Cyber Threat Intelligence serves as a crucial pillar in the modern cybersecurity landscape, equipping organizations with the insights needed to anticipate and mitigate potential threats. This discipline not only involves the collection and analysis of data regarding existing and emerging threats but also emphasizes the importance of understanding the motivations and tactics of cyber adversaries. By leveraging various types of intelligence—strategic, tactical, operational, and technical—businesses can enhance their threat detection capabilities and bolster their overall security posture.
The ever-evolving nature of cyber threats necessitates that organizations remain agile and informed. With a wealth of methodologies at their disposal, including the utilization of open-source intelligence and insights from the dark web, businesses can gather actionable intelligence that empowers them to proactively defend against cyber incidents. This ongoing process of monitoring and analysis is vital for maintaining resilience in an increasingly complex digital environment.
Cyber Threat Intelligence Defined
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) is the process of gathering, analyzing, and disseminating information regarding existing or emerging threats targeting an organization. By understanding the potential dangers posed by cyber adversaries, organizations can better prepare their defenses and respond proactively to prevent breaches or mitigate damage. The importance of CTI in cybersecurity cannot be overstated; it acts as a cornerstone for risk management strategies, allowing organizations to make informed decisions based on current threat landscapes. This intelligence aids in identifying vulnerabilities, improving response protocols, and enabling strategic planning to protect critical assets.
The relationship between cyber threat intelligence and threat detection is pivotal in the realm of cybersecurity. CTI enhances threat detection capabilities by providing contextual information about threat actors, their methodologies, and the tools they use. This enriched understanding allows security teams to recognize patterns and anomalies that may indicate a cyber-attack. For instance, if an organization is aware of an impending attack involving specific malware, its security systems can be configured to monitor for signs of that particular threat, leading to a quicker detection time. Moreover, the integration of CTI into security operations centers (SOCs) enables a more proactive stance on cybersecurity, as real-time intelligence feeds can guide the monitoring of system activity and alerts on suspicious behavior. This synergy reduces the dwell time of attackers within a network, ultimately limiting damage and enhancing the organization’s overall security posture.
Types of Cyber Threat Intelligence
Understanding the various types of cyber threat intelligence is crucial for tailoring security measures to the specific needs of an organization. The primary categories of CTI include strategic, tactical, operational, and technical intelligence. Each type serves a distinct purpose within an organization’s cybersecurity framework.
- Strategic Intelligence: This type provides high-level insights aimed at influencing decision-making within an organization. It often includes analysis of long-term trends, motivations of threat actors, and emerging threats across industries. For example, reports on geopolitical tensions can inform organizations about potential cyber risks associated with political instability.
- Tactical Intelligence: Tactical intelligence focuses on the specific techniques and tactics employed by threat actors. This type of intelligence helps security teams understand how attacks are executed and what defensive measures can be adopted to counteract them. For instance, insights into phishing techniques can lead to enhanced email security protocols.
- Operational Intelligence: This type bridges tactical and strategic intelligence, providing context about specific campaigns or incidents. It assists organizations in understanding the operational patterns of adversaries, such as the timing and methods of attacks, which can inform real-time defense strategies. An example could be a detailed analysis of a recent ransomware attack and its implications for similar organizations.
- Technical Intelligence: This encompasses in-depth information regarding specific threat indicators, such as IP addresses, domain names, and malware hashes. This type of intelligence is essential for technical teams and security tools to identify and mitigate threats quickly and effectively. For example, having a list of known malicious IPs can help organizations block access to potential attack vectors.
The Process of Gathering Cyber Threat Intelligence
The collection of cyber threat intelligence is a vital component for organizations aiming to bolster their security posture against evolving threats. This multifaceted process involves various methodologies and tools designed to gather relevant data for analysis. Understanding the nuances of these methodologies is essential for effective intelligence gathering.
Methodologies for Collecting Cyber Threat Intelligence
The methodologies employed in gathering cyber threat intelligence can be categorized broadly into two domains: open-source intelligence (OSINT) and dark web intelligence. Each of these domains plays a critical role in providing comprehensive insights into cyber threats.
Open-source intelligence refers to the collection and analysis of information that is publicly available. This includes data from various sources such as social media platforms, news articles, forums, and specialized threat intelligence platforms. The importance of OSINT lies in its ability to provide early warnings of potential cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Organizations can leverage tools like Maltego, Shodan, and OSINT frameworks to gather and analyze this data effectively. The information collected can help identify emerging threats and assess their relevance to the organization’s specific environment.
