockchain technology. As the number of users and transactions increases, many blockchain networks struggle to maintain speed and efficiency.
The current limitations often result in slower transaction times and higher fees, which can deter users. Several potential solutions are being explored to address these scalability challenges:
- Layer 2 solutions: Technologies like the Lightning Network for Bitcoin and state channels for Ethereum aim to conduct transactions off-chain, reducing the load on the main blockchain and increasing speed and efficiency.
- Sharding: This technique involves splitting the blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces (shards), allowing for parallel processing of transactions. This can significantly enhance throughput and reduce congestion.
- Transitioning to proof-of-stake: Shifting from energy-intensive proof-of-work to proof-of-stake consensus mechanisms can improve efficiency and scalability, as seen in Ethereum’s transition with its upgrade to Ethereum 2.0.
Regulatory concerns in various jurisdictions
Regulatory uncertainty is a prevalent concern surrounding blockchain technology. Different jurisdictions have adopted varying stances on blockchain and cryptocurrency regulation, which can create challenges for developers and businesses attempting to operate across borders.
In some countries, such as the United States, regulations are still evolving. Agencies like the SEC and CFTC are working to define regulations regarding the trading of digital assets, while others like China have imposed strict bans on cryptocurrency transactions.
This regulatory patchwork can create complexities for companies that wish to innovate with blockchain technology. Businesses must remain agile and informed about the regulatory landscape in their operating jurisdictions to mitigate risks and ensure compliance.
“The future of blockchain hinges not just on technological advancements, but also on how effectively we navigate the regulatory landscape.”
In summary, while blockchain technology holds tremendous promise, addressing its challenges, scalability issues, and regulatory uncertainties will be critical for its successful integration into mainstream applications.
Examine the future trends of blockchain technology
As we look toward the next decade, blockchain technology promises to reshape various sectors beyond its traditional boundaries. With emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and smart contracts, the evolution of blockchain is poised to vastly expand its use cases. The ongoing adoption of this technology hints at a transformative impact on industries ranging from supply chain management to healthcare and beyond.
Forecast of Blockchain Evolution
The future of blockchain technology is expected to be driven by advancements in several key areas. This evolution will likely enhance scalability, interoperability, and regulatory compliance, leading to broader adoption across different industries. Notably, the integration of AI with blockchain could allow for more intelligent data management and automated processes, significantly improving operational efficiencies.
Innovations in consensus algorithms, such as Proof of Stake (PoS) and delegated Proof of Stake (dPoS), promise to reduce energy consumption and improve transaction speed. This shift is critical as concerns about the environmental impact of traditional Proof of Work (PoW) systems become more prominent. As more organizations prioritize sustainability, these enhanced algorithms will play a crucial role in determining blockchain’s future relevance.
Emerging Use Cases Beyond Finance
Blockchain’s potential extends far beyond the financial sector, opening up new avenues in various fields. The following trends highlight how different industries are beginning to harness blockchain technology:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can enhance transparency and traceability, allowing stakeholders to track products from origin to consumer. For example, companies like IBM and Walmart are using blockchain to monitor food supply chains, ensuring food safety and reducing waste.
- Healthcare: The secure sharing of patient data through blockchain can streamline processes, reduce fraud, and improve patient outcomes. Initiatives such as MediLedger are exploring how blockchain can facilitate drug supply chain transparency and integrity.
- Digital Identity Verification: Blockchain offers a secure way to manage digital identities. Projects like uPort and Sovrin are developing decentralized identity solutions that enable individuals to control their data, minimizing identity theft risks.
- Smart Contracts in Real Estate: The use of smart contracts can simplify property transactions by automating agreements and ensuring compliance. This reduces the need for intermediaries and speeds up processes, as seen with platforms like Propy.
Innovative Projects Pushing Blockchain Boundaries
Numerous projects are currently redefining the capabilities of blockchain technology. These initiatives are exploring novel applications and solutions that highlight the versatility of blockchain.
1. Ethereum 2.0 – A significant upgrade aimed at improving scalability and security through a shift to PoS, which is set to significantly increase transaction throughput while reducing energy use.
2. Filecoin – A decentralized storage network that incentivizes users to rent out their unused storage space, providing a new paradigm for cloud storage by ensuring data is securely stored and easily retrievable.
3. Chainlink – A decentralized oracle network that connects smart contracts with real-world data, enabling them to execute based on external conditions. This has broad implications for various industries utilizing automated agreements.
4. Holochain – An open-source framework designed for distributed applications, focusing on scalability and performance without relying on a central blockchain, thus enabling a more decentralized internet.
5. Polkadot – Facilitating interoperability between different blockchains, Polkadot allows multiple blockchains to share information and functionalities, which could lead to a more connected ecosystem of decentralized applications.
These projects exemplify the innovative spirit within the blockchain community and underscore the technology’s potential to transform industries by enabling decentralized solutions that enhance efficiency and trust.
