Kicking off with 5G Network, the latest evolution in mobile technology is set to revolutionize how we connect, communicate, and conduct business. This innovation promises not only faster speeds and lower latency but also a myriad of applications that could redefine entire industries. From healthcare to transportation, 5G is more than just an upgrade; it’s a pivotal change in our digital landscape.
The fundamental principles of 5G technology differentiate it from its predecessors through advanced architecture and diverse applications. With components designed for high efficiency, including enhanced bandwidth and real-time data processing capabilities, 5G enables a connected world where smart devices and applications thrive. This introduction to 5G lays the groundwork for understanding its significant impact across various sectors.
The potential impacts of 5G Network on various industries must be examined.

The introduction of 5G technology is set to revolutionize numerous industries by enhancing connectivity, efficiency, and innovation. As a significant leap from previous network generations, 5G offers faster speeds, lower latency, and greater capacity, making it an ideal catalyst for advancements across diverse sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and transportation. By exploring these impacts, we can understand how businesses can harness 5G to optimize operations and drive future innovations.
Healthcare transformations through 5G
The healthcare industry stands to gain tremendously from the capabilities of 5G. Real-time data sharing and high-definition video conferencing can enhance telemedicine, enabling doctors to consult with patients remotely while ensuring timely treatment. For instance, remote surgeries conducted through robotics require ultra-reliable low-latency communication, which 5G can provide.
Key impacts include:
-
Remote patient monitoring improved by wearable devices that transmit data in real time, allowing for swift medical responses.
-
Enhanced imaging technology that allows radiologists to analyze high-resolution images instantly from anywhere, speeding up diagnosis.
-
Emergency response improvements, where ambulances equipped with 5G can transmit patient data to hospitals before arrival, enabling better-prepared medical teams.
Agricultural innovation via 5G
In agriculture, 5G’s ability to support a plethora of IoT devices can greatly enhance operational efficiency. Smart farming initiatives utilize connected sensors to monitor soil conditions, crop health, and weather patterns, leading to more informed decisions and resource management.
Notable advancements include:
-
Precision farming techniques that optimize water usage by using sensors to determine the exact moisture levels in the soil.
-
Autonomous farming equipment, such as drones and tractors, that operate with minimal human intervention, maximizing productivity.
-
Data analytics driven by real-time feedback to improve crop yields and reduce waste.
Transportation enhancements through 5G
Transportation systems are also set to benefit significantly from 5G technology. With the rise of connected vehicles, 5G allows for seamless communication between vehicles and infrastructure, promoting safety and efficiency in traffic management.
Key applications include:
-
Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication that enhances road safety by alerting drivers to potential hazards or traffic conditions.
-
Smart traffic lights that adjust based on real-time traffic flow, reducing congestion and travel time.
-
Fleet management systems that utilize 5G to track vehicle locations and optimize routing in real time.
The future innovations driven by 5G across these industries could lead to unprecedented efficiencies and capabilities, transforming how businesses operate and interact with their customers. By leveraging the full potential of this next-generation network, sectors like healthcare, agriculture, and transportation will not only improve their operational frameworks but also contribute to a more connected and efficient world.
The fundamental principles of 5G Network technology should be elaborated upon.
The transition to 5G network technology marks a significant leap forward in mobile communication, driven by the need for faster data speeds, reduced latency, and increased connectivity. This next-generation technology builds on its predecessors—3G and 4G—by introducing innovative features that enhance user experience and support a wide array of applications.
The core components that differentiate 5G from previous generations include a new radio access technology known as New Radio (NR), advanced antenna technologies such as Massive MIMO (Multiple Input Multiple Output), and the adoption of millimeter-wave (mmWave) frequencies. These advancements not only enhance the network’s speed and capacity but also facilitate device connectivity on an unprecedented scale. The integration of edge computing into the 5G architecture allows data processing to occur closer to the end-users, thereby minimizing latency and improving performance.
Technologies enabling faster speeds and lower latency in 5G connectivity
Several key technologies play a pivotal role in achieving the remarkable capabilities of 5G networks. These technologies include:
- Massive MIMO: This technology employs a large number of antennas at base stations to improve the capacity and efficiency of wireless communication. It enables simultaneous connections to multiple devices, drastically increasing throughput.
- Beamforming: By directing signals towards specific users rather than broadcasting them indiscriminately, beamforming enhances signal quality and reduces interference, resulting in faster and more reliable connections.
- Millimeter Waves: Utilizing higher frequency bands (24 GHz and above) allows 5G to carry more data at faster speeds compared to lower frequency bands used in earlier networks. This is essential for supporting high-bandwidth applications.
