Internet of Things (IoT) sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset.
The Internet of Things refers to the interconnected network of devices that communicate and exchange data seamlessly without human intervention. Ranging from smart home appliances to sophisticated industrial machines, IoT encompasses an extensive scope that spans multiple sectors, each harnessing the power of connectivity to enhance efficiency and innovation. With real-time data collection and analysis, these devices not only improve user experiences but also facilitate smarter decision-making processes.
The Definition and Scope of the Internet of Things
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the way we interact with technology and our environment. It refers to the interconnection of everyday devices to the internet, allowing them to send and receive data. This concept encapsulates a vast ecosystem where physical objects are embedded with sensors, software, and other technologies to communicate and exchange information seamlessly.
The fundamental principles of IoT are based on connectivity, data collection, and automation. Devices communicate with each other through various connectivity protocols, including Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee. These devices gather data from their surroundings, which can be analyzed to improve efficiency, enhance user experience, or inform decision-making processes. The scope of IoT spans multiple domains, including healthcare, smart homes, industrial automation, transportation, and agriculture, showcasing its versatility and transformative potential across various sectors.
Domains of IoT Application
IoT technology is applicable in numerous domains, each utilizing its capabilities to solve specific challenges and improve operational efficiency. Below are some key areas where IoT has made significant contributions:
- Smart Homes: Devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and lighting systems allow homeowners to control their environment remotely, enhancing comfort and security.
- Healthcare: Wearable devices, such as fitness trackers and smartwatches, monitor health metrics, enabling real-time health management and data collection for healthcare providers.
- Industrial IoT (IIoT): Sensors and automation systems streamline manufacturing processes, monitor equipment conditions, and predict failures, leading to reduced downtime and increased productivity.
- Transportation: Connected vehicles utilize IoT to enhance navigation, monitor performance, and improve safety through features like emergency braking and lane-keeping assistance.
- Agriculture: Precision farming technologies use soil moisture sensors and weather data to optimize irrigation and crop management, thereby increasing yield and resource efficiency.
The range of devices that fall under the IoT umbrella is extensive, reflecting the diverse applications of this technology. Examples include:
- Smart Thermostats: These devices learn user preferences and adjust home heating and cooling systems accordingly, saving energy.
- Wearable Health Monitors: Devices like the Fitbit track physical activity, heart rates, and sleep patterns, providing insights for healthier living.
- Connected Appliances: Refrigerators that monitor food freshness and suggest recipes based on available ingredients help streamline meal planning.
- Smart Security Systems: Cameras and motion detectors enable real-time surveillance and alerts, enhancing home security.
- Smart Agriculture Equipment: Drones and sensor systems monitor crop health and soil conditions, allowing for data-driven farming decisions.
In summary, the Internet of Things encompasses a broad range of applications and devices, fundamentally reshaping how we live and work. Its ability to connect and analyze data from various sources presents unique opportunities for innovation and efficiency in multiple sectors.
The Technological Foundations of IoT
The Internet of Things (IoT) is built on a sophisticated foundation of technologies that work in harmony to create a seamless network of interconnected devices. Understanding these technologies is essential to appreciate how IoT systems function effectively in various applications, from smart homes to industrial automation.
Key technologies that enable the Internet of Things include sensors, actuators, connectivity protocols, and cloud computing infrastructures. Sensors and actuators collect and execute data-driven commands, while connectivity protocols ensure reliable communication between devices. Each of these components plays a crucial role in the IoT ecosystem, allowing for efficient data exchange and automation.
Importance of Cloud Computing and Data Analytics
Cloud computing serves as the backbone of IoT systems, providing the necessary infrastructure to store and process vast amounts of data generated by connected devices. This centralized approach allows for scalability, reliability, and accessibility, enabling organizations to manage their IoT solutions more effectively.
Data analytics is critical for turning raw data into actionable insights. By employing various analytical techniques, businesses can identify patterns, forecast trends, and optimize operations. The combination of cloud computing and data analytics empowers organizations to make informed decisions and enhance the overall performance of IoT implementations. Consider the following aspects:
- Scalability: Cloud platforms can easily scale to accommodate increasing data loads from additional devices.