Evaluate the role of smart contracts in blockchain ecosystems
Smart contracts are a cornerstone of blockchain technology, providing essential functionality that enhances the capabilities of decentralized applications (dApps) and various blockchain networks. These self-executing contracts are encoded with terms and conditions that automatically execute transactions when predefined conditions are met. This automation transforms traditional contractual agreements by eliminating the need for intermediaries, thereby increasing efficiency and trust among parties involved.
Smart contracts operate within blockchain frameworks by utilizing the immutable and distributed nature of the blockchain. Once deployed, a smart contract resides on the blockchain and is accessible to all participants in the network, ensuring transparency and security. Each transaction related to the contract is recorded on the blockchain, making it tamper-proof and auditable. The coding language used to create smart contracts, such as Solidity for Ethereum-based contracts, dictates the logic that governs how the contract functions and interacts with other contracts and external data sources.
Real-world applications of smart contracts
The real-world applications of smart contracts span various industries, showcasing their versatility and transformative potential. Below are key examples of how smart contracts are being utilized:
- Financial Services: Smart contracts facilitate automated lending and borrowing processes through platforms like Aave and Compound. These decentralized finance (DeFi) projects enable users to lend assets and earn interest without relying on traditional banks.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies like IBM and Walmart use smart contracts to enhance supply chain transparency. By recording each step of the supply chain on the blockchain, stakeholders can track the origin and movement of goods, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Real Estate Transactions: Smart contracts streamline property transactions by automatically executing the transfer of ownership upon payment completion. Platforms like Propy aim to simplify the process while reducing the need for intermediaries.
- Insurance Claims Processing: Insurers can automate claims payments by using smart contracts that trigger payouts based on verified conditions, such as flight delays or natural disasters, ensuring timely compensation to policyholders.
The benefits of using smart contracts are numerous. They provide enhanced efficiency by automating processes, reduce costs by eliminating intermediaries, and ensure greater accuracy by minimizing human error. Moreover, the decentralized nature of blockchain means that contracts are secure and resistant to tampering.
However, there are potential risks associated with smart contracts. The reliance on code means that any bugs or vulnerabilities can lead to significant financial losses, as seen in various high-profile hacks. Additionally, the legal framework surrounding smart contracts is still evolving, which raises questions about enforceability and jurisdiction. It is essential for developers and users to perform comprehensive audits and understand the legal implications before deploying smart contracts to mitigate these risks.
Investigate the intersection of blockchain and cybersecurity
The integration of blockchain technology within the realm of cybersecurity presents a fascinating opportunity to enhance data security and integrity. With increasing cyber threats and data breaches making headlines, organizations are exploring innovative solutions like blockchain to protect sensitive information. This decentralized ledger technology not only provides a secure framework for storing data but also offers an immutable record that can significantly bolster cybersecurity measures.
Blockchain’s inherent characteristics, such as decentralization, transparency, and immutability, are essential in enhancing security measures for data protection and integrity. By distributing data across a network of computers, blockchain minimizes the risk of centralized data breaches. Each transaction or data entry is encrypted and linked to the previous one, creating a chain that is virtually tamper-proof. This ensures that even if hackers attempt to alter the data, the changes would be easily detectable due to the consensus mechanisms employed in blockchain systems.
Security Enhancements Through Blockchain Technology
Blockchain can play a critical role in fortifying security measures, particularly in the following areas:
- Data Integrity: The use of cryptographic hashing in blockchain ensures that any alteration of data will be evident, thereby preserving the integrity of the information stored.
- Decentralized Storage: Unlike traditional databases, which are vulnerable to single points of failure, decentralized storage distributes data across multiple nodes, making it significantly harder for cybercriminals to access or corrupt sensitive information.
- Audit Trails: Blockchain’s ability to create comprehensive and immutable audit trails allows organizations to trace back any unauthorized changes or access to data, thereby enhancing accountability and compliance.
- Smart Contracts: These self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code can automate security protocols, reducing the human error factor and ensuring that agreed-upon security measures are enforced.
The potential of blockchain technology to prevent cybersecurity breaches is demonstrated through various high-profile incidents. For instance, the 2017 Equifax data breach affected over 147 million individuals due to vulnerabilities in its database. By employing blockchain, this sensitive information could have been stored securely across a decentralized network, significantly reducing the risk of a single point of failure. Moreover, the transparent nature of blockchain would have allowed for real-time monitoring of access and changes, potentially flagging suspicious activities before they resulted in a data compromise.
Blockchain and Identity Verification in Cybersecurity
Identity verification is a critical component of cybersecurity and can benefit greatly from blockchain technology. Traditional identity verification processes are often plagued by inefficiencies and vulnerabilities, including the risk of identity theft and fraud. Blockchain offers a more secure and efficient alternative through decentralized identity management systems.
This approach allows individuals to control their personal information without relying on centralized authorities. For example, a blockchain-based identity system could enable users to prove their identity with a digital signature, eliminating the need to share sensitive personal data. By leveraging cryptographic techniques, users can authenticate their identities while maintaining privacy and security.
