Kicking off with Identity Access Management (IAM), this vital framework serves as the backbone of security in modern enterprises, ensuring that the right individuals access the right resources at the right times. As organizations increasingly face digital threats and regulatory demands, IAM not only streamlines access processes but also fortifies security, making it essential for business operations.
In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, the importance of IAM cannot be overstated. It encompasses various components such as authentication, authorization, and user management, which collectively safeguard sensitive information and maintain regulatory compliance. The increasing reliance on IAM solutions across diverse industries illustrates its critical role in mitigating risks associated with identity theft and data breaches.
The Importance of Identity Access Management in Modern Enterprises
In today’s digital landscape, organizations are increasingly reliant on technology to streamline operations, enhance customer engagement, and drive innovation. As a consequence, the need for robust security frameworks becomes paramount. One critical component of these frameworks is Identity Access Management (IAM), which ensures that the right individuals have the right access to technology resources. IAM not only protects sensitive information but also supports a broader security strategy in modern enterprises.
A well-implemented IAM system plays a vital role in reinforcing organizational security by controlling user access to critical systems and data. It facilitates the identification, authentication, and authorization of users, managing their identities and their access rights effectively. By providing a centralized platform for managing user identities, IAM helps prevent unauthorized access, mitigates potential security breaches, and enhances the overall security posture of the organization. Furthermore, IAM solutions often include features such as single sign-on (SSO) and multi-factor authentication (MFA), which bolster security by adding additional layers of verification before granting access to sensitive resources.
Impact of IAM on Regulatory Compliance and Risk Management
Implementing IAM solutions is essential for meeting various regulatory requirements and managing risks effectively. Organizations across diverse industries are subject to stringent regulations that govern data protection and user privacy, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. IAM helps organizations maintain compliance by ensuring that access controls are in place, enabling audit trails, and facilitating the reporting process.
The integration of IAM in risk management strategies further enhances an organization’s ability to identify and manage potential threats. By enforcing the principle of least privilege, IAM minimizes exposure to risk by ensuring users have access only to the information necessary for their roles. This not only reduces the surface area for attacks but also simplifies incident response and recovery efforts in the event of a breach.
Industries that heavily rely on IAM solutions include healthcare, finance, and government sectors, where protecting sensitive information is critical. For instance, healthcare organizations utilize IAM to comply with HIPAA regulations, ensuring that patient data is accessed only by authorized personnel. Similarly, financial institutions employ IAM to protect financial assets and ensure compliance with PCI-DSS standards. In the government sector, IAM is crucial for safeguarding national security and sensitive citizen information through strict access controls and auditing capabilities.
“The effectiveness of an organization’s security framework is often directly correlated with how well it implements identity and access management.”
Key Components of an Effective IAM Framework

An effective Identity Access Management (IAM) framework is essential for organizations looking to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance with various regulations. A well-structured IAM framework not only helps in managing user identities but also streamlines access controls across digital environments. This section discusses the vital components that contribute to a successful IAM strategy.
Essential Elements of an IAM Framework
A robust IAM framework comprises several critical elements that work together to enhance security and efficiency. These components include user identity management, policy management, access control, and continuous monitoring.
- User Identity Management: This element involves the processes for creating, maintaining, and deleting user identities within the organization. It ensures that every user has a unique identity that is regularly updated.
- Policy Management: Effective IAM frameworks require comprehensive policy management, defining who can access what resources under which conditions. This includes setting up rules for password management, data access, and compliance with regulatory standards.
- Access Control: Access control mechanisms determine how and when users can access resources. This could involve role-based access control (RBAC), attribute-based access control (ABAC), or other mechanisms to ensure users only have access to the data they need.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly monitoring user activities and access patterns is crucial for identifying potential security breaches. Continuous auditing can help organizations respond proactively to unusual behaviors.
Role of Authentication and Authorization in IAM Processes
Authentication and authorization are pivotal in any IAM framework, serving distinct yet interconnected purposes. Authentication verifies the identity of users, while authorization determines what those authenticated users are allowed to access.
“Authentication is about ensuring the person is who they say they are, whereas authorization is about what that person can do.”
Authentication methods can vary from traditional username and password combinations to more advanced techniques such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) or biometric verification. This layered approach enhances security and reduces the risk of unauthorized access. On the other hand, authorization processes should be implemented in a way that aligns user roles with access privileges, ensuring that sensitive information is safeguarded while enabling productivity.