Dark web intelligence, on the other hand, involves probing into the hidden parts of the internet where illicit activities and cybercriminal discussions take place. This domain is crucial for organizations aiming to understand the tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) of cyber adversaries. Tools such as DarkOwl, Recorded Future, and IntSights are commonly used to monitor the dark web for stolen data, malware, and discussions among threat actors. The insights gained from analyzing dark web activities can be instrumental in proactively defending against cyber threats.
Both OSINT and dark web intelligence provide a well-rounded view of the threat landscape. By integrating findings from both domains, organizations can enhance their situational awareness and make informed decisions regarding their security strategies. The combination of these methodologies ensures that organizations are not only reactive but also proactive in their approach to cyber threat management.
Tools and Technologies for Data Collection
To effectively gather and process cybersecurity data, organizations utilize a variety of tools and technologies. The choice of tools often depends on the specific requirements of the intelligence gathering process. Key tools include:
1. Threat Intelligence Platforms (TIPs): These platforms aggregate threat data from multiple sources, facilitating streamlined analysis and dissemination. Examples include Anomali and ThreatConnect.
2. Web Scraping Tools: Tools like Scrapy and Beautiful Soup are employed to extract data from various web sources, particularly in the OSINT realm.
3. Data Visualization Tools: Visualizing data through platforms such as Tableau and Power BI helps analysts identify patterns and trends within the gathered intelligence.
4. Machine Learning Algorithms: Leveraging machine learning can enhance the analysis of large datasets, allowing for the identification of previously unnoticed threats.
By utilizing these tools and methodologies, organizations can create a robust framework for gathering cyber threat intelligence, enhancing their ability to respond effectively to cyber threats.
Key Sources of Cyber Threat Intelligence
Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) plays a crucial role in enhancing an organization’s security posture by providing insights into potential threats. Understanding the primary sources of CTI helps in foreseeing, mitigating, and responding to cyber threats effectively. The landscape of CTI is diverse, encompassing various sources that can be leveraged for comprehensive threat analysis.
Primary Sources of Cyber Threat Intelligence
The primary sources of cyber threat intelligence are vital for organizations looking to build robust defenses against cyber threats. These sources include threat feeds, security research, and community forums, each serving a unique purpose in the CTI ecosystem.
- Threat Feeds: These are streams of data comprising indicators of compromise (IoCs), tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used by cyber adversaries. Threat feeds can be sourced from various organizations and are crucial for real-time threat monitoring. Examples include commercial feeds from companies like Recorded Future and open-source feeds such as the Malware Information Sharing Platform (MISP).
- Security Research: Research papers, blogs, and reports published by security experts and organizations provide in-depth analyses of emerging threats and vulnerabilities. Reports from entities like the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) and the MITRE ATT&CK framework are excellent sources for understanding the latest trends in cyber threats.
- Community Forums: Cybersecurity practitioners often share insights, experiences, and knowledge through community forums and platforms like Reddit, Stack Exchange, and specialized cybersecurity forums. These platforms foster collaboration and provide informal intelligence on potential threats and vulnerabilities.
Significance of Collaboration Among Organizations
Collaboration among organizations in sharing threat intelligence is instrumental in creating a more resilient cybersecurity environment. When organizations share their insights on threats, it results in a collective understanding and faster response to incidents. This collaborative approach is crucial in combating sophisticated cyber threats that often target multiple organizations simultaneously.
Organizations can benefit from shared intelligence by identifying patterns and trends that may not be visible when analyzing data in isolation. For instance, the Information Sharing and Analysis Centers (ISACs) play a pivotal role in facilitating this collaboration across various sectors, enabling members to share threat information and best practices.
“The more we share, the stronger we become.”
This principle underscores the importance of collective defense strategies in cybersecurity. By pooling resources and knowledge, organizations can better prioritize their defenses and respond more effectively to emerging threats. Notable examples of platforms that promote collaboration include the Cyber Threat Alliance and the FS-ISAC, which provide frameworks for sharing threat intelligence across industries.
In conclusion, leveraging these key sources of cyber threat intelligence and fostering collaboration is essential for organizations aiming to safeguard their assets against the evolving cyber threat landscape.
The Role of Cyber Threat Intelligence in Incident Response

Cyber threat intelligence (CTI) plays a crucial role in enhancing incident response capabilities for organizations. By gathering and analyzing information about potential and existing threats, CTI enables organizations to proactively prepare for, detect, respond to, and recover from cyber incidents. The integration of intelligence into incident response processes not only improves decision-making but also helps in minimizing damage and ensuring rapid recovery.
Integrating cyber threat intelligence into the incident response framework involves several essential steps that organizations must follow to optimize their response capabilities. These steps create a structured approach to effectively utilize intelligence in incident management.
