Delving into Application Programming Interface (API) reveals a fundamental aspect of modern software development that connects systems and enhances functionality. APIs serve as bridges, allowing disparate applications to communicate seamlessly, share data, and access services. They play a crucial role in enabling innovation and efficiency across various industries, simplifying complex processes, and enhancing user experiences.
In today’s digital landscape, the significance of APIs cannot be overstated. They empower developers to integrate third-party services, leverage cloud capabilities, and build scalable applications. By understanding the core concepts of APIs, one can appreciate how they facilitate collaboration and drive technological advancement, making them essential tools in the evolving tech ecosystem.
Understanding the Core Concepts of Application Programming Interfaces
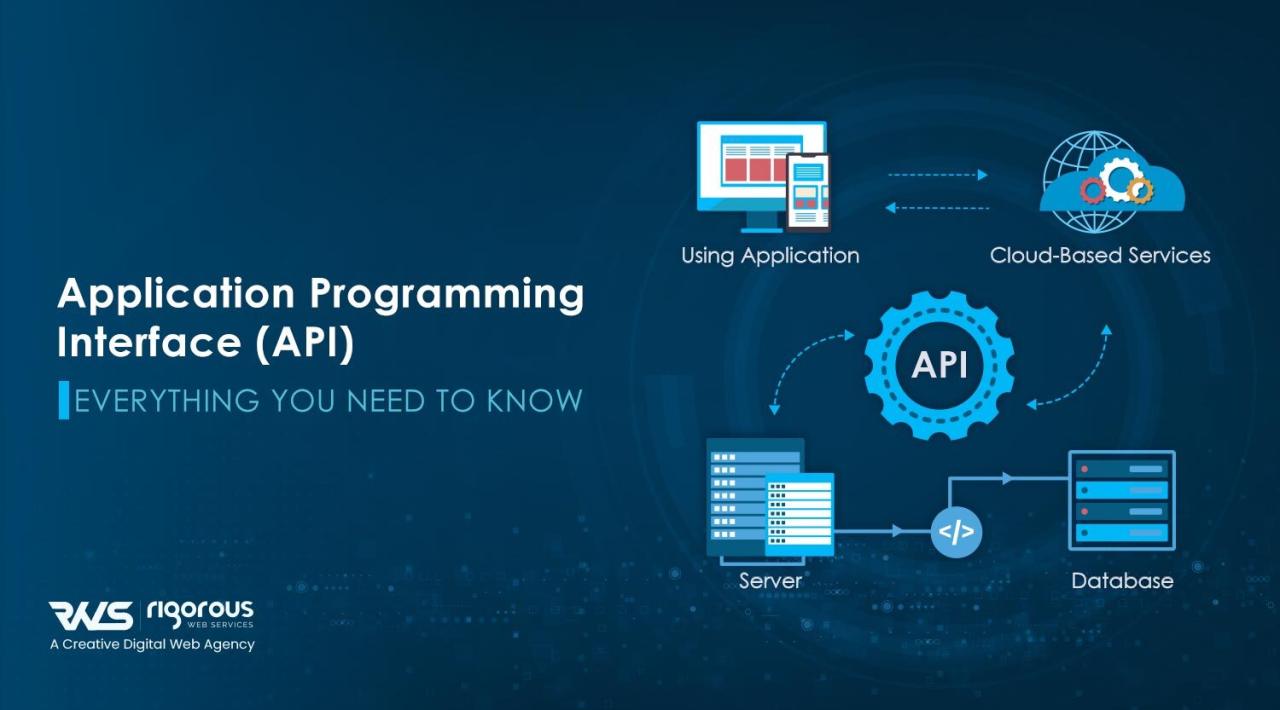
APIs, or Application Programming Interfaces, serve as critical building blocks in modern software development, allowing different software applications to communicate and share data seamlessly. In essence, an API is a set of rules and protocols for building and interacting with software applications. They enable developers to leverage existing functionalities of another application or service, thus streamlining the development process and fostering innovation. For instance, when using a travel booking application, the integration of APIs allows users to search for flights, book hotels, and compare prices, all in real-time, without needing to build those functionalities from scratch.
APIs can be categorized into various types based on their accessibility and use cases. The main types include:
Types of APIs
Understanding the types of APIs helps clarify their diverse applications and functionalities in the tech ecosystem.
- Open APIs (Public APIs): These are accessible to external developers and are designed to encourage third-party applications. A prime example is the Twitter API, which allows developers to pull tweets or post updates programmatically.