- Real-time processing: Cloud computing enables real-time data processing, allowing businesses to respond swiftly to changes.
- Cost-effectiveness: Reduces the need for on-premises infrastructure, minimizing operational costs for organizations.
Role of Communication Protocols
Communication protocols are fundamental to the functionality of IoT devices, facilitating the transfer of data between devices and the cloud. These protocols define the rules and standards for data exchange, ensuring that devices can communicate effectively, regardless of their manufacturer or underlying technology.
Several communication protocols are widely used in IoT applications, each serving distinct purposes and environments. The following list highlights some of the most significant protocols:
- MQTT: A lightweight messaging protocol ideal for low-bandwidth and high-latency networks, commonly used in home automation.
- CoAP: Designed for resource-constrained devices, CoAP allows for efficient communication in IoT networks, particularly in smart cities.
- HTTP/HTTPS: The foundational web protocols are still relevant in IoT for RESTful APIs and cloud communications.
- LoRaWAN: A long-range, low-power protocol used for wide-area networks, suitable for agricultural and environmental monitoring.
The choice of communication protocol can significantly impact the performance and reliability of IoT devices, making it critical for developers and engineers to select the right one for their specific application needs.
Real-World Applications of IoT Across Industries
The Internet of Things (IoT) is rapidly reshaping various industries, proving to be a powerful force for innovation and efficiency. By connecting devices and enabling seamless communication, IoT solutions are enhancing productivity, reducing costs, and improving overall operational effectiveness. This exploration delves into the transformative impact of IoT in key sectors, highlighting specific case studies that exemplify its significant benefits.
Healthcare Innovations
In the healthcare sector, IoT devices are revolutionizing patient care and operational workflows. Wearable devices, remote monitoring systems, and smart medical equipment are enabling healthcare professionals to track patient conditions in real-time, leading to more personalized and timely interventions.
A notable case study is the implementation of remote patient monitoring systems by a leading healthcare provider. Patients with chronic illnesses use connected devices that send vital signs to healthcare teams. This continuous data flow allows for early detection of potential health issues, reducing hospital readmissions by up to 30%.
The integration of IoT in healthcare not only enhances patient outcomes but also significantly streamlines administrative processes, allowing healthcare providers to allocate resources more efficiently.
Agricultural Advancements
The agriculture industry is another area where IoT is making substantial strides. Smart farming techniques, powered by IoT, enable farmers to monitor soil conditions, weather patterns, and crop health through sensors and connected devices.
For example, a successful initiative in precision agriculture involved a large farm that deployed soil moisture sensors and climate monitoring systems. These devices provided real-time data, allowing the farmers to optimize irrigation schedules. As a result, the farm reported a 20% increase in crop yield and a 15% reduction in water usage, showcasing the critical role of IoT in sustainable farming practices.
The application of IoT in agriculture not only boosts productivity but also supports environmental sustainability, making it a win-win for the industry.
Manufacturing Efficiency
In the manufacturing sector, IoT is a catalyst for enhanced operational efficiency and smarter decision-making. Through the use of connected machinery and sensors, manufacturers can monitor equipment health, predict maintenance needs, and optimize production processes.
One compelling case study is a global manufacturing firm that implemented IoT-based predictive maintenance solutions. By analyzing data from connected machines, the company was able to foresee equipment failures before they occurred, leading to a 25% reduction in maintenance costs and a significant decrease in unplanned downtime.
This proactive approach not only saves costs but also enhances productivity, allowing manufacturers to meet market demands more effectively.
“IoT is not merely a technological advancement; it’s a transformative strategy that enhances efficiency and decision-making across industries.”
Security Challenges in the IoT Landscape
The Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way we interact with technology, enabling countless devices to connect and communicate seamlessly. However, this connectivity brings a host of security challenges that must be addressed to protect sensitive information and maintain user trust. Understanding these security threats and implementing effective measures is crucial for safeguarding IoT environments.