Comparison of IAM Tools Based on Functionality and Integration Capabilities
Choosing the right IAM tool is vital for aligning with organizational needs. Below is a comparative table highlighting various IAM tools based on their functionalities and integration capabilities.
| IAM Tool | Key Functionalities | Integration Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Okta | Single Sign-On, MFA, User Provisioning | Supports integration with over 7,000 applications |
| Microsoft Azure AD | Identity Protection, Conditional Access, Self-Service Password Reset | Seamless integration with Microsoft products and third-party apps |
| Auth0 | Universal Login, Social Login, API Authorization | Flexible integration options with various frameworks and languages |
| Ping Identity | Single Sign-On, Adaptive Authentication, Identity Governance | Integrates with cloud and on-premises applications |
Challenges and Risks Associated with Identity Access Management
Implementing Identity Access Management (IAM) systems presents various challenges that organizations need to tackle if they aim for effective security and compliance. Despite the critical importance of IAM in protecting sensitive data, organizations often find themselves grappling with several hurdles that can inhibit their success.
One of the most significant challenges is the complexity of managing user identities across diverse systems and platforms. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services and mobile solutions, ensuring that IAM solutions seamlessly integrate with existing infrastructures becomes vital. Another challenge is keeping up with regulatory compliance requirements that vary by industry and geography. Organizations are often overwhelmed by the necessity to continuously monitor and adapt their IAM systems to comply with evolving laws, such as GDPR or HIPAA.
User education and awareness also play a crucial role in the effectiveness of IAM solutions. Employees may not understand the importance of using strong passwords or recognizing phishing attempts, leading to security vulnerabilities. Additionally, organizations face difficulties in the onboarding and offboarding process, where lack of streamlined procedures can lead to unauthorized access if former employees retain access privileges.
Comparison of IAM Solution Risks
The risks associated with inadequate IAM solutions are starkly contrasted with those posed by robust IAM systems. Inadequate IAM can lead to unauthorized data access, data breaches, and identity theft, resulting in financial losses, legal repercussions, and reputational damage. For instance, the 2017 Equifax breach, which exposed sensitive information of 147 million people, highlighted the severe consequences of poor IAM practices.
In contrast, a robust IAM system mitigates these risks by ensuring that only authorized users gain access to specific data, employing measures like multi-factor authentication and continuous monitoring. Organizations adopting comprehensive IAM solutions can significantly reduce potential threats, enhance regulatory compliance, and improve overall data security posture.
The consequences of identity theft and unauthorized access incidents can be catastrophic for businesses. Beyond immediate financial loss, organizations may face legal liabilities, compromised customer trust, and long-term reputational damage. According to a report by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2021 was approximately $4.24 million, showcasing the financial impact that can stem from inadequate IAM practices. Additionally, the fallout from such incidents often leads to increased scrutiny from regulators and stakeholders, further complicating recovery efforts.
Emerging Trends in Identity Access Management Technology
The landscape of Identity Access Management (IAM) is rapidly evolving, driven by innovative technologies that enhance security and streamline processes. As organizations become increasingly digital, they must adapt to new trends that not only improve user experiences but also safeguard sensitive data. This section delves into the cutting-edge advancements shaping the future of IAM, highlighting the impact of biometrics, artificial intelligence (AI), and cloud computing.
Innovative Technologies Shaping IAM
The integration of innovative technologies is revolutionizing IAM strategies across various industries. Biometrics, including fingerprint scanning, facial recognition, and iris scanning, are gaining prominence due to their ability to provide secure and convenient access methods. These technologies enhance user authentication by leveraging unique biological traits, making unauthorized access significantly more challenging.
AI is also playing a pivotal role in IAM by enabling organizations to analyze vast amounts of data for threat detection and response. Machine learning algorithms can identify unusual access patterns, flag potential security breaches, and automate responses in real-time, thus minimizing risks associated with identity theft and unauthorized access.
Impact of Cloud Computing on IAM Strategies
Cloud computing has fundamentally altered how IAM solutions are implemented. The flexibility and scalability of cloud-based IAM systems allow organizations to manage user identities and access controls from anywhere, facilitating remote work and collaboration. This transition to the cloud ensures that IAM solutions can rapidly adapt to changing business needs and regulatory requirements.
Moreover, cloud IAM solutions often come with advanced security features, including multi-factor authentication (MFA) and single sign-on (SSO), which enhance user convenience while maintaining high-security standards. As businesses increasingly migrate their operations to the cloud, IAM strategies must evolve to ensure comprehensive security across all digital assets.