- Partner APIs: These are shared with specific business partners and require authentication for access. An example would be the Facebook Marketing API, which allows advertisers to access marketing data and manage ads.
- Internal APIs (Private APIs): Used within an organization, these APIs facilitate communication between internal systems. For instance, a company may use an internal API to connect its customer relationship management (CRM) system with its sales platform.
- Composite APIs: These allow developers to access multiple endpoints in one call. For example, a composite API could retrieve user information, purchase history, and product recommendations from a single request.
Key components that make up an API play essential roles in ensuring effective communication between applications. These components include endpoints, methods, and data formats.
Key Components of APIs
The understanding of API components is vital for developers aiming to utilize or create APIs efficiently.
- Endpoints: These are specific URLs that represent a resource or a service within the API. Each endpoint is a point of interaction for users or applications.
- Methods: These represent the actions that can be performed on the endpoints, such as GET (retrieve data), POST (submit data), PUT (update data), and DELETE (remove data).
- Data Formats: APIs commonly use data formats like JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) or XML (Extensible Markup Language) for data exchange. JSON is favored for its simplicity and ease of integration.
- Authentication: This component ensures that only authorized users can access the API. Common methods include API keys, OAuth tokens, and JWT (JSON Web Tokens).
APIs not only save development time but also enhance the functionality and scope of applications by allowing seamless integration of various services.
The Role of APIs in Modern Software Development
In the rapidly evolving landscape of software development, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) have become a cornerstone for creating versatile, integrated, and efficient applications. They allow different software systems to communicate and share data seamlessly, paving the way for innovation and enhanced user experiences. Their significance extends beyond mere connectivity; APIs enable developers to build scalable and modular applications that can adapt to changing demands and integrate with new technologies easily.
APIs facilitate integration between different software applications by providing a standardized set of rules and protocols for interaction. This standardization allows diverse systems, regardless of their underlying technologies, to work together harmoniously. When a developer creates an application, they often need to incorporate functionalities that go beyond their own coding capabilities. For example, instead of building a payment processing system from scratch, developers can use APIs from established services like Stripe or PayPal. This not only saves time but also leverages the security, reliability, and expertise of these specialized services.
The following points illustrate the critical role APIs play in integration:
- Interoperability: APIs enable disparate systems to communicate effectively, allowing data exchange and functionality sharing.
- Reduced Development Time: By utilizing APIs, developers can focus on their application’s core features rather than reinventing the wheel.
- Access to Advanced Features: APIs provide access to sophisticated technologies, such as machine learning algorithms and cloud services, allowing developers to integrate features without deep expertise in those areas.
- Data Accessibility: With APIs, applications can retrieve and manipulate data from various sources, fostering a rich, dynamic user experience.
The significance of APIs also lies in their ability to promote software scalability and modularity. Scalability refers to the application’s ability to handle increased loads without compromising performance. APIs support this by allowing developers to build applications in a modular fashion. Each module can function independently, communicating with other modules through APIs. As user demand grows, developers can enhance specific modules without overhauling the entire system.
The following points highlight how APIs contribute to scalability and modularity:
- Modular Architecture: APIs allow applications to be broken down into smaller, manageable components, making it easier to update and scale specific areas.
- Load Balancing: APIs facilitate load distribution across different servers or services, enhancing performance during peak usage.
- Incremental Upgrades: Developers can upgrade or replace individual components of an application without disrupting the entire system.
- Cloud Integration: APIs enable seamless integration with cloud services, allowing applications to scale resources on-demand as traffic fluctuates.
Real-world applications that rely heavily on APIs include platforms like Google Maps, which provides location services to countless apps, and social media platforms like Facebook, which enable login functionality and content sharing across various websites. Another example is Amazon Web Services (AWS), where businesses utilize APIs to manage cloud resources, facilitating everything from data storage to machine learning applications. These examples underscore the transformative power of APIs, illustrating their essential role in modern software development and their ability to foster innovation and connectivity in the tech world.
API Design Principles and Best Practices
In the world of software development, API design is a critical aspect that influences the usability, scalability, and maintainability of applications. A well-designed API serves as a bridge between different software systems, enabling them to communicate effectively. Adhering to certain principles and best practices during the design phase can lead to robust and user-friendly APIs.