The sheer volume of devices connected to the Internet has led to an increase in potential vulnerabilities. As IoT devices communicate over networks, they become prime targets for cybercriminals. Security threats such as unauthorized access, data breaches, and DDoS attacks pose significant risks that can compromise both individual privacy and organizational integrity. Addressing these challenges is essential for fostering a secure IoT ecosystem.
Major Security Threats Associated with IoT
The IoT landscape faces numerous security threats that can have severe implications. Recognizing these threats helps in developing robust security protocols. Some of the major threats include:
- Unauthorized Access: Many IoT devices lack proper authentication, making them vulnerable to unauthorized users who can exploit system weaknesses.
- Data Interception: Data transmitted between devices can be intercepted, leading to exposure of sensitive information if not properly encrypted.
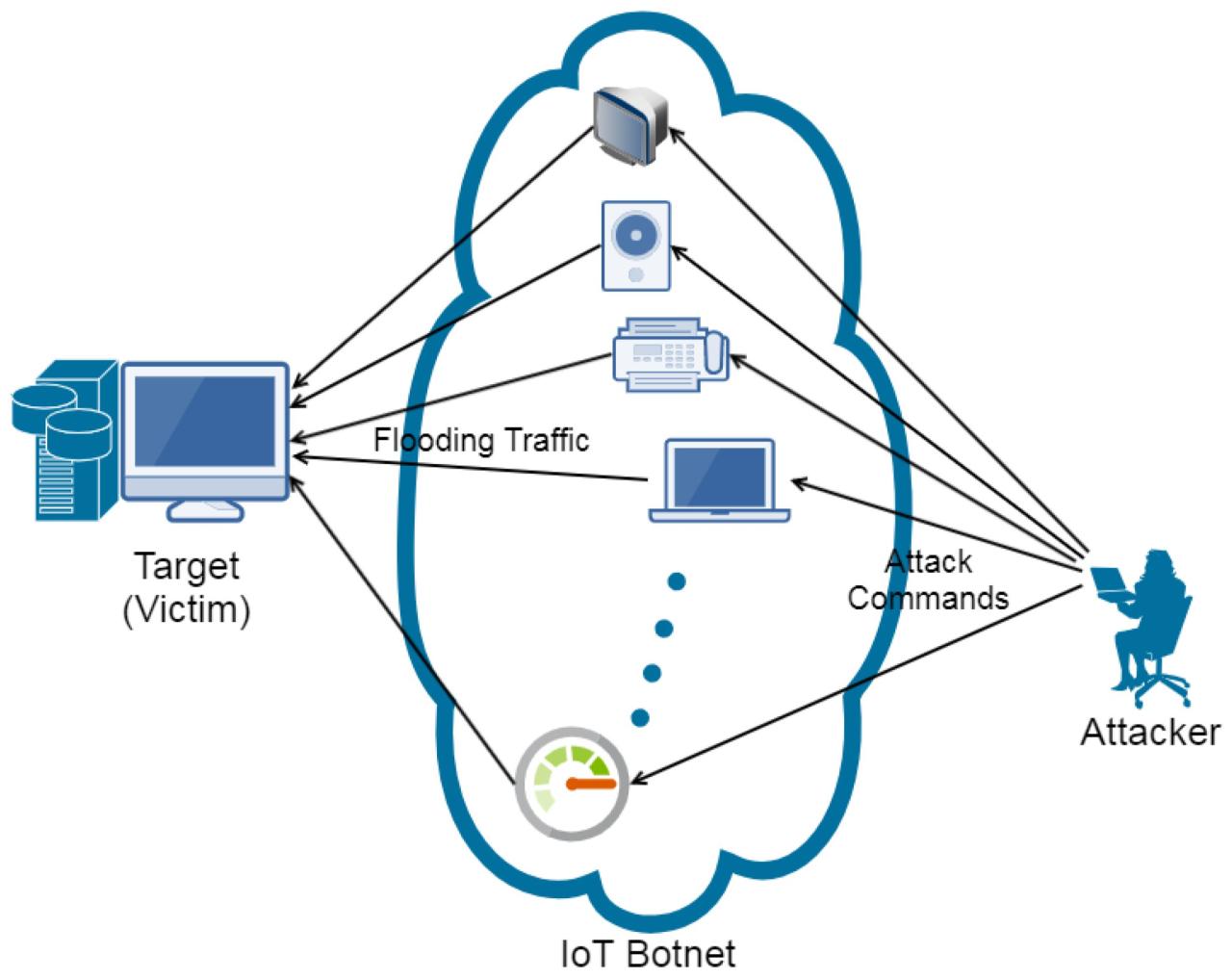
- Botnets and DDoS Attacks: Compromised IoT devices can be used to create botnets, which are often employed in Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, overwhelming targeted servers and networks.