Upcoming IAM Trends and Their Potential Impacts on Businesses
Several emerging trends in IAM are poised to shape the future of business operations. Understanding these trends can help organizations stay ahead of the curve and mitigate potential risks associated with identity and access management.
Here are some key trends to watch:
- Zero Trust Security: This model requires strict identity verification for every person and device trying to access resources, regardless of whether they are inside or outside the organization’s network.
- Decentralized Identity: This trend promotes user control over personal data, allowing individuals to manage their identities without relying on central authorities.
- Enhanced Privacy Regulations: As data protection laws grow stricter, businesses will need to ensure their IAM strategies comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA, focusing on transparent data practices.
- Unified Access Management: Organizations are moving towards solutions that consolidate access management across multiple platforms and applications, streamlining user experiences and administrative efforts.
- Continuous Authentication: Beyond initial login, continuous monitoring of user behavior ensures consistent verification, enhancing security throughout the user session.
These trends highlight the necessity for businesses to rethink their IAM strategies proactively. Adopting advanced technologies and staying informed on industry developments will not only enhance security but also improve operational efficiency, enabling organizations to thrive in an increasingly digital world.
Best Practices for Implementing IAM Solutions
Implementing Identity Access Management (IAM) solutions is crucial for organizations seeking to protect sensitive information and ensure compliance with regulations. The deployment of IAM systems can enhance security, streamline user access, and improve overall operational efficiency. To achieve a successful IAM implementation, it’s essential to follow best practices that have been established within the industry.
Establishing a robust IAM framework involves careful planning, user education, and continuous improvement. Organizations should focus on integrating IAM solutions seamlessly into existing systems while prioritizing user experience and security. Below are key best practices that can lead to a successful deployment of IAM solutions.
Comprehensive IAM Deployment Guide
A successful IAM deployment requires meticulous planning and execution. Here are some best practices to consider during the implementation process:
- Define Clear Objectives: Establish specific goals for your IAM deployment, such as enhancing security, improving compliance, or reducing operational costs.
- Conduct a Risk Assessment: Identify potential security risks and vulnerabilities to inform the design and implementation of your IAM system.
- Select Suitable IAM Technologies: Choose IAM tools that align with your organization’s needs and infrastructure, considering factors such as scalability and integration capabilities.
- Implement Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on user roles to streamline access management and reduce the risk of unauthorized access.
- Integrate with Existing Systems: Ensure the IAM solution works cohesively with your current IT infrastructure and applications to avoid disruption.
- Establish Strong Policies and Procedures: Develop clear policies governing user access and authentication methods to maintain security and compliance.
- Regularly Review and Update IAM Processes: Conduct periodic reviews of IAM policies and procedures to adapt to evolving security threats and organizational changes.
User Education and Training Importance
User education and training play a pivotal role in enhancing the effectiveness of IAM solutions. Effective training programs ensure that users understand the importance of security protocols and how to navigate the IAM system confidently. Implementing training initiatives can significantly reduce human errors that may compromise security.
Organizations should develop ongoing training sessions that cover topics such as password management, recognizing phishing attacks, and understanding role-based access. Regular updates and refresher courses can help reinforce best practices and keep security at the forefront of user consciousness.
“Education is the most powerful weapon which you can use to change the world.” – Nelson Mandela
Encouraging a culture of security awareness among users fosters a proactive approach to identity management, minimizing the likelihood of breaches and enhancing the overall IAM strategy.
Expert Tips for IAM Implementation
Industry experts emphasize several key tips for a successful IAM implementation. These insights can provide valuable guidance throughout the deployment process:
“Start by understanding your users, their access needs, and the data they interact with.” – IAM Specialist
“Don’t underestimate the power of automation; it can drastically reduce manual errors and enhance your security posture.” – Cybersecurity Advisor
“Regular audits and updates are essential; IAM is not a set-it-and-forget-it solution.” – IT Security Consultant
By adhering to these expert recommendations, organizations can improve their IAM strategies and ensure their systems remain secure and efficient.
The Role of IAM in Cybersecurity
Identity Access Management (IAM) is a critical component of a comprehensive cybersecurity strategy. It ensures that the right individuals have access to the right resources at the right times for the right reasons. As organizations increasingly rely on digital systems, the integration of IAM into broader cybersecurity measures becomes essential for defending against cyber threats. This integration not only streamlines access control but also enhances the overall security posture by ensuring that user identities are managed effectively and securely.