One fundamental principle in API design is simplicity. An API should be straightforward, allowing developers to understand how to use it without extensive documentation. A clean and intuitive interface encourages adoption and reduces the learning curve. Additionally, consistency is crucial; similar operations should follow a similar pattern in naming conventions, data formats, and response structures, making it easier for developers to predict behaviors.
Comparative Analysis of RESTful APIs and SOAP APIs
Understanding the differences between RESTful APIs and SOAP APIs is essential for selecting the appropriate type for a specific use case. Here’s a comparative table that highlights their key differences:
| Feature | RESTful APIs | SOAP APIs |
|---|---|---|
| Protocol | HTTP/HTTPS | HTTP, SMTP, TCP, etc. |
| Data Format | JSON, XML, HTML | XML only |
| Statefulness | Stateless | Can be stateful or stateless |
| Security | Less secure (depends on HTTPS) | Built-in security features (WS-Security) |
| Use Cases | Web services, mobile applications | Enterprise-level applications requiring ACID compliance |
This comparison illustrates that RESTful APIs are often preferred for web and mobile applications due to their flexibility and ease of use, while SOAP APIs are favored in enterprise contexts where reliability and security are paramount.
Importance of Documentation and Versioning in API Management
Comprehensive documentation is vital for the success of any API, providing developers with the necessary resources to understand how to implement and utilize the API effectively. Good documentation should include clear descriptions of endpoints, request/response examples, and error codes. An illustrative diagram of the API architecture can further enhance comprehension by visually representing how various components interact.
Versioning is equally important, as it allows developers to introduce new features or make changes without disrupting existing integrations. By implementing a clear versioning strategy, such as using URL versioning (e.g., /v1/resource), developers can maintain backward compatibility and ensure that users can transition to newer versions at their own pace.
“Proper documentation and versioning are the cornerstones of successful API management, paving the way for seamless integration and long-term usability.”
Security Considerations in API Development
APIs play a crucial role in modern applications, enabling seamless interaction between different software systems. However, with their growing significance comes an array of security risks that developers must address to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data. Understanding these security threats is vital for creating robust API frameworks that can withstand malicious attacks.
APIs are increasingly becoming prime targets for cybercriminals due to their accessibility and the sensitive information they often handle. Common security threats associated with APIs include:
– Injection Attacks: This involves attackers inserting malicious code or commands into the API to manipulate its behavior. SQL injection is a prevalent form of this threat, where attackers exploit vulnerabilities in input fields to gain unauthorized access to databases.
– Authentication Vulnerabilities: Weak authentication mechanisms can lead to unauthorized access. Attackers may exploit poorly implemented token management or inadequate verification processes to impersonate legitimate users.
– Data Exposure: APIs that do not properly manage permissions may expose sensitive data. This can happen if endpoints inadvertently allow access to restricted information without appropriate user validation.
– Denial of Service (DoS): Attackers can overwhelm an API with traffic, leading to service unavailability. This type of attack can disrupt services, causing financial losses and reputational damage.
To mitigate these security threats, adopting best practices for API security is essential. Here are some important recommendations:
– Implement Strong Authentication and Authorization: Use OAuth 2.0 or similar protocols to ensure that access tokens are securely managed and validated.
– Use HTTPS: Always encrypt data in transit using HTTPS to protect against man-in-the-middle attacks.
– Validate Input: Implement stringent validation for all input parameters to prevent injection attacks. Ensure that only expected data formats are accepted.
– Rate Limiting: Implement rate limiting to prevent DoS attacks by controlling the number of requests a user can make in a given timeframe.
– Logging and Monitoring: Maintain detailed logs of API access and monitor them for unusual patterns that may indicate a security breach.
Data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA significantly impact API design and implementation. Developers must ensure that APIs comply with these regulations by incorporating data protection measures, such as:
– Data Minimization: Only collect and process data that is necessary for the intended purpose, thereby reducing exposure.
– User Consent: Ensure that explicit user consent is obtained for data collection and processing activities.
– Access Controls: Implement robust access controls to restrict data access based on user roles, ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized users.
By addressing these security considerations, developers can enhance the resilience of their APIs against potential threats while ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
The Future of APIs in the Tech Ecosystem
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) are becoming increasingly integral to the tech ecosystem. They serve as the backbone for seamless interactions between systems, enabling businesses to adapt and innovate. The future of APIs is being shaped by various trends that promise to redefine how applications communicate, ultimately enhancing the user experience and driving efficiency across industries.