- Malware Infiltration: IoT devices can be infected with malware, enabling cybercriminals to gain control over them and manipulate their functions.
- Physical Security Risks: Devices that are easily accessible can be tampered with or physically stolen, leading to unauthorized access and data breaches.
Measures and Strategies to Enhance IoT Security
To combat the various security threats faced by IoT devices, it is essential to implement proactive measures and strategies. These practices help enhance the overall security posture of IoT networks:
- Robust Authentication Protocols: Implementing strong authentication methods, such as two-factor authentication, can significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data in transit and at rest ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Regular Software Updates: Keeping IoT device firmware and software updated protects against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
- Network Segmentation: Segmenting IoT devices from critical systems can limit the potential impact of a security breach.
- Security by Design: Integrating security measures in the design phase of IoT devices ensures that security is not an afterthought but a foundational element.
Implications of Data Privacy within IoT Ecosystems
Data privacy is a significant concern within IoT ecosystems, where vast amounts of personal and sensitive information are collected and transmitted. The implications of inadequate data privacy can lead to serious consequences, including identity theft and unauthorized surveillance. Addressing these concerns is paramount for maintaining user trust.
The collection and sharing of data in IoT environments must adhere to strict privacy regulations to protect user information. Implementing privacy-enhancing technologies, such as data anonymization and user consent management, can help mitigate risks. Additionally, organizations should actively communicate their data privacy practices to users, fostering transparency and accountability.
“Security is not just a technical problem; it’s a holistic approach that encompasses people, processes, and technology.”
Future Trends and Innovations in IoT
As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to evolve, it is becoming increasingly clear that its future will be shaped by a range of innovative technologies and emerging trends. These developments not only enhance the capabilities of IoT devices but also pave the way for new applications and use cases across various sectors. By understanding these trends, businesses and individuals alike can prepare for the transformative impact of IoT in the coming years.
One significant trend influencing the future of IoT is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into IoT systems. This combination allows for smarter devices that can learn from data, adapt to changing environments, and make autonomous decisions. As AI algorithms improve, IoT systems will become more efficient, leading to enhanced user experiences and optimized operations.
Edge Computing Enhancements
Edge computing is revolutionizing the way IoT devices process data by moving computation closer to the source of data generation. This trend is crucial for applications requiring real-time decision-making, as it reduces latency and bandwidth usage. The importance of edge computing can be highlighted in various sectors:
- Industrial Automation: In manufacturing, edge computing allows machines to analyze data on-site, leading to faster responses and reduced downtime.
- Smart Cities: Traffic management systems can process data from sensors in real-time to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion.
- Healthcare: Wearable devices can monitor patient vitals in real-time, ensuring immediate action can be taken if anomalies are detected.
The integration of edge computing with IoT is expected to mitigate the challenges of data overload and improve overall system responsiveness.
Another transformative innovation is the development of 5G networks, which promise to significantly enhance the capabilities of IoT. With faster data transmission speeds and increased connectivity, 5G will enable more devices to communicate simultaneously without lag. This technology is crucial for applications such as autonomous vehicles, which require instantaneous data sharing to navigate safely.