IAM systems provide various mechanisms that help mitigate the risks posed by cyber threats. By enforcing strict authentication protocols, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), IAM reduces the likelihood of unauthorized access. For instance, a financial institution that implements IAM solutions can ensure that only verified personnel can access sensitive customer data, significantly lowering the risk of data breaches. Moreover, IAM enhances visibility and control over user activities, making it easier to detect unusual behaviors that may indicate potential cyber attacks. The incorporation of role-based access control (RBAC) limits access based on user roles, further reducing the attack surface.
Critical Metrics for Assessing IAM Effectiveness
To evaluate the effectiveness of IAM within a cybersecurity strategy, it is essential to monitor several key metrics. These metrics provide insights into how well IAM is functioning and its impact on reducing cyber risks.
The following metrics are crucial for assessment:
- Authentication Success Rate: Measures the percentage of successful login attempts versus failures. A high rate suggests effective authentication processes.
- Time to Provision/Deprovision Users: Evaluates the efficiency of user account management. Faster times indicate a streamlined IAM process, which is vital for maintaining security.
- Access Review Frequency: Tracks how often access rights are reviewed to ensure they align with current user roles. Regular reviews help prevent privilege creep.
- Incident Response Time: Assesses how quickly IAM can respond to security incidents involving user access. Quicker response times indicate a robust IAM framework.
- User Activity Monitoring: Involves analyzing user actions within systems. Anomalies in behavior can signal potential security threats.
Implementing these metrics allows organizations to pinpoint weaknesses and enhance their IAM systems, ultimately leading to a more secure environment.
IAM not only safeguards sensitive data but also plays a pivotal role in maintaining compliance with various regulations, ensuring that organizations meet their security obligations.
Identity Access Management and User Experience
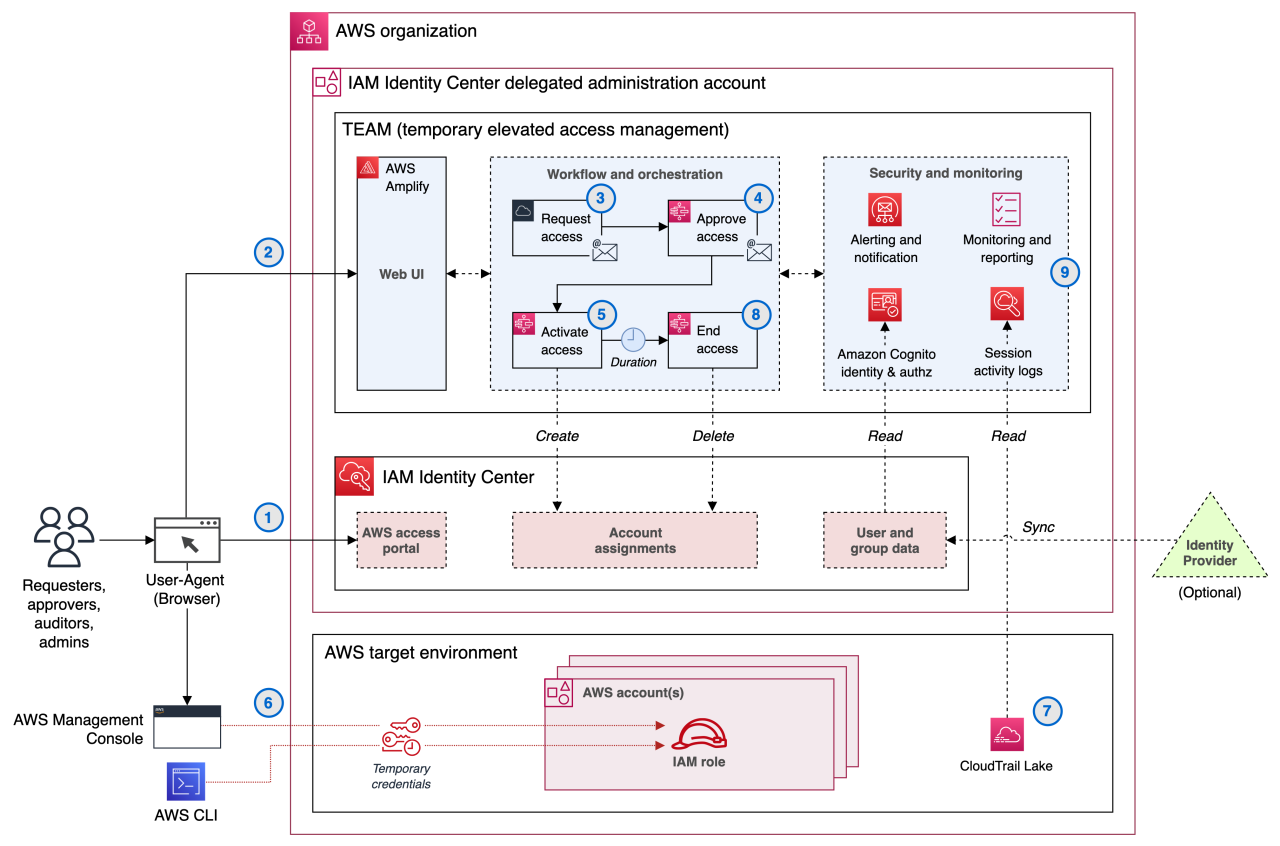
In the realm of digital security, Identity Access Management (IAM) plays a pivotal role in ensuring that users have the right access to resources while maintaining robust security protocols. However, the challenge lies in striking the perfect balance between stringent security measures and providing a seamless user experience. As organizations increasingly adopt IAM solutions, understanding this balance becomes crucial in enhancing both security and accessibility.