The growing integration of emerging technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) is significantly influencing API development. These technologies are not only enhancing the functionality and capabilities of APIs but also paving the way for new and innovative approaches to data exchange and system interaction. The rise of AI, in particular, is leading to the creation of smarter APIs that can learn from user interactions, optimize performance, and even automate processes. Concurrently, IoT devices, which generate massive amounts of data, necessitate APIs that are capable of handling real-time data streams and ensuring secure communication among diverse devices.
Emerging Trends in API Development
Several key trends are shaping the future of API development, reflecting the changing landscape of technology and business needs. Understanding these trends can help organizations prepare for the future and harness the full potential of APIs.
- Microservices and API-First Architecture: Companies are increasingly adopting microservices architecture where applications are built as a collection of small services, each with its own API. This approach allows for greater flexibility, scalability, and easier maintenance.
- GraphQL Adoption: GraphQL is emerging as a powerful alternative to traditional REST APIs, allowing clients to request only the data they need. This reduces over-fetching and under-fetching of data, improving efficiency and performance.
- API Security Enhancements: With growing concerns over data breaches, organizations are prioritizing API security. This includes implementing standards like OAuth and OpenID Connect, along with advanced techniques such as API gateways and threat detection.
- Low-Code and No-Code Development: The rise of low-code and no-code platforms is allowing non-technical users to create and manage APIs. This democratizes API development, enabling faster innovation and reducing dependency on specialized technical skills.
- API Monetization Strategies: Businesses are recognizing the value of APIs as revenue-generating assets. Companies like Twilio and Stripe have successfully implemented monetization strategies, offering APIs that provide services such as messaging and payment processing.
APIs are becoming a vital part of business strategies, with companies leveraging them to create competitive advantages. For example, retail giants like Amazon and Walmart utilize their APIs to integrate various services, enhancing customer experiences through personalized recommendations and streamlined order processing. Similarly, financial institutions are adopting APIs to facilitate secure transactions and improve customer service through seamless integration with third-party applications, thus adapting to the fast-paced digital landscape.
In conclusion, as AI, IoT, and other emerging technologies continue to advance, APIs will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in determining the future landscape of technology, enabling businesses to innovate and thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
Tools and Technologies for API Development
API development hinges on a variety of tools and technologies that streamline the process and enhance the quality of the final product. As APIs become increasingly integral to modern software architecture, selecting the right tools is essential for efficient development, robust testing, and seamless deployment. This section explores various tools available for API testing and development, compares API management platforms, and discusses the significant role of API gateways in improving performance and security.
API Testing and Development Tools
Numerous tools are available for API testing and development, providing developers with capabilities to ensure their APIs function correctly and securely. Here are some notable examples:
- Postman: A widely used tool for API testing, Postman offers a user-friendly interface, allowing developers to send requests, analyze responses, and automate tests. It supports various types of APIs, including REST and GraphQL.
- Swagger: Known for its OpenAPI Specification, Swagger aids in designing, building, and documenting APIs. Its user interface helps visualize API endpoints and parameters, making it easier to collaborate with teams.
- Insomnia: A powerful REST client, Insomnia is favored for its simplicity and ease of use, allowing developers to manage HTTP requests and responses efficiently. It also supports GraphQL queries.
- JMeter: This open-source performance testing tool is used to load test APIs. JMeter can simulate multiple users, providing insight into how an API performs under stress.
- SoapUI: Tailored for SOAP APIs, SoapUI also supports REST APIs. It provides advanced testing features such as functional testing, security testing, and load testing.
The above tools play a crucial role in ensuring that APIs are not only functional but also reliable and secure.
Comparison of API Management Platforms
Various API management platforms offer distinct features that cater to different needs. Below is a comparison table highlighting key aspects of popular API management solutions:
| Platform | Key Features | Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Apigee | API analytics, traffic management, security policies, developer portal | Starts at $500/month |
| Kong | Plugin architecture, load balancing, API gateway, open-source | Free for community version; enterprise pricing available |
| AWS API Gateway | Integrated with AWS services, auto-scaling, pay-as-you-go pricing | Free tier available; usage-based pricing |
| MuleSoft Anypoint Platform | Integration capabilities, monitoring, API designer, governance | $1,000/month |
| Azure API Management | Multi-cloud support, built-in security, API versioning | Starts at $0; various tiers available |
This comparison illustrates how each platform caters to different needs, from basic API management to enterprise-level integration and analytics.