Steps for Integrating Intelligence into Incident Response Framework
To successfully integrate cyber threat intelligence into an incident response framework, organizations should consider the following steps:
1. Define Objectives: Clearly Artikel the goals of integrating CTI into the incident response process. These objectives should align with the organization’s overall security posture and business goals.
2. Identify Relevant Intelligence Sources: Determine which sources of threat intelligence will be most beneficial. This can include open-source intelligence, commercial threat feeds, and internal data from previous incidents.
3. Establish Information Flow: Create a streamlined process for collecting, analyzing, and disseminating threat intelligence. Ensure that the right stakeholders have access to the information they need in a timely manner.
4. Train Incident Response Teams: Conduct regular training sessions to ensure that incident responders understand how to utilize threat intelligence effectively. Scenarios and simulations can help reinforce this knowledge.
5. Integrate Tools and Technologies: Leverage security tools that support threat intelligence integration, such as SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems and threat intelligence platforms.
6. Develop Playbooks: Create incident response playbooks that reference specific threat intelligence. These should include indicators of compromise, attack vectors, and suggested response actions based on intelligence gathered.
7. Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of the integration process. Evaluate how well the threat intelligence is being used in real incidents and adjust strategies as necessary.
Creating a response plan that incorporates relevant cyber threat intelligence involves a clear understanding of the types of threats the organization may face. The response plan should include the following components:
– Threat Modeling: Analyze and categorize potential threats specific to the organization’s environment.
– Incident Classification: Define different types of incidents based on severity and impact, allowing for prioritized responses.
– Response Actions: List specific actions to be taken for each type of incident, guided by intelligence insights.
– Recovery Strategies: Develop strategies for restoring services and data after an incident, ensuring they are informed by the lessons learned from previous incidents.
By utilizing cyber threat intelligence effectively, organizations can enhance their incident response plans, ensuring that they are prepared to face the evolving threat landscape with confidence.
Challenges in Cyber Threat Intelligence
Implementing effective cyber threat intelligence (CTI) practices is not without its challenges. Organizations often face various obstacles that can hinder their ability to maintain robust cybersecurity measures. From resource limitations to the complexities of data analysis, these challenges can significantly impact the effectiveness of CTI initiatives, making it crucial for businesses to understand and address them.
One of the prominent issues organizations encounter is the prevalence of false positives and inaccurate threat data. False positives can lead to unnecessary alarm, causing cybersecurity teams to expend valuable resources investigating non-threats while potentially overlooking critical real threats. The implications of false positives are significant: they can disrupt normal business operations, diminish team morale, and erode trust in the security systems in place. Inaccurate threat data can result in misguided strategies that fail to address actual vulnerabilities, exposing organizations to greater risks. For example, if a company believes it is under attack from a specific threat actor based on flawed intelligence, it may invest time and money in defensive measures that do not align with the real threat landscape. This misallocation of resources can have severe financial and reputational consequences.
Impact of Information Overload on Cybersecurity Teams
In today’s digital landscape, cybersecurity teams are inundated with vast amounts of threat data from various sources. This information overload can overwhelm personnel, making it difficult to discern actionable intelligence from noise. As teams grapple with excessive data, the risk of missing critical alerts increases.
To effectively manage information overload, organizations can adopt several strategies:
- Utilizing automation tools to filter and prioritize threats, allowing teams to focus on the most pertinent information.
- Implementing a centralized threat intelligence platform that aggregates data from multiple sources, providing a more cohesive view of the threat landscape.
- Encouraging collaboration among teams to share insights and streamline responses to threats, reducing individual workloads.
“Effective threat intelligence is not just about collecting data, but about transforming it into actionable insights.”
By addressing these challenges, organizations can improve their CTI practices, leading to a more resilient cybersecurity posture and better protection against evolving threats.