Blockchain Applications in IoT
Blockchain technology is emerging as a key player in securing IoT ecosystems. By providing a decentralized framework for data exchange, blockchain enhances security and transparency in IoT communications. This is particularly relevant for industries like supply chain management, where tracking the authenticity of goods is critical.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Blockchain can uniquely identify products at each stage of the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and reducing fraud.
- Smart Contracts: Automated contracts can be executed without intermediaries, streamlining processes such as payment and delivery.
- Data Integrity: By securely logging transactions, blockchain ensures that data shared between IoT devices remains unaltered and trustworthy.
The growth of IoT is projected to be exponential, with estimates suggesting that the number of connected devices could reach over 75 billion by 2025. This growth will lead to profound societal impacts, such as improved resource management, enhanced healthcare outcomes, and increased automation in everyday life.
As IoT continues to expand, it will create opportunities for smarter living and more efficient industries, fundamentally transforming how we interact with technology daily.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Enhancing IoT Experiences
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) are two transformative technologies that, when combined, create a powerful synergy capable of enhancing user experiences and operational efficiencies. By integrating AI with IoT ecosystems, businesses can analyze vast amounts of data generated by interconnected devices, enabling smarter decision-making processes and more personalized interactions. This collaboration is paving the way for innovative applications across various industries, from healthcare to smart cities.
Integration of AI and IoT for Smarter Applications
The integration of AI with IoT leads to the development of smarter applications that respond to user needs with increased accuracy and efficiency. By employing AI algorithms, IoT systems can learn from historical data, adapt to changing environments, and automate processes. For instance, smart home devices can analyze usage patterns and predict user behavior, allowing for energy savings and enhanced comfort through proactive adjustments. In industrial settings, AI-driven IoT devices can monitor equipment health, predict failures, and optimize maintenance schedules, significantly reducing downtime and costs.
Benefits of Machine Learning Algorithms in Processing IoT Data
Machine learning algorithms play a crucial role in processing the massive volumes of data generated by IoT devices. These algorithms can identify patterns and trends within the data that would be nearly impossible for humans to discern. The benefits include:
- Real-Time Analytics: Machine learning enables real-time data analysis, allowing businesses to respond immediately to changes in their environment, enhancing operational agility.
- Predictive Insights: Algorithms can forecast future events based on historical data, such as predicting equipment failures or optimizing supply chain logistics.
- Improved User Experience: By personalizing recommendations and interactions, businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Anomaly Detection: Machine learning can identify unusual patterns that may indicate security threats or system malfunctions, allowing for timely intervention.
Future Possibilities for AI and IoT Collaborations
The potential for future AI and IoT collaborations is vast and exciting, with numerous possibilities that could reshape industries. For example, the healthcare sector could benefit from AI-enabled wearable devices that continuously monitor vital signs and predict health issues before they become critical, leading to proactive care and better patient outcomes. In smart cities, AI can analyze data from IoT sensors to optimize traffic flow, reduce energy consumption, and enhance public safety.
“The convergence of AI and IoT will create a smarter world where everyday objects work intelligently, learning from their interactions and continuously improving.”
As these technologies evolve, the integration of AI and IoT is anticipated to lead to autonomous systems capable of making decisions without human intervention. This could include everything from automated factories to smart agriculture systems that optimize crop yields based on real-time environmental data. The synergy between AI and IoT not only enhances operational efficiencies but also elevates the overall quality of life through smarter, more responsive technologies.
Environmental Impact of IoT Technologies
The Internet of Things (IoT) is reshaping how we interact with our environment, offering innovative solutions to promote sustainability and enhance environmental conservation. By connecting devices and systems, IoT technologies create opportunities to monitor, manage, and optimize resource usage, significantly reducing the ecological footprint.
IoT solutions contribute to sustainability and environmental conservation by enabling real-time data collection and analysis. This capability allows organizations and individuals to make informed decisions regarding resource consumption, waste management, and energy efficiency. For instance, smart sensors can track air and water quality, enabling timely interventions to protect natural resources and ecosystems.