Role of API Gateways in Performance and Security
API gateways serve as vital components in API architecture, acting as intermediaries between clients and backend services. They enhance performance and security through several mechanisms.
API gateways manage traffic effectively by implementing load balancing and rate limiting, ensuring that backend services are not overwhelmed. Additionally, they can cache responses, which significantly improves the response time for frequent requests.
Security is another fundamental aspect of API gateways. They enforce authentication and authorization processes, ensuring that only legitimate users access the API. Moreover, they can provide threat protection through mechanisms like request validation and traffic filtering, safeguarding against common attacks such as SQL injection and DDoS attacks.
In summary, tools and technologies are essential for API development, enhancing testing, management, and security, which collectively contribute to building robust and scalable APIs.
Case Studies of Successful API Implementations
![What An Application Programming Interface API Is [2024] | Nexcess What An Application Programming Interface API Is [2024] | Nexcess](https://freyablog.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/kg7jeue1w3.jpg)
The transformative world of Application Programming Interfaces (APIs) has led many companies to innovate their service offerings and improve their operational efficiencies. By integrating APIs into their infrastructure, businesses have not only streamlined their processes but also enhanced user experiences. Below, we delve into specific case studies that spotlight the remarkable outcomes achieved through effective API use.
Stripe and Online Payment Processing
Stripe is a leading online payment processing platform that has gained significant traction through its intuitive API design. By providing developers with straightforward tools to integrate payment functionalities directly into their applications, Stripe revolutionized the way businesses handle transactions online. Companies like Shopify and Lyft utilize Stripe’s APIs to facilitate seamless payment processing, enabling them to focus on core business activities while minimizing the complexities associated with finance and compliance.
Stripe’s API allows for customizable payment experiences, supporting multiple currencies and payment methods, thus attracting a wide array of businesses, from startups to large enterprises. As a result, Stripe has managed to grow its market share by offering a developer-friendly interface, significantly reducing the time and resources required for companies to implement payment solutions.
Twilio and Communication Solutions
Twilio is an exemplary case of API innovation in the communication sector. Its platform provides APIs that allow businesses to embed messaging, voice, and video capabilities into their own applications. Companies like Airbnb and Uber leverage Twilio’s APIs to communicate with users via SMS notifications, call routing, and customer support functionalities.
The flexibility of Twilio’s API enables companies to tailor communication methods that best suit their user base, enhancing overall customer experience. For instance, Airbnb uses Twilio to send booking confirmations and host messages, ensuring timely updates that keep users informed.
Lessons Learned from Successful API Implementations
The following bullet points summarize key takeaways from these case studies that can serve as guiding principles for other companies looking to leverage APIs:
- Focus on Developer Experience: Streamlined and intuitive APIs attract more developers, facilitating faster integration and adoption.
- Customization and Flexibility: Providing options for customization allows businesses to adapt the API to their unique needs, enhancing user satisfaction.
- Robust Documentation: Comprehensive and clear documentation is crucial for developers to implement APIs effectively and troubleshoot issues.
- Scalability: APIs should be designed to scale with businesses, accommodating growth without compromising performance.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Incorporating analytics into API usage can help companies optimize performance and user engagement by understanding usage patterns.
The successful implementation of APIs like Stripe and Twilio showcases their potential to transform business operations. By reducing friction in payment processing and communication, companies not only enhance their internal workflows but also significantly elevate customer experiences. Organizations that embrace API technology position themselves to respond more nimbly to market changes while staying focused on strategic growth.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the journey through the world of Application Programming Interfaces (API) underscores their transformative impact on software development and business operations. As we embrace new technologies and navigate the complexities of integration, APIs will continue to evolve, offering innovative solutions that shape the future of digital interactions. Adopting best practices and prioritizing security will ensure that these powerful tools remain effective and trustworthy as we move forward.
Query Resolution
What is an API?
An API is a set of rules and protocols that allow different software applications to communicate and interact with each other.
How do APIs improve software development?
APIs streamline the development process by enabling code reuse, facilitating integration, and allowing developers to leverage existing services.
What types of APIs are there?
Common types of APIs include web APIs, operating system APIs, library APIs, and hardware APIs, each serving unique functions in software integration.
What is API documentation?
API documentation is a technical manual that provides details on how to effectively use and implement an API, including its endpoints and functionalities.
Why is API security important?
API security is vital to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access, ensuring that applications remain safe and reliable for users.