Future Trends in Cyber Threat Intelligence
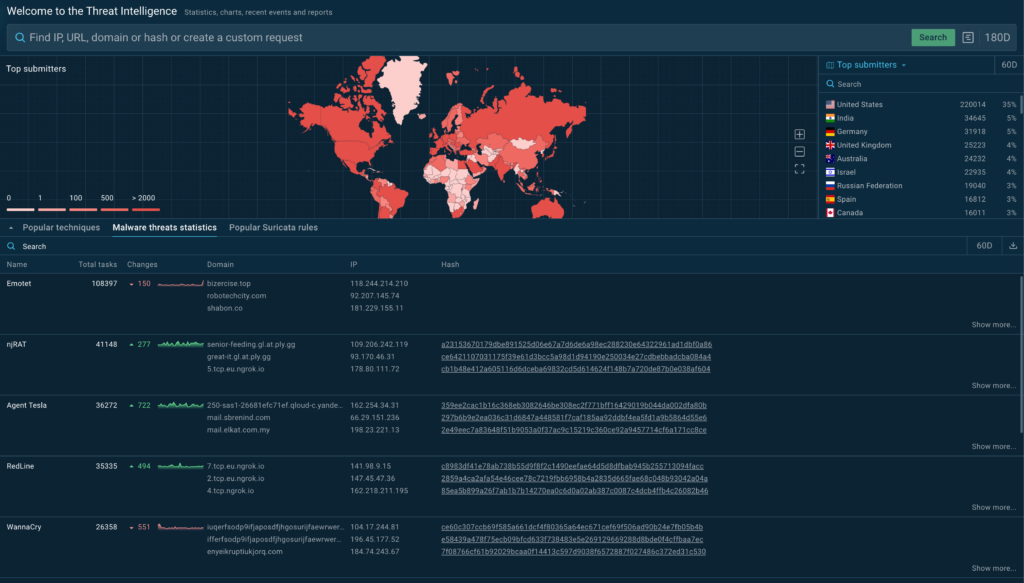
As the digital landscape evolves, so too does the complexity of cyber threats. Organizations must stay one step ahead to safeguard their assets and information. Future trends in cyber threat intelligence are rapidly emerging, driven by technological advancements and the increasing sophistication of cybercriminals. Understanding these trends is crucial for developing robust cybersecurity strategies that can adapt to dynamic threat environments.
Emerging Trends in Cyber Threat Intelligence
The landscape of cyber threat intelligence is undergoing significant changes, influenced by various emerging trends that are reshaping cybersecurity strategies. Notable trends include the rise of collaborative threat intelligence sharing, the increasing use of automation in threat detection, and the incorporation of real-time data analytics. These trends enable organizations to enhance their security posture by allowing for more timely and informed decision-making.
One of the most impactful developments in cyber threat intelligence is the role of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). These technologies are transforming how organizations analyze threats and respond to incidents. By leveraging AI and ML, businesses can automate the processing of vast amounts of security data, identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate malicious activity.
The integration of AI and ML into threat intelligence provides several benefits:
- Enhanced Detection Capabilities: AI algorithms can detect previously unseen threats by analyzing behavior patterns, making it easier to identify zero-day vulnerabilities.
- Automated Incident Response: Machine learning systems can trigger automated responses to certain types of incidents, significantly reducing response times and minimizing damage.
- Predictive Analytics: By analyzing historical data, AI can help predict future attack vectors, allowing organizations to proactively strengthen defenses.
Organizations need to prepare for future cyber threats through proactive intelligence gathering and analysis. This involves establishing a culture of continuous monitoring and investing in advanced threat intelligence platforms. Collaborating with other entities, such as government agencies and industry peers, can enhance information exchange, enabling quicker identification of emerging threats. Additionally, training employees on the latest threat trends and fostering an awareness culture will further strengthen an organization’s defensive capabilities.
In summary, the future of cyber threat intelligence is set to be influenced by advancements in AI and ML, along with collaborative efforts in threat sharing. Organizations that embrace these trends will be better positioned to mitigate risks and protect their critical assets effectively. Understanding and implementing these strategies will be essential as cyber threats continue to evolve.
Last Word
In conclusion, Cyber Threat Intelligence is not merely about understanding threats, but rather about transforming that understanding into actionable strategies that enhance organizational resilience. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the importance of effective threat intelligence practices cannot be overstated. By embracing collaboration, leveraging advanced technologies like artificial intelligence, and staying ahead of emerging trends, organizations can effectively equip themselves for the challenges of tomorrow’s cyber landscape.
Top FAQs
What is the main goal of Cyber Threat Intelligence?
The main goal is to provide actionable insights that help organizations anticipate, prepare for, and respond to cyber threats effectively.
How does Cyber Threat Intelligence benefit incident response?
It enhances incident response by providing critical information that informs decision-making, enabling quicker and more effective responses to incidents.
What types of intelligence are most commonly used?
The four primary types are strategic, tactical, operational, and technical intelligence, each serving different purposes within cybersecurity.
What challenges do organizations face in implementing Cyber Threat Intelligence?
Common challenges include managing false positives, dealing with information overload, and ensuring collaboration among teams.
How can organizations prepare for future cyber threats?
Proactive intelligence gathering and analysis, coupled with a focus on emerging trends, can significantly improve preparedness for future threats.