Smart Agriculture and Precision Farming
One of the most impactful applications of IoT in the environmental sector is in agriculture. Smart agriculture and precision farming utilize IoT technologies to enhance crop yields while minimizing resource usage. The following points illustrate the environmental benefits of this approach:
- Water Conservation: IoT-enabled soil moisture sensors allow farmers to optimize irrigation by providing real-time data on soil conditions. This minimizes water waste and promotes sustainable water management.
- Pesticide Reduction: Precision farming techniques utilize data analytics to identify pest outbreaks early, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and promoting healthier ecosystems.
- Energy Efficiency: Smart farming equipment can operate only when necessary, conserving energy and lowering greenhouse gas emissions associated with agricultural practices.
Smart Cities and Urban Sustainability
The concept of smart cities leverages IoT technologies to enhance urban living while addressing environmental challenges. Smart city initiatives focus on improving infrastructure and reducing waste through efficient resource management:
- Waste Management: IoT waste bins equipped with sensors can monitor fill levels and optimize collection routes, reducing fuel consumption and CO2 emissions from garbage trucks.
- Energy Management: Smart grids use IoT systems to monitor energy consumption and distribution, facilitating the integration of renewable energy sources and promoting energy efficiency.
- Traffic Management: IoT traffic sensors can analyze vehicle flow and adjust traffic signals in real-time, reducing congestion and lowering emissions from idling vehicles.
Balancing Technological Advancements with Ecological Considerations
While IoT technologies offer significant environmental benefits, it is crucial to address the balance between technological advancements and ecological considerations. The production and disposal of IoT devices can lead to electronic waste and resource depletion. To mitigate this impact, the following strategies should be considered:
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Encourage the use of recyclable materials and environmentally friendly production processes in the manufacturing of IoT devices.
- Lifecycle Management: Implement programs that promote the responsible disposal and recycling of outdated devices, reducing e-waste and conserving valuable resources.
- Energy-Efficient Devices: Develop IoT devices that consume minimal energy and use low-power communication technologies to enhance overall sustainability.
“The effective integration of IoT into environmental initiatives represents a pivotal step towards a sustainable future.”
User Experience and Design Considerations in IoT Devices
The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed the way users interact with technology, making user experience (UX) and design critical components in the development of IoT products. A well-designed IoT device not only performs its intended functions but also enhances the user’s overall experience, making it more intuitive, enjoyable, and efficient. In a market flooded with devices, prioritizing user-centered design can be the differentiator that leads to success.
User-centered design emphasizes the importance of understanding the needs, preferences, and behaviors of the users throughout the product development process. By involving users early and often, designers can create solutions that resonate with the target audience. This approach ensures that the final product meets user expectations and reduces the likelihood of abandonment or dissatisfaction.
Importance of User-Centered Design in IoT
Integrating user-centered design into the IoT development process is essential for several reasons:
-
Enhanced Usability: A user-friendly design allows users to navigate and operate devices effortlessly, leading to higher satisfaction.
-
Increased Adoption: Devices that align with user needs are more likely to be adopted and integrated into daily routines.
-
Reduced Learning Curve: Intuitive interfaces decrease the time users spend learning how to operate the device, fostering quicker engagement.
-
Improved Customer Loyalty: Satisfied users are more likely to recommend the product and remain loyal to the brand.
Design Challenges in the IoT Space
The IoT landscape presents unique design challenges that developers must address to ensure a seamless user experience. Common issues include:
-
Device Interoperability: Ensuring that different devices can communicate effectively with one another is crucial for a cohesive user experience.
-
Data Privacy and Security: Users are increasingly aware of their data privacy, necessitating transparent security measures in design.
-
Complex User Interfaces: Balancing functionality with simplicity is key; overly complex interfaces can alienate users.
-
Real-time Feedback: Users expect immediate responses from devices, making it essential to design systems that can provide real-time feedback.