The integration of user-centric design principles into IAM solutions can significantly enhance user experience without undermining security. By prioritizing the needs and preferences of end-users, organizations can develop IAM systems that are not only secure but also intuitive and easy to navigate. This approach encourages user engagement and compliance, ultimately leading to a more secure environment.
Balancing Security and Accessibility
Finding the right equilibrium between security and user accessibility is essential for successful IAM implementations. Security measures, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA) and stringent password policies, can sometimes hinder users’ ease of access. To mitigate this, organizations can adopt the following strategies:
- Implementing Single Sign-On (SSO): This method allows users to access multiple applications with one set of credentials, streamlining the user experience while maintaining security.
- Using adaptive authentication: This approach assesses risk factors, such as the user’s location or device, to apply different authentication measures based on the perceived threat level, thus minimizing unnecessary friction for low-risk access.
- Incorporating self-service password reset features: Allowing users to reset their passwords independently not only enhances user experience but also reduces the burden on IT support teams.
User-Centric Design Enhancements
User-centric design focuses on creating IAM systems that are tailored to the needs and behaviors of users. By employing this design philosophy, organizations can enhance the usability of IAM solutions while ensuring security protocols are upheld. Key enhancements include:
- Streamlined user interfaces: Simplifying navigation and reducing clutter in IAM portals can significantly improve user satisfaction and efficiency.
- Personalized user journeys: Allowing users to customize their experience based on preferences can encourage engagement and reduce frustration.
- Clear communication of security processes: Transparently explaining why certain security measures are in place helps users understand their importance, fostering compliance and minimizing pushback.
Successful IAM Implementations
Several organizations have successfully implemented IAM solutions that improved user experience while maintaining robust security. Notable examples include:
- A major financial institution adopted SSO, allowing users to access various banking services seamlessly. This not only reduced password fatigue but also improved overall user satisfaction.
- A leading technology firm implemented adaptive authentication that adjusted security measures based on user context, resulting in increased user confidence and a reduction in helpdesk calls related to access issues.
- A healthcare provider introduced a self-service password reset tool, reducing the time spent on password-related inquiries by 40%, thus allowing IT staff to focus on more critical tasks.
“User-centric design in IAM not only enhances usability but also strengthens adherence to security policies.”
Closing Notes
In summary, Identity Access Management (IAM) stands at the forefront of cybersecurity strategies, ensuring organizations remain secure while facilitating user access. By understanding its components, challenges, and emerging trends, businesses can effectively implement IAM solutions that enhance security posture and user experience. As the digital landscape evolves, staying informed about IAM practices will be crucial for all enterprises aiming to protect their assets and comply with regulatory standards.
FAQ Resource
What is Identity Access Management (IAM)?
Identity Access Management (IAM) is a framework that manages digital identities and controls user access to resources within an organization.
Why is IAM important for businesses?
IAM is crucial for protecting sensitive information, ensuring regulatory compliance, and minimizing the risk of data breaches.
How does IAM support regulatory compliance?
IAM helps businesses comply with regulations by ensuring that access is granted based on established policies and that user activities are monitored and audited.
What technologies are commonly used in IAM?
Common IAM technologies include single sign-on (SSO), multi-factor authentication (MFA), and identity governance tools.
How can organizations improve their IAM systems?
Organizations can enhance their IAM systems by implementing best practices such as regular training, adopting new technologies, and conducting frequent security assessments.