- Self-Sovereign Identity: Individuals can create, own, and manage their digital identities on a blockchain, reducing reliance on third parties that often become targets for cyberattacks.
- Immutable Identity Records: Blockchain’s immutable nature ensures that once identity data is added, it cannot be altered or deleted without consensus, thereby preventing identity fraud.
- Verification Efficiency: Automated verification processes enabled by blockchain can significantly reduce the time and cost associated with traditional identity verification methods.
By harnessing the power of blockchain for identity verification, organizations can not only enhance their cybersecurity posture but also improve user trust and engagement. The successful implementation of such systems can lead to a more secure digital environment, ultimately reducing the occurrences of identity-related cybercrimes.
Illustrate the environmental impacts of blockchain technology
The rise of blockchain technology has brought innovative solutions and transformations across various sectors. However, with these advancements come significant concerns regarding their environmental impact, particularly due to the high energy consumption associated with certain blockchain models. Understanding both the implications of this energy use and the initiatives aimed at mitigating these impacts is crucial for fostering sustainable development within the blockchain ecosystem.
Energy Consumption of Blockchain Models
Different blockchain models exhibit varying levels of energy consumption. Proof of Work (PoW) blockchains, like Bitcoin, are notorious for their high energy usage, as they require extensive computational power to validate transactions. In fact, Bitcoin mining alone consumes more energy than entire countries such as Argentina. This intensive energy requirement raises concerns regarding sustainability, especially when much of the energy consumed is sourced from fossil fuels.
In contrast, Proof of Stake (PoS) models, such as Ethereum 2.0, offer a more energy-efficient alternative. PoS significantly reduces energy consumption by eliminating the need for extensive computational resources to validate transactions. Instead, validators are chosen based on the number of coins they hold and are willing to “stake” as collateral, resulting in a dramatic decrease in the carbon footprint associated with blockchain operations.
“The shift from PoW to PoS could reduce Ethereum’s energy use by over 99%.”
Initiatives for Environmental Sustainability
Recognizing the environmental challenges posed by blockchain technology, various initiatives have emerged to promote more sustainable practices. These initiatives often focus on enhancing energy efficiency, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and fostering eco-friendly blockchain designs. Here are some noteworthy examples:
- Carbon Credits and Offsetting: Several blockchain projects are now utilizing carbon credit systems to offset their environmental impact. By integrating carbon credits into their operations, these projects contribute to reforestation and renewable energy initiatives.
- Green Mining: Some mining operations are committing to using renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind power, to reduce their carbon emissions. This shift not only lessens the environmental burden but also demonstrates the potential for a more sustainable mining ecosystem.
- Eco-friendly Protocols: New blockchain protocols are being developed with sustainability in mind, focusing on minimal energy consumption while still providing robust security and scalability.
Blockchain Projects Promoting Ecological Initiatives
Numerous blockchain projects are leveraging this technology to support ecological initiatives, creating positive environmental impacts through innovative applications. Here are a few examples:
- Energy Web Chain: This project aims to accelerate the transition to a decentralized, decarbonized energy system. It facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources and supports peer-to-peer energy trading.
- Verra: A leading carbon credit standard, Verra utilizes blockchain to enhance transparency, reduce fraud, and improve the tracking of carbon credits, ensuring that environmental claims are credible and verifiable.
- Plastic Bank: This initiative encourages the recycling of plastic by providing incentives in the form of cryptocurrency for individuals collecting plastic waste. By connecting consumers with recyclers through blockchain, it promotes a circular economy.
The environmental impacts of blockchain technology are significant, but through innovation and responsible practices, the industry is actively working towards a more sustainable future.
Wrap-Up
The discussion surrounding Blockchain reveals its vast potential and the challenges it faces as it continues to evolve. From redefining traditional banking systems to exploring new applications across multiple industries, Blockchain stands at the forefront of technological advancement. As we look ahead, the possibilities seem limitless, and staying informed about its developments is essential for anyone interested in the future of innovation.
User Queries
What is Blockchain technology?
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger system that records transactions across multiple computers in a way that ensures the information is secure, transparent, and immutable.
How secure is Blockchain?
Blockchain’s security is primarily ensured through cryptographic techniques and consensus mechanisms, which make it extremely difficult to alter or manipulate recorded data.
What are the main types of Blockchain networks?
The three main types of Blockchain networks are public, private, and consortium blockchains, each serving different purposes and offering varying levels of access and control.
Can Blockchain be used outside of finance?
Yes, Blockchain has potential use cases in various sectors, including supply chain management, healthcare, voting systems, and digital identity verification.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code, allowing for automated and secure transactions on the Blockchain.
How does Blockchain impact the environment?
Blockchain can have significant environmental impacts due to energy consumption, but initiatives are underway to create more energy-efficient models and leverage Blockchain for ecological projects.
What are some challenges facing Blockchain technology?
Some challenges include scalability issues, regulatory uncertainty, and limited public awareness or understanding of how Blockchain works.