Successful IoT Designs Prioritizing User Experience
Several IoT devices exemplify best practices in user-centered design. Notable examples include:
-
Philips Hue Smart Lighting: The app interface allows users to control lighting easily, set schedules, and integrate with voice assistants, creating a seamless experience.
-
Nest Learning Thermostat: This device learns user schedules and preferences, automatically adjusting temperatures, which simplifies climate control.
-
Amazon Echo: With a straightforward voice-command interface, it allows users to interact with various smart home devices, making technology accessible to all age groups.
Economic Implications of Widespread IoT Adoption
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) into various industries is poised to create significant economic impacts. This technological transformation is not just about connectivity; it influences productivity, operational efficiency, and ultimately the financial performance of businesses. By analyzing these economic implications, we can better understand how IoT reshapes markets and job landscapes.
The economic effects of IoT adoption can be seen across multiple sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, and agriculture. In manufacturing, for instance, IoT-enabled devices facilitate predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and improving efficiency. This translates to cost savings and enhanced product quality. According to a report by McKinsey, IoT has the potential to create $4 trillion to $11 trillion in economic value by 2025, showcasing how deeply interwoven these technologies are becoming in the fabric of industry.
Job Creation and Transformation Due to IoT Technologies
The proliferation of IoT technologies is expected to create new job opportunities while also transforming existing roles. As companies adopt IoT solutions, they will require a workforce skilled in data analysis, software development, and system integration. This shift will not only enhance the demand for tech-oriented professionals but also necessitate upskilling for workers in traditional roles who will now interact with IoT systems.
The following points illustrate the job market evolution driven by IoT:
- Creation of new roles such as IoT architects, data scientists, and cybersecurity experts, which are essential for deploying and maintaining IoT solutions.
- Transformation of traditional roles like manufacturing technicians who will need to adapt to smart machinery and IoT interfaces.
- Increased demand for IoT-related educational programs and training initiatives to prepare the workforce for these emerging roles.
According to a report from the World Economic Forum, IoT is predicted to generate 133 million new roles by 2022, demonstrating its capacity to not only create jobs but also enhance the skill set of the workforce.
Market Trends and Investment Opportunities within the IoT Sector
As IoT technology continues to evolve, various market trends emerge that signal investment opportunities. The growth of smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and connected healthcare devices are just a few areas where investors can find promising returns. The global IoT market is projected to grow from $381 billion in 2021 to over $1 trillion by 2028, indicating a robust upward trend.
Key investment opportunities within the IoT sector include:
- Smart home devices, such as smart thermostats and security systems, which are gaining traction due to consumer demand for convenience and energy efficiency.
- Industrial IoT solutions that streamline supply chains and increase operational efficiency in manufacturing processes.
- Healthcare IoT applications like remote patient monitoring and telemedicine, which have seen increased adoption as a result of the pandemic.
Investors are encouraged to focus on sectors that demonstrate strong growth potential, as companies leveraging IoT technologies are likely to gain a competitive edge. This growth not only offers financial returns but also contributes to the broader economic landscape by promoting innovation and productivity.
Ultimate Conclusion
In summary, the Internet of Things represents a transformative shift in how we interact with technology and the environment around us. As we delve deeper into its applications, security challenges, and future trends, it becomes clear that IoT is not just a technological trend; it’s a paradigm shift that has the potential to reshape industries and daily life. The journey of IoT is just beginning, and its implications for society are nothing short of revolutionary.
Common Queries
What is the Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of interconnected devices that can collect and exchange data over the internet, enhancing automation and efficiency.
How does IoT impact daily life?
IoT impacts daily life by enabling smart home technologies, improving healthcare monitoring, and optimizing transportation, making everyday tasks easier and more efficient.
What are some common IoT devices?
Common IoT devices include smart thermostats, wearable fitness trackers, smart refrigerators, and connected cars.
How secure is IoT technology?
While IoT technology offers many benefits, it also presents security challenges, making it crucial to implement robust security measures to protect data and devices.
What industries are most affected by IoT?
Industries such as healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, and transportation are significantly impacted by IoT, leveraging its capabilities for improved operations and services.