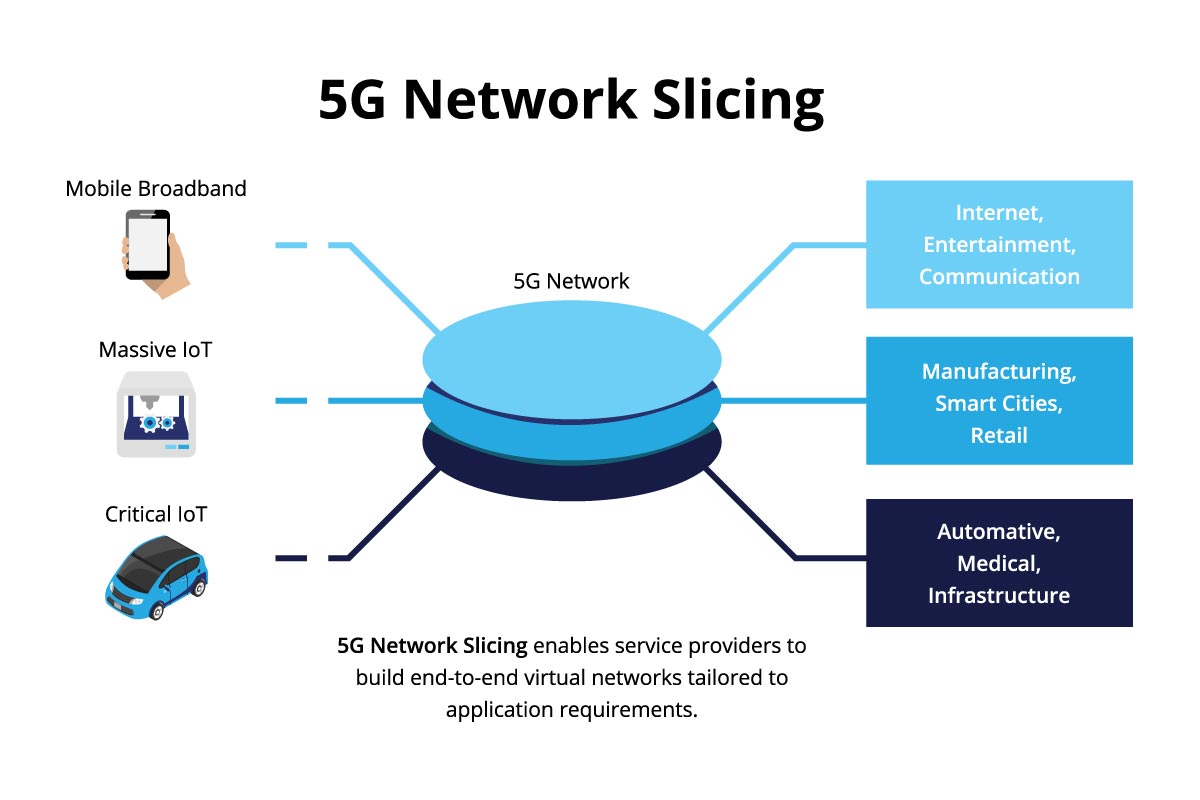
- Network Slicing: 5G enables the creation of virtual networks with tailored resources for different applications, ensuring that critical services receive the necessary bandwidth and low latency required for optimal performance.
The architecture of 5G is designed to support a wide range of applications and services, including smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and virtual reality. By utilizing virtualization and a service-based architecture, 5G can efficiently adapt to various demands. For example, a smart city may require a network with real-time data processing capabilities for traffic management, while an autonomous vehicle demands ultra-reliable low-latency connectivity for safety-critical communications.
The implementation of 5G technology is not just about faster internet; it represents a transformative shift enabling a plethora of advanced applications, from healthcare innovations to the Internet of Things (IoT), thereby unlocking new possibilities for industries and society as a whole.
Conclusion
In summary, the 5G Network stands at the forefront of technological advancement, promising to enhance connectivity, drive industry innovations, and reshape our daily lives. While challenges such as infrastructure hurdles and security concerns must be navigated, the potential of 5G to transform industries is immense. As we look ahead, embracing this technology could lead to groundbreaking developments that we are only beginning to imagine.
Common Queries
What is 5G Network technology?
5G Network technology is the fifth generation of mobile networks that provides significantly faster speeds, lower latency, and improved connectivity compared to previous generations.
How does 5G improve IoT devices?
5G enhances IoT devices by offering greater connectivity, allowing for real-time data processing and improved communication between devices.
What industries will benefit the most from 5G?
Industries such as healthcare, agriculture, transportation, and entertainment are expected to see substantial benefits from the capabilities of 5G.
Are there environmental concerns with 5G?
Yes, concerns include energy consumption, potential e-waste, and the environmental impact of increased infrastructure needed for 5G deployment.
What are the security risks associated with 5G?
5G networks face cybersecurity risks such as data breaches and network vulnerabilities that require robust security measures to